INTRODUCTION
Allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT) could be the only curative therapy for patients with hematological malignancies due to graft effect against tumor. However, approximately 40% of patients develop post-transplantation complications such as acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD). Cytokines and their receptors are involved in regulatory and inflammatory processes that occur during GVHD. Therefore, the analysis of polymorphisms (SNPs) that affect the expression or activity of these genes could be used as biomarkers to predict the development of these complication. The aim of this study was to select new polymorphisms in cytokine genes (interleukins, chemokines and their receptors) to build models to predict the development of aGVHD after allo-HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling donor.
METHODS
We retrospectively selected 88 patients with hematological malignancies who received an allo-HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling donor from 2000 to 2015. A total of 176 pre-transplant recipient (R) and donor (D) peripheral blood samples were collected. The genotyping was performed using an enrichment-capture gene panels (include 132 genes (73 interleukins, 59 chemokines) in a HiSeq platform (Illumina, USA). The bioinformatic analysis was carried out with the GeneSystemssoftware (Sistemas Genómicos, Spain). Variants located in coding region, splicing sites, and UTR, 5'upstream and 3'downstream zones (+ 200pb) were analyzed. We selected polymorphisms corresponding to non-synonymous variants, represented in at least 5% of our cohort, with readings ≥30X in the canonical isoformwith an allele frequency ≥ 0.4. Fisher test was used to compare the differences among groups. Multiple logistic regression models were performed using combination of interleukins and chemokines polymorphisms selected previously that could be applied to clinical practice to predict aGVHD. The models with the highest AUC value, sensitivity and specificity value and the lowest number of genetic variants used were selected.Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS, Chicago, USA) was used for statistical test.
RESULTS
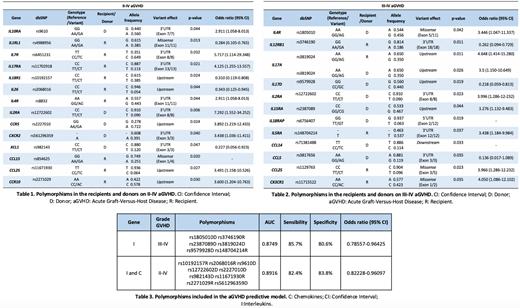
The cumulative incidence rates for aGVHD of grades II-IV and III-IV at 100 days after transplantation were 48.93% and 18.08%, respectively. The clinical variables (age, gender, pathology, stem cell source and previous transplantation) were not correlated with II-IV or III-IV aGVHD. However, patients who received ablative conditioning regimen presented a lower incidence of III-IV aGVHD (p= 0.041). Using filters defined previously, we detected 481 polymorphisms (350 coincident, 68 specific R and 63 for D) in the interleukins group. On the other hand, we detected 339 polymorphisms (267 coincident, 29 specific R and 43 for D) in the group of chemokines. Finally, 17 polymorphisms were selected in the interleukin group and 10 in the chemokine group for its correlation with the aGVHD (p <0.05). Specifically, 14 SNPs were correlated with II-IV aGVHD (Table 1) and 12 SNPs with III-IV aGVHD (Table 2). Most polymorphisms found are located in regulatory regions, which until have been little studied, but these regions are involved in the expression genes, therefore could be affecting the function of these genes.
We developed multiple logistic regression models for II-IV and III-IV aGVHD in interleukins and chemokines genes (Table 3). The identification of these 15 polymorphisms could help us to prevent the developing II-IV and III-IV aGVHD.
CONCLUSIONS
We have identified new genetic polymorphisms correlate with the risk of developing aGVHD after allo-HSCT from an HLA-identical sibling donor. Based on these data, we have developed a genetic score that encompasses polymorphisms of greater relevance. In this way, patients at greatest risk for developing this type of post-transplantation complication who could benefit from personalized management through immunosuppression and other drugs.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal