Introduction: The risk of developing a follicular lymphoma (FL) begins to be better understood with the identification in large epidemiological studies of familial predisposition, some occupational exposures and genetic factors. Genome wide-association studies (GWAS) identified constitutional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at risk of FL in HLA region (rs12195582), in 11q23.3 (near CXCR5), in 11q24.3 (near ETS1), in 3q28 (near LPP), in 18q21.33 (near BCL2), and 8q24 (near PVT1); three suggestive loci are localized at 17q25.3 (near CYBC1), 3q13.33 (CD86), 18q12.3 (SLC14A2) (Skibola, Am J Hum Genet. 2014). High t(14;18) frequency in blood years before diagnosis from healthy individuals was also defined as a predictive biomarker for FL (Roulland, J Clin Oncol 2014). It is currently unknown whether any relationship exists between inherited genetic variants associated with FL susceptibility and t(14;18) frequency and if the combination of the two biomarkers could be useful for a better stratification of risk of FL development in healthy individuals.
Methods: We used quantitative PCR assays to estimate t(14;18) frequency in prediagnostic blood samples from 105 individuals that were obtained on average 6.4 years before FL diagnosis (pre-FL group) together with 236 age and gender-matched individuals (control group) that were issued from the participants in the EPIC cohort ( European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition). Constitutional DNA was analyzed for the genotyping of the nine SNPs associated with FL risk (HLA, rs12195582; CXCR5, rs4938573; ETS1, rs4937362; LPP, rs6444305; BCL2, rs17749561; PVT1, rs13254990; CYBC1, rs3751913; CD86, rs2681416; SLC14A2, rs11082438). Genotyping were performed in duplicate using TaqMan® assays on Fluidigm platform. The nine SNPs were analyzed individually and combined in a polygenic risk score (PRS). PRS is a weighted average of the number of risk alleles with the weights being the log of the odds-ratio (OR) reported in the FL GWAS (Skibola, Am J Hum Genet. 2014). A model for FL risk was developed using multivariable logistic regression. Predictive ability was assessed by area under Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve, with 10-fold cross-validation. This work is supported by the French NCI (INCA, PRT-K16-167).
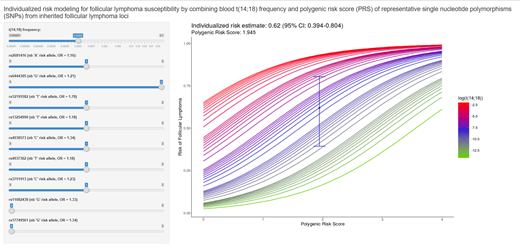
Results: t(14;18) frequency as a log-transformed continuous variable is predictive of FL risk (OR: 1.50; 95%CI: 1.29-1.78, P<0.001); PRS is also strongly associated with FL risk (OR: 3.31; 95%CI: 2.01-5.62, P<0.001). Age at screening (OR: 0.98; 95%CI: 0.95-1.01, P=0.24) did not influence FL risk. A weak but statistically significant correlation between t(14; 18) frequency and PRS was observed (Pearson correlation=0.18, P=0.002). In multivariable analysis, both PRS (OR: 2.84, 95%CI: 1.66-4.99, P<0.001) and t(14;18) frequency (OR: 1.45, 95%CI: 1.18-1.84, P<0.001) remained statistically significant. No departure from log-linear effect was observed in the modeling nor statistical interaction between PRS and log-transformed t(14;18), confirming that t(14; 18) frequency and genetic markers (PRS) were two independent factors of FL risk. Sensitivity analyses showed that these results were not influenced by the delay between the date of the screening and the FL diagnosis. Combining t(14;18) frequency and the PRS in a prediction model allowed the identification of some individuals at very high risk of developing FL and a shiny web application was developed to provide an easy-to-use tool to obtain individualized risk predictions for new patients (Figure). Area under ROC curve (AUC) showed that the model that integrated t(14;18) frequency and PRS (AUC: 0.69, 95%CI: 0.62-0.76) had a better prediction of FL risk than t(14;18) frequency (AUC: 0.62, 95%CI: 0.55-0.70) and PRS alone (AUC: 0.68, 95%CI: 0.61-0.75).
Conclusions: Genetic variants combined in PRS and t(14;18) frequency allowed the identification of individuals at high-risk of FL development and provided a better way, when these two biomarkers were combined, to discriminate healthy individuals from pre-FL cases many years before malignant transformation. These findings could be used for screening test of populations with some environmental exposures positively associated with FL development in epidemiological studies and may contribute in the future to monitoring or early intervention.
Salles:Roche, Janssen, Gilead, Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Educational events; Autolus: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Educational events; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Educational events; Novartis, Servier, AbbVie, Karyopharm, Kite, MorphoSys: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Educational events; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal