Background: BL is associated with a high risk of primary or secondary CNS involvement, warranting intrathecal (IT) and/or systemic therapy that penetrates the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The lower-intensity DA-EPOCH-R regimen has recently shown high survival rates in BL (Dunleavy, NEJM 2013), but it omits drugs traditionally used for CNS prophylaxis (like high-dose methotrexate [HDMTX]). The objective of this multi-institutional retrospective study was to examine treatments, risk factors, and CNS-related outcomes among patients (pts) with BL.
Methods: We collected data from 26 US centers on adult BL pts diagnosed (dx) in 6/2009-6/2018. Using institutional expert pathology review and 2016 WHO criteria, we excluded other high-grade lymphomas (including BL-like/unclassifiable), or cases with inadequate clinicopathologic data. We studied factors associated with baseline CNS involvement (CNSinv) using logistic regression reporting odds ratios (OR). Progression-free (PFS), overall survival (OS), and cumulative incidence function of CNS recurrence (in a competing risk analysis) were examined in Cox or Fine-Gray models reporting hazard (HR) or subhazard ratios (SHR), respectively. All estimates report 95% confidence intervals (in square brackets).
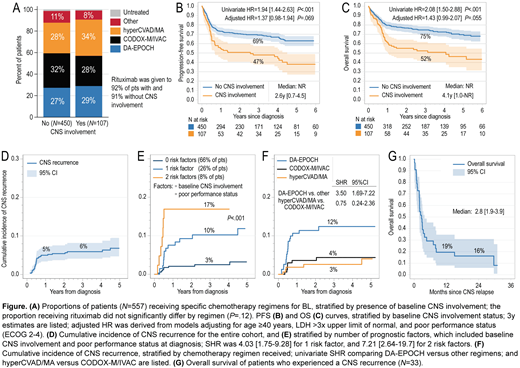
Results: Among 557 BL pts (median age, 47 years [yr], 24% women, 23% HIV+), 107 (19%) had CNSinv at dx, including 89 (16%) with leptomeningeal, and 15 (3%) with parenchymal CNS disease. In a multivariable model, factors significantly associated with CNSinv at dx included stage 3/4 (OR, 11.2 [1.47-85.9]), poor performance status (PS; OR, 2.12 [1.22-3.69]), ≥2 extranodal sites (OR, 3.77 [2.02-7.03]), or marrow involvement (OR, 2.44 [1.35-4.39]), whereas intestinal involvement conferred low risk of CNSinv (OR, 0.27 [0.11-0.65]). CNSinv at dx was not significantly associated with use of specific chemotherapy regimens (Fig. A,P=.75) or receipt of IT chemotherapy (91% vs 84%, P=.065). Pts with CNSinv were less likely to achieve a complete response (62% vs 76%, P=.005), had worse 3 yr PFS (47% vs 69%; P<.001, Fig. B) and OS (52% vs 75%; P<.001, Fig. C). However, these associations were not significant when adjusted for other prognostic factors (age ≥40y, poor PS, LDH>3x upper limit of normal [LDH>3x]; see Evens AM et al, ASH 2019 for further details).
With median follow up of 3.6 yrs, 33 pts (6%) experienced a CNS recurrence (82% within 1 yr from dx; 79% purely in CNS, and 21% with concurrent systemic BL). The cumulative risk of CNS recurrence was 6% [4-8%] at 3y (Fig. D). Univariate significant predictors of CNS recurrence included baseline CNSinv, HIV+ status, stage 3/4, poor PS, LDH>3x, involvement of ≥2 extranodal sites, marrow, or testis. However, in a multivariate model only baseline CNSinv (SHR, 3.35 [1.53-7.31]) and poor PS (SHR, 2.24 [1.03-4.90]) retained significance. The 3 yr risk of CNS recurrence varied from 3% for pts with no risk factor, to 10% with one, and 17% with both factors (Fig. E). In addition, the risk of CNS recurrence differed according to chemotherapy regimen, and was significantly higher for pts treated with DA-EPOCH (12% at 3y [8-18%]; Fig. F) compared with CODOX-M/IVAC (4% [2-8%]) or hyperCVAD/MA (3% [1-6%]; SHR for DA-EPOCH vs. others, 3.50 [1.69-7.22]). All pts recurring after DA-EPOCH had received IT chemotherapy. Higher risk of CNS recurrence persisted with DA-EPOCH regardless of baseline CNSinv (Pinteraction=.70), poor PS (Pint=.14), or HIV status (Pint=.89). Baseline CNSinv was the strongest factor associated with CNS recurrence after DA-EPOCH (3 yr risk, 30% vs 8%, P<.001). Of 7 pts who received HDMTX with DA-EPOCH (6 with leptomeningeal CNSinv at dx), 3 (43%) experienced CNS recurrence. Median OS among all BL pts with CNS recurrence was 2.8 months [1.9-3.9] (Fig. G). After recurrence, 67% of pts received salvage systemic and 9% IT chemotherapy, 3% radiation, and 21% hospice care.
Conclusions: In adult BL, baseline CNSinv and poor PS predicted subsequent CNS recurrence, an outcome that is associated with a dismal prognosis. Furthermore, treatment with DA-EPOCH was associated with a significantly increased risk of CNS recurrence in this real-world analysis. For BL pts with baseline CNSinv treated in routine clinical practice, regimens with highly BBB-penetrant drugs (e.g. CODOX-M/IVAC, hyperCVAD/MA) may be preferred. Studies should delineate ways to mitigate the risk of CNS recurrence with lower-intensity programs.
Evens:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Research to Practice: Honoraria; Verastem: Consultancy, Honoraria; Affimed: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Other: DMC; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding. Smith:Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Portola Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma BV: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Ignyta (spouse): Research Funding; Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp: Consultancy, Research Funding; Denovo Biopharma: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb (spouse): Research Funding; Ayala (spouse): Research Funding. Naik:Celgene: Other: Advisory board. Reddy:KITE Pharma: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Genentech: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy. Farooq:Celgene: Honoraria; Kite Pharma: Research Funding. Epperla:Verastem Oncology: Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria. Khan:Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Other: Educational Content/Symposium; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers: Other: Research Funds. Alderuccio:Puma Biotechnology: Other: Immediate family member; Agios: Other: Immediate family member; Inovio Pharmaceuticals: Other: Immediate family member; Targeted Oncology: Honoraria; OncLive: Consultancy; Foundation Medicine: Other: Immediate family member. Yazdy:Bayer: Honoraria; Genentech: Research Funding; Octapharma: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy. Diefenbach:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Denovo: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; LAM Therapeutics: Research Funding; MEI: Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Research Funding; Trillium: Research Funding. Karmali:Astrazeneca: Speakers Bureau; Takeda, BMS: Other: Research Funding to Institution; Gilead/Kite; Juno/Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Martin:Celgene: Consultancy; Teneobio: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Sandoz: Consultancy; I-MAB: Consultancy. Magarelli:Tevan Oncology: Speakers Bureau. Kamdar:Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; University of Colorado: Employment. Portell:Xencor: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; BeiGene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite: Consultancy, Research Funding; Acerta/AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Lossos:Janssen Scientific: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NIH: Research Funding. Olszewski:Genentech: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal