Introduction:
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare but aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). CD20 antibodies (e.g. rituximab), BTK inhibitors (e.g. ibrutinib and acalabrutinib), and BCL-2 inhibitors (e.g. venetoclax) alone or in combination have shown great anti-MCL efficacy. However, primary and acquired resistance to one or multiple therapies commonly occurs, resulting in poor clinical outcome. Overcoming such mechanisms of resistance holds promise to significantly improve survival, meeting a significant medical need for patients with refractory/relapsed MCL. Recent studies showed Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) play important roles in controlling therapeutic efficacy. FcgRIIB (CD32B), the inhibitory FcγR, negatively controls antibody efficacy through distinct inhibitory mechanisms in immune effector cells and lymphoma cells, respectively. When expressed on leukemic or lymphoma cells, FcgRIIB promotes rituximab internalization and removal from the tumor cell surface, resulting in reduced immune effector cell activation and ultimately decreased in vivo therapeutic efficacy. We recently developed antagonistic antibodies to FcgRIIB and demonstrated that these antibodies blocked rituximab internalization and helped prevent and overcome rituximab resistance in a PDX model of CLL. In this study, we investigated the expression of FcgRIIB in MCL cell lines and primary patient MCL samples, and we assessed the in vivo efficacy of BI-1206, a monoclonal antibody against FcgRIIB, in MCL PDX models.
Methods:
Flow cytometry analysis was performed to examine the cell surface expression of FcgRIIB in MCL cell lines (n=8) and primary patient MCL samples (n=27). An orthotopic patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model was established from a MCL patient with dual resistance to ibrutinib-venetoclax. In the first mouse cohort, single-agent ibrutinib, venetoclax, or vehicle control were administrated in mice carrying the orthotopic PDX model to assess their in vivo efficacies. In the second mouse cohort, mice were treated with vehicle, single agent BI1206, rituximab plus lenalidomide, or a combination of BI-1206, rituximab, and lenalidomide (triple combination) to assess their in vivo efficacies in the same PDX model.
Results:
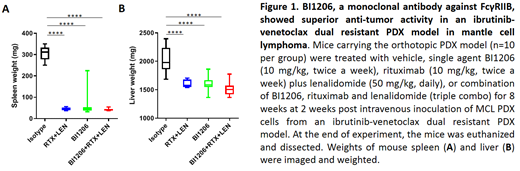
Flow cytometry analysis showed that all 8 MCL cell lines and all 27 primary patient MCL samples expressed high levels of FcgRIIB, highlighting the potential importance of FcgRIIB on the control of therapeutic efficacy in MCL. In the first mouse cohort, we validated the ibrutinib and venetoclax resistance in the PDX model established from a MCL patient with resistance to both therapies. In the second mouse cohort, single agent BI-1206 (10 mg/kg, twice a week) potently diminished PDX growth in spleen, liver, bone marrow, and peripheral blood (Figure 1). Treatment with rituximab (10 mg/kg, twice per week) plus lenalidomide (50mg/kg, daily) or the triple combination showed similar potency (Figure 1). To investigate whether BI-1206 mediates boosting of rituximab-based targeted drug therapies, and/or overcoming of resistance to such therapies, a follow-up experiment with revised treatment setting using the same PDX model or an alternative CD20/FcγRIIb co-expressing PDX model is currently under investigation.
Conclusions:
All MCL cell lines and all primary MCL cells tested highly express FcγRIIb on the tumor cell surface. Single agent BI-1206 has potent anti-MCL activity in the FcγRIIb-expressing MCL PDX model to overcome ibrutinib-venetoclax dual resistance. Our data suggests FcγRIIb may be an important target for anti-MCL therapies.
Wang:Guidepoint Global: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; MoreHealth: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BioInvent: Consultancy, Research Funding; Aviara: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; VelosBio: Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal