Background
Oral arsenic trioxide (oral-As2O3)-based regimens are highly effective in the treatment of newly-diagnosed or relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)1,2. Data on the long-term outcome of patients who received prolonged maintenance with oral-As2O3-based regimens in first complete remission (CR1) following non-arsenic-based induction is lacking.
Methods
Patients aged ≥ 18 years with APL in first complete remission (CR1) were recruited for maintenance treatment with oral-As2O3 (10mg/day), all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) (45mg/m2/day in 2 divided doses), ascorbic acid (1g/day) (AAA). AAA was administered for 2 weeks every 2 months for a total of 2 years. Prior induction treatment comprised ATRA (45mg/m2/day in 2 divided doses for 42 days) and daunorubicin (50mg/m2/day for 3 days). Consolidation comprised 2 monthly cycles of daunorubicin (50 mg/m2/day for 2 days) and cytarabine (100 mg/m2/day for 5 days). Daunorubicin induction and consolidation chemotherapy were omitted in patients aged ≥ 70 years or those with cardiac co-morbidities.
Results
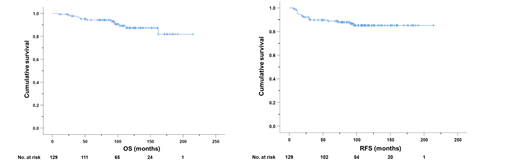
Between 1 August 2002 and 31 July 2019, 129 patients (63 men and 66 women) with a median age of 46 (18-82) years underwent maintenance with AAA. After a median follow-up of 100 (8-215) months, 117 (90.1%) patients completed 2 years of AAA maintenance. Seventeen (13.2%) patients relapsed after a median of 19 (17-96) months from CR1 (morphologic relapse, N=14; molecular relapse; N=3). Two patients had central nervous system (CNS) involvement at first relapse (R1). There were 13 (10.1%) deaths. Five patients died from refractory APL. Eight patients died in remission (pneumonia, N=4; acute myocardial infarction, N=2; second malignancy, N=2). The 5-year and 10-year relapse-free survival (RFS) were 88.8% and 85.1% respectively. The 5-year and 10-year overall survival (OS) were 94.2% and 87.4%. On univariate analysis, PML-RARA bcr3 (short) isoform (P=0.02), FLT3-ITD (P=0.005) and CNS involvement at diagnosis (P=0.002) were associated with worse RFS. On multivariate analysis, FLT3-ITD (P=0.005) and central nervous system (CNS) involvement at diagnosis (P=0.004) were associated with worse RFS. On univariate analysis, PML-RARA bcr3 isoform (P=0.03), FLT3-ITD (P=0.01) and relapsed APL (P=0.002) were associated with worse OS. On multivariate analysis, therapy-related APL (P=0.03), FLT3-ITD (P=0.03) and relapsed APL (P=0.03) were associated with worse OS. Grade 1 leucopenia occurred in 7 (5.4%). The commonest non-hematological toxicity was headache and occurred in 38 (29.5%) (Grade 1/2, N=38; Grade 3/4, N=0). Grade 1 hepatoxicity occurred in 7 (5.4%) patients during AAA maintenance. Cutaneous herpes zoster infection occurred in 6 (4.7%) patients.
Conclusion
Maintenance therapy with oral-As2O3, ATRA and ascorbic acid in CR1 was safe and resulted in excellent long-term survivals in APL.
References:
1. Gill H, Yim R, Lee HKK, Mak V, Lin SY, Kho B et al. Long-term outcome of relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with oral arsenic trioxide-based reinduction and maintenance regimens: A 15-year prospective study. Cancer 2018; 124(11): 2316-2326.
2. Gill H, Kumana CR, Yim R, Hwang YY, Chan TSY, Yip SF et al. Oral arsenic trioxide incorporation into frontline treatment with all-trans retinoic acid and chemotherapy in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: A 5-year prospective study. Cancer 2019 [Epub].
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal