Introduction: Severe thrombocytopenia (platelet count <50,000/μL) in myelofibrosis (MF) patients is a well-established prognostic factor associated with greater symptom burden and poor survival. In 2 large (>1000 patient) retrospective analyses, MF patients with severe thrombocytopenia had a median survival of 15 months, compared to 34-44 months for those with a platelet count 50,000-100,000/μL and 47-89 months with a platelet count >100,000/μL (Masarova L, et al. EJH 2018;100:257-263; Alhuraiji A, et al. JCO 2016;34:7068). Options for patients with severe thrombocytopenia are limited, and clinical trials often exclude them due to risk of treatment-related cytopenias. Pacritinib (PAC) is an oral JAK2/IRAK1 inhibitor that was evaluated for spleen volume reduction (SVR) and total symptom score (TSS) in two phase 3 studies (PERSIST-1 [P1] and PERSIST-2 [P2]) in MF patients, including those with severe thrombocytopenia. P1 studied JAK inhibitor naive patients with no lower platelet limitation, and P2 was limited to patients with a platelet count <100,000/μL, with or without prior JAK inhibitors (eg, ruxolitinib). To better evaluate PAC in MF patients with baseline platelet count <50,000/μL, a retrospective pooled analysis was performed on data from P1/P2. Clinical trial outcomes from this high-risk MF population have not previously been reported.
Methods: This analysis was performed in patients treated on P1 and P2 with a baseline platelet count <50,000/μL. P1 and P2 included adult patients with primary or secondary MF, intermediate-1, intermediate-2, or high-risk, and palpable splenomegaly ≥5 cm below the left costal margin. In P1, patients were randomized 1:1 to receive PAC 400 mg once daily (QD) or best available therapy (BAT). In P2, patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive PAC 400 mg QD, PAC 200 mg twice daily (BID), or BAT. In both studies, BAT included physician-selected treatment for MF, including watch and wait (no active treatment); treatment with JAK inhibitors were allowed as prior therapy and BAT in P2 only. Endpoints included the percentage of patients achieving ≥35% SVR at week 24 and the percentage achieving ≥50% reduction in TSS. Efficacy was analyzed in the intention-to-treat (ITT) efficacy population, and the safety population was defined as all patients who received study drug. Cardiac and hemorrhagic events were as defined by Standardised MedDRA Queries.
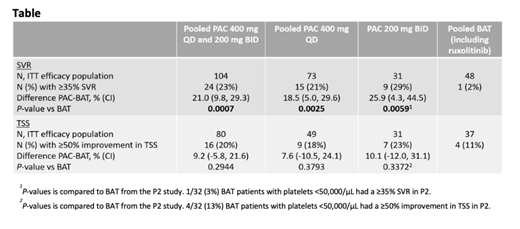
Results: Of 189 patients in the safety population, 152 were evaluable for ITT efficacy for SVR and 117 for ITT efficacy for TSS. Baseline characteristics were as follows: median platelet count was 29,000/μL, 80% had a hemoglobin <10 g/dL, 70% were >65 years of age, and 50% had grade 3 bone marrow fibrosis. At 24 weeks, significantly more patients achieved ≥35% SVR with PAC compared with BAT (P-values <0.01; Table 1). Although not statistically significant, TSS reductions ≥50% nearly doubled for those receiving PAC versus BAT. The safety profile in patients with severe thrombocytopenia was generally manageable and consistent with the overall study populations from the two phase 3 trials. Gastrointestinal events were the most common TEAE with PAC but were primarily grade 1/2 and rarely required dose reduction or discontinuation. Grade 3/4 hemorrhages occurred in 14% of patients on PAC (400 mg QD=13%, 200 mg BID=15%) and 14% on BAT; grade 3/4 cardiac events occurred in 8% of PAC patients (400 mg QD=8%, 200 mg BID=9%) and 12% of BAT patients. Deaths on study or within 30 days of last study dose occurred in 23 (17%) PAC patients (400 mg QD=18 [21%], 200 mg BID=5 [11%]) and 8 (14%) BAT patients. Of these deaths, 3 (2%) PAC patients and 2 (4%) BAT patients had grade 5 hemorrhagic events; grade 5 cardiac events occurred in 4 (3%) PAC patients and 4 (7%) BAT patients.
Conclusions: This retrospective analysis represents the largest population of patients with MF and severe thrombocytopenia to be studied in clinical trials, a population with a serious unmet medical need. These results illustrate the clinical activity of PAC in the treatment of these patients. A prospective, randomized Phase 3 study of PAC is planned (the PACIFICA trial) and designed to confirm the benefits of PAC in MF patients with severe thrombocytopenia.
Mesa:Novartis: Consultancy; Samus: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Genotech: Research Funding; La Jolla Pharma: Consultancy; CTI Biopharma: Research Funding; Sierra Onc: Consultancy. Talpaz:Novartis: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Constellation: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Imago BioSciences: Consultancy, Research Funding; Samus Therapeutics: Research Funding. Kiladjian:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; AOP Orphan: Honoraria, Research Funding. Harrison:Janssen: Speakers Bureau; CTI: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Honoraria; Promedior: Honoraria; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Sierra Oncology: Honoraria; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AOP: Honoraria. Verstovsek:Promedior: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma Corp: Research Funding; Genetech: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines Corp: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sierra Oncology: Research Funding; Pharma Essentia: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Research Funding; Ital Pharma: Research Funding; Protaganist Therapeutics: Research Funding; Constellation: Consultancy; Pragmatist: Consultancy; Gilead: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Buckley:CTI BioPharma: Employment, Equity Ownership. Roman-Torres:CTI BioPharma: Other: Contractor. Mascarenhas:Janssen: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; CTI Biopharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Merus: Research Funding; Pharmaessentia: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal