Drugs targeting chromatin-modifying enzymes have entered clinical trials for myeloid malignancies, including INCB059872, a selective irreversible inhibitor of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1). LSD1 is a component of the CoREST complex, in which it associates with histone deacetylases 1 and 2, the transcriptional co-repressor, mSin3A or mSin3B, and the REST corepressor (RCOR1), so a role in gene expression was expected. While initial studies of LSD1 inhibitors have suggested these compounds may be used to induce differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia, the mechanisms underlying this effect and dose-limiting toxicities are not well understood. Here, we have used precision nuclear run-on sequencing (PROseq) and single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNAseq) to show that INCB059872 de-represses GFI1/GFI1B-regulated genes to promote a myeloid differentiation gene signature in AML cells while stalling maturation of megakaryocyte progenitor cells.
Within 3 days of treatment with INCB059872, the majority of THP-1, which contain an the MLL-translocation, undergo myeloid differentiation. RNAseq analysis indicated that 24h drug treatment upregulated genes involved in hematopoietic cell lineage, which is consistent with the differentiation. In addition, PROseq was used to measure the effects of INCB059872 on nascent transcription at genes and enhancers, as this is one of the best methods to define enhancer activity. In THP-1 cells after 24h treatment, there were 203 genes with at least a 1.5-fold increase in transcription, while there are nearly 1300 enhancers meeting this threshold. Upregulated genes include those associated with myeloid cell differentiation, such as CSF1R and CD86. Given that LSD1 catalyzes the removal of mono- and di-methyl marks from histone H3, we expected that INCB059872 would cause a buildup of histone methylation. Surprisingly, ChIPseq for H3K4me2 and H3K4me1 showed only subtle changes in these marks after 48h drug treatment in THP-1. Only a handful of LSD1i-induced enhancers overlapped with detectable changes in H3K4 methylation. However, our PROseq data is consistent with the increases in H3K27 acetylation seen with OG86 (a compound that disrupts the LSD1:GFI1 interaction) at GFI1 binding sites (PMID: 29590629). Indeed, motif analysis of INCB059872-upregulated enhancers identified the GFI1 recognition sequence as the most highly enriched. Moreover, siRNA inhibition of key components of LSD1-containing chromatin remodeling complexes pinpointed the CoREST complex as mediating the THP-1 myeloid differentiation effects of INCB059872.
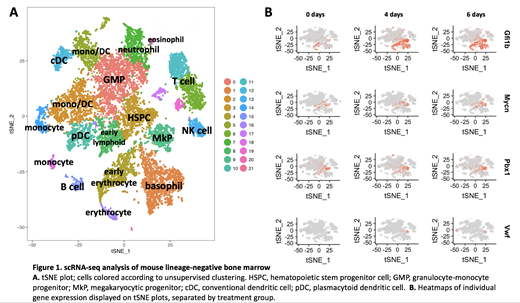
To investigate on-target thrombocytopenia seen with LSD1 inhibitors in preclinical studies, we analyzed the bone marrow of wild-type mice treated daily with INCB059872 for 0, 4, or 6 days before harvesting and sorting lin-bone marrow cells for scRNA-seq. Notably, one of the most highly upregulated genes in treated cells was Gfi1b. Unsupervised clustering identified 22 clusters, corresponding to unique subpopulations (Fig. 1A). While the distribution of cells into different progenitor populations was mostly unaffected by drug treatment, these data revealed a striking increase in the proportion of cells from treated mice assigned to a megakaryocyte stem/progenitor cluster. Cells within this expanded cluster expressed stem cell markers such as MYCN and PBX1, but also expressed VWF (Fig. 1B). Thus, LSD1 inhibition caused accumulation of megakaryopoiesis-biased stem cells that failed to mature into efficient platelet producers.
Finally, we used scRNAseq to analyze bone marrow from an AML patient who responded to treatment with INCB059872 plus azacytidine (AZA). A pre-treatment bone marrow sample was divided into separate cultures to study the effects of INCB059872, AZA, or the combination. Remarkably, unsupervised clustering of patient cells assigned the majority of INCB059872 and combination-treated cells to clusters that were not found in control- or AZA-treated samples. Cells exposed to INCB059872 had upregulated GFI1 and GFI1B, as well as differentiation-related genes that were also observed in AML cell lines. Overall, these data indicate that INCB059872 affects gene expression with kinetics consistent with a loss of CoREST activity to stimulate differentiation of AML blasts, but the inactivation of GFI1/GFI1B impairs megakaryocyte maturation likely explaining thrombocytopenia seen in preclinical models.
Stubbs:Incyte Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Burn:Incyte: Employment, Equity Ownership. Hiebert:Incyte Corporation: Research Funding. Savona:Karyopharm Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Selvita: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Patents & Royalties; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal