Introduction
Current adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector-based gene therapy strategies for hemophilia rely on systemic administration of the vector. Durable expression of the transgene over the span of years has been reported from several trials, yet information on the clearance of vector material from bodily fluids is still limited and monitoring of "shedding" is required during trials despite lack of evidence of environmental or transmission risk. Here, we examined the magnitude and duration of the presence of vector DNA in participants from a Phase I/II study of an AAV5-hFIX wildtype construct (AMT-060; NCT02396342) and from a Phase IIb study utilizing the enhanced version, AAV5-hFIX Padua (AMT-061; NCT03489291).
Methods
Adult male participants with severe or moderately severe hemophilia B received a single intravenous infusion of either AMT-060 at 5x1012 genome copies(gc)/kg (low dose) or 2×1013 gc/kg (high dose), or AMT-061 at 2x1013gc/kg in one of two ongoing trials. Assessments in both trials included efficacy and safety outcomes as well as vector shedding in whole blood and semen. Vector shedding was also measured in nasal secretions, feces, urine, and saliva in participants receiving AMT-060. Vector shedding was analyzed using a validated quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) based assay measuring presence of vector DNA in the bodily fluids. Vector clearance was reached when vector DNA was either zero or below the limit of detection (LOD) for three consecutive measurements. The range in time to the first and the third consecutive negative measurement for each dose group are provided.
Results
Treatment with AMT-060 resulted in sustained improvement in FIX activity for up to 3.5 years [Mean FIX activity was 5.1% (low dose group at 3.5 years) and 7.5% (high dose group at 3 years)] and treatment with AMT-061 resulted in mean FIX activity of 45% over 36 weeks. AMT-060 and AMT-061 reduced the mean number of annualized bleeds by between 82% and 100% respectively. AMT-060 reduced the requirement for exogenous FIX administration by 86% and was abrogated with AMT-061. Both AAV5-hFIX and AAV5-hFIX Padua were safe and well tolerated and no unexpected TRAEs have been observed with longer-term follow up.
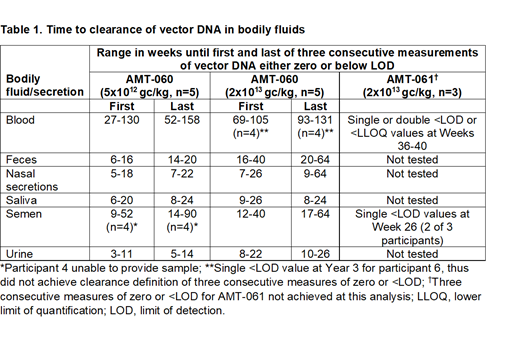
Table 1 describes the time in weeks to the first and last of three consecutive measures of vector DNA of either zero or <LOD for all bodily fluids for AMT-060 and AMT-061. AMT-060 at the higher dose was cleared from semen, feces, urine, nasal secretions and saliva in all participants by week 64 (range 7-64 weeks). In blood, the lower dose of AMT-060 was cleared in all participants by 3 years (range 1.0-3.0 years). The higher AMT-060 dose was cleared in 4 of 5 participants by 2.5 years (range 1.8-2.5 years), and while below the LOD in the 5th participant by year 3, had not achieved the definition of vector clearance. With AMT-061, vector DNA were <LOD or below the lower limit of quantification in blood in all 3 participants by weeks 36-40 and in semen by week 26 in 2 of 3 participants but had not achieved the definition of vector clearance.
Conclusions
Post-AMT-060 treatment, vector DNA was undetectable in all participants in the high dose group by 10 months and considered cleared by 16 months in all bodily fluids except blood. AMT-060 was cleared from the blood in 100% of participants in the low dose group at 3 years and 80% of participants in the high dose group by 2.5 years. As expected, AMT-061 vector DNA was detectable at 36 weeks in blood and in the semen of 1 of 3 participants, although clearance had not yet been established in the remaining participants. The presence of vector DNA in bodily fluids assessed was not associated with any adverse safety or efficacy findings.
Sawyer:Uniqure BV: Employment. Gielen:uniQure Biopharma: Employment. Twisk:uniQure Biopharma: Employment. Long:Uniqure BV: Employment. Gut:Uniqure BV: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal