BACKGROUND:
Large number of rejuvenated antigen-specific T cells generated from iPS cells (iPSCs) may have a large impact on the T-cell immunotherapy field. We previously reported the generation of functional CD8 single positive (SP) cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTLs) from iPSCs (Minagawa etal. CellStemCell, 23: 850-858. (2018)), and a regenerative CTL-based immunotherapy is about to begin in clinical trials. However, these two-dimensional differentiation protocols using the OP9DL1 murine feeder cell line or DLL4 recombinant proteins could differentiate iPSCs into CD8SP CTLs but not into robust CD4SP helper T (Th) cells. It is clear that, we could better control immune reactions if we could produce each Th cell fraction. For example, we could enhance antitumor immunity if we could specifically induce Th1 cells to command cellular immunity. The drastic therapeutic effect of CD19 CAR modified T cells including both CD8SP CTLs and CD4SP Th cells is clearly based on the role of CD4SP Th cells in helping CD8SP CTLs prolong the therapeutic effect against B-cell malignancy. This led us to hypothesize that Th cell induction from iPSCs is essential for efficient immunotherapy.
In this situation, a three-dimensional (3D) method called artificial thymic organoid (ATO) was reported to support robust differentiation of both CD4SP and CD8SP TCRαβ cells from primary hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (Seet etal. NatureMethods, 14: 521-530. (2017)) and hematopoietic progenitor cells derived from ES cells and iPSCs (Montel-Hagen etal. CellStemCell, 24: 376-389. (2019)).
Here, we evaluated the advantages and unsolved tasks of the 3D method to induce antigen-specific and functional CD4SP Th cell subsets from iPSCs.
METHODS and RESULTS:
By applying the ATO methods, we cultured mixed pellets of iPSC-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) and Notch ligand-expressing MS5 feeder cells on cell culture inserts for up to 9 to 12 weeks. Next, we analyzed differentiated T cells in the ATOs. We used iPSCs derived from antigen-specific Th cells containing HLA class II restricted TCR genes corresponding to an original Th cell clone.
Most importantly, the ATO method supported robust differentiation of CD4SP T cells as expected even from these iPSCs. These CD4SP T cells showed high expression of Th-POK as a master regulator of Th cells, and high secretion ability of several key cytokines produced by Th cells-IL-2, IFN-γ, and IL-4. However, the majority of iPSC-derived CD4SP T cells showed simultaneous secretion of both IFN-γ and IL-4 unlike normal peripheral CD4SP Th cells. We tried to make the regenerated CD4SP T cells separately produce the Th1 (IFN-γ) and Th2 (IL-4) cytokines by optimizing culture conditions, but we failed to achieve separated Th1/2 differentiation. To understand the reason for the bipolarized cytokine production profile of regenerated CD4SP T cells, we checked the master regulator expression profile. We found that a majority of the CD4SP T cell population highly expressed T-bet, the master regulator of Th1. Contrary to our expectation, GATA3's expression levels were not high in most CD4SP T cells. And, GATA3 is master regulator not only of Th2 but of T cell differentiation itself, so we guessed knock out (KO) of GATA3 led to failure of differentiation into T cell.
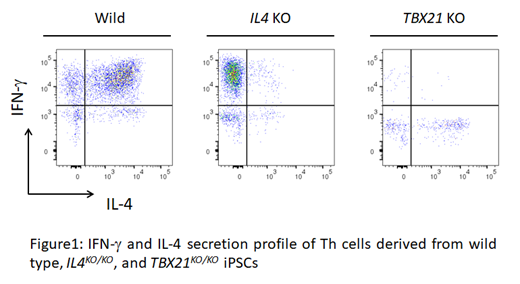
To "polarize" the CD4SP T cells to have Th1 or Th2 functions, we knocked out TBX21 (coding T-bet) or the Th2 "master cytokine" IL4 of undifferentiated iPSCs using CRISPR-Cas9 to obtain TBX21KO/KO iPSCs or IL4KO/KO iPSCs, respectively. Those iPSCs were successfully differentiated into HPCs, and ATOs were then prepared using these cells. After 9 to 12 weeks, mature CD4SP T cells and CD8SP T cells were observed in both ATOs with the same surface marker profile as T cells from wild type iPSCs, and TBX21KO/KO CD4SP T cells or IL4KO/KO CD4SP T cells from iPSCs with selective production of IL-4 or IFN-γ, respectively (Figure1).
These results also suggested the potential utility of ATO-based invitro T cell differentiation from genome-edited iPSC for understanding of human developmental immunology.
CONCLUSIONS:
"Polarized" CD4SP Th cells were successfully obtained from master regulator or cytokine gene-knockout iPSCs in ATO-based invitro differentiation. We are now investigating the actual helper function of these "polarized" iPS-Th cells that could be induced by the target peptide on HLA Class II molecules of antigen presenting cells.
Shinohara:Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Employment. Koga:Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Employment. Kassai:Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Employment. Kiyoi:Zenyaku Kogyo Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; FUJIFILM Corporation: Research Funding; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Eisai Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Pfizer Japan Inc.: Honoraria; Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Perseus Proteomics Inc.: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd: Research Funding; Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd.: Research Funding. Kaneko:KIRIN holdings Co.,Ltd.: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Other: Scientific adviser, Research Funding; TERUMO Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; TOSOH Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Thyas Co., Ltd.: Other: Founder, Shareholder, Chief Science Officer, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal