Introduction
US Food and Drug Administration has recently approved the use of rivaroxaban 2.5mg BID in patients with coronary heart disease based on Cardiovascular Outcomes for People Using Anticoagulation Strategies (COMPASS) trial. However, it's unclear whether there is net clinical benefit with use of rivaroxaban in such patients. Therefore, we did a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the effects of rivaroxaban on clinical outcomes in coronary heart disease patients.
Methods:
Embase, Ovid, Pubmed and Scopus were extensively searched from inception of these databases to April 2019 by two independent reviewers. Only randomized controlled trials of low dose rivaroxaban (2.5 mg BID) reporting mortality and cardiovascular outcomes of interest in baseline coronary heart disease patients (≥ 18 years) with at least 1000 patients and follow-up of ≥ 1 year were included. The co-primary outcomes were cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality. The secondary endpoints were myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, major adverse cardiovascular events, major bleeding and cerebral nervous system (CNS) bleeding. Cochrane Collaboration's tool was used for risk of bias assessment. Statistical heterogeneity was quantified using I2 statistics whereas publication bias was assessed with Eggers regression test. We combined estimates using DerSimonian and Laird random effects models. Outcomes were reported as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results:
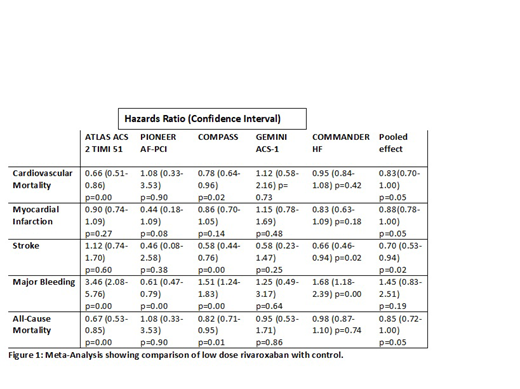
Five randomized control trials including 39,979 patients were included in our meta-analysis. Trials ATLAS and Commander HF used placebo as their control while COMPASS and GEMINI ACS-1 used aspirin as control. Pioneer AF-PCI used vitamin K antagonist as the control. Mean age (SD) of the patients was 65.6 ± 3.7 years with 74.3% females. Mean follow up in years was 1.6 ±0.5. Majority of the patients in each trial had hypertension. Our pooled analysis showed reduction in all-cause mortality (HR, 0.85, 95% CI, 0.72-1.00, P=0.05), cardiovascular mortality (HR, 0.83, 95% CI, 0.70-1.00, P=0.05), MI (HR, 0.88, 95% CI, 0.78-1.00, P=0.05) and stroke (HR, 0.70, 95% CI, 0.53-0.94, P=0.02) with low dose rivaroxaban. No significant difference in risk of bleeding was observed (HR, 1.45, 95% CI, 0.83-2.51, P=0.19). Our pooled analysis also showed reduction in major cardiovascular events (HR, 0.91, 95% CI, 0.85-0.98, P=0.01). CNS bleeding was only reported by ATLAS and COMPASS trials and net effect showed no statistically significant bleeding risk (HR, 1.63, 95% CI, 0.70-3.79, P=0.26).
Conclusion:
Our data suggest that the use of rivaroxaban is associated with reduction in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in coronary heart disease patients without significantly increasing the risk of bleeding. To further decrease the residual risk of cardiovascular events in coronary heart disease patients, low dose rivaroxaban can be considered by clinicians.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal