The CD3/CD19-targeted bispecific T-cell engager blinatumomab (BLIN) is active in pts w/ relapsed/refractory B-ALL or persistent minimal residual disease. Notable toxicities include cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a constellation of symptoms related to brisk systemic inflammatory response, and a spectrum of neurologic toxicities (NTX). BLIN prescribing information provides basic CRS/NTX management guidance, but limited reports describe "real-world" toxicity management strategies (TMS) and outcomes. We further previously reported association between higher baseline and peak levels of acute phase reactants (APR; C-reactive protein [CRP]/ferritin), time to APR peak, and incidence of CRS/NTX post-BLIN (King et al. ASH Annual Meeting, 2017). While CRS is also mediated in part by IL-6, routine monitoring of IL-6 levels during BLIN is not currently standard. As such, we sought to determine rates/severity of CRS/NTX at our institution, efficacy of TMS, and utility of APR/IL-6 in predicting CRS/NTX post-BLIN.
We reviewed electronic medical records of pts ≥ 18 years (yrs) old w/ previously treated B-ALL receiving BLIN between 1/1/2011 and 3/31/19 at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). NTX was classified/graded w/ CTCAEv5.0 (Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events). CRS was graded per CTCAEv5.0 and American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) criteria. The primary objective was to characterize rates/clinical features of CRS/NTX. Secondary objectives included assessing the nature/efficacy of TMS, and association of APR/IL-6 levels w/ CRS. Maximal (max) fold increase in APR/IL-6 was measured from pre-BLIN baseline to peak value during BLIN cycle 1 (C1). APR/IL-6 levels/fold changes were compared between groups using the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test w/o adjustment for multiple comparisons.
59 pts were identified, including 31 male pts (52%). Median age at start of BLIN was 57 yrs (range, 20-76). Median number of prior therapies was 1, including 8 pts w/ previous allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (alloHCT) and 5 w/ prior chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T). No pt had baseline organ dysfunction or central nervous system (CNS) disease. All pts were admitted for initiation of BLIN C1. BLIN was started at 9 mcg/day IVCI w/ escalation to 28 mcg/day IVCI on day 8 (per recommended dosing for R/R ALL) in 52 pts and at 28 mcg/day IVCI in 7 pts for MRD (per Gökbuget et al., Blood, 2018).
During BLIN C1, 34/59 pts experienced CRS (57%), w/ max grade (G) 1 (n=24), G2 (n=9) or G3 (n=1). CTCAEv5.0/ASTCT grading was concordant in all cases. Eight of 34 (23%) were managed w/ brief interruption of blinatumomab (BIB) for G1 (n=3) and G2 (n=5) CRS. Median duration of BIB was 39 hours (h) (range, 21-91h). Three pts had concomitant NTX and received brief courses of dexamethasone (DEX, daily dose of 24 mg). One pt w/ grade 2 CRS received tocilizumab for hypotension suboptimally responsive to fluid boluses (FB) w/ IL-6 level = 25754 pg/mL. Remaining pts w/ BIB (5/8) received FBs for hypotension. One pt permanently discontinued BLIN during C1 due to rapidly progressive B-ALL. All pts managed w/ BIB were successfully re-challenged w/ BLIN and finished C1 w/o recurrence of CRS. Of the 25/34 (74%) pts w/ CRS not managed w/ BIB, 5 received FBs, w/ 1 pt receiving a FB and a single dose of DEX. Five pts developed recurrent CRS (≥24 hours after resolution); 4/5 recurrences occurred in pts not managed w/ BIB.
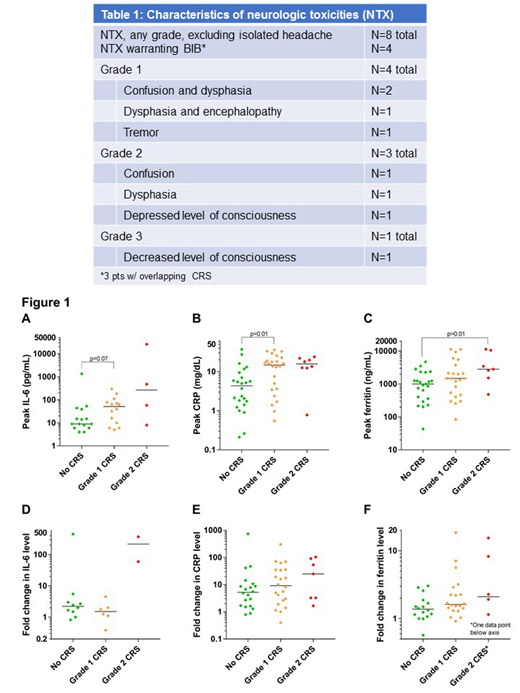
NTX, excluding isolated headache, was observed in 8/59 pts (14%) during BLIN C1 (Table 1) w/ max G1 (n=4), G2 (n=3), or G3 (n=1). Four pts w/ NTX were managed w/ BIB and a brief course DEX; 3/4 had concomitant CRS.
Median time to onset of CRS and NTX were 1 day (d) (range 0-15) and 2 d (range 0-10), respectively.
Non-significant trend toward higher peak IL-6 was noted in pts w/ G1 vs. G0 CRS (p=0.07; Fig 1A, note log scale); median peak levels of CRP were higher in pts w/ G1 vs G0 CRS (p=0.01, Fig 1B); median peak ferritin levels were higher in pts w/ G2 vs. G0 CRS (p=0.01, Fig 1C).
While CRS was common during C1 of BLIN, supportive management was sufficient in most pts; BIB was an effective strategy and allowed successful BLIN re-challenge. The incidence of ≥G2 NTX was low and all cases of NTX were reversible w/ supportive care or BIB ± DEX. Peak APR levels correlated w/ CRS severity. Authors noted concordance of CRS grading between CTCAE and ASTCT, suggesting the feasibility of a single, BITE-specific grading system.
King:Astrazeneca: Other: Advisory board; Genentech: Other: Advisory Board ; Incyte: Other: Advisory Board. Park:Amgen: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Autolus: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Allogene: Consultancy. Geyer:Amgen: Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal