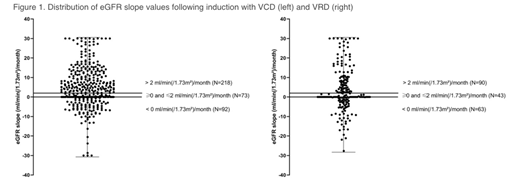
IntroductionThe kidney is an important target organ in plasma cell dyscrasias, subjected to various mechanisms of injury such as tubular obstruction, hypercalcemia, and pre-existing disease. Preservation of kidney function in newly diagnosed (ND) multiple myeloma (MM) is of concern as treatment-related toxicity (for instance infections and mucositis) is known to increase with renal impairment (RI). However, even severe MM-induced RI may recover with anti-myeloma treatment. We set out to compare three induction regimens in patients (pts) with transplant-eligible NDMM in terms of renal recovery and toxicity, MM response and associated adverse events (AEs). Pts from two prospective trials (NCT00833560, NCT01685814) were analyzed, provided post-induction (PInd) restaging data was available. They received three 3-week induction cycles with bortezomib (btz), cyclophosphamide, and dexamethasone (dex; VCD); btz, lenalidomide (len), and dex (VRD); or three 4-week cycles with len, adriamycin, and dex (RAD). All pts had to have measurable disease, an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of >30 ml/min and to be up to 60 (VCD) and 65 years (yrs) of age, respectively. VCD consisted of intravenous (IV) btz 1.3 mg/m² on day (D) 1, 4, 8, 11; IV cyclophosphamide 900 mg/m2D1; dex 20 mg D 1+2, 4+5, 8+9, 11+12. VRD of subcutaneous (SQ) btz 1.3 mg/m² D 1, 4, 8, 11; len 25 mg, D1-14; dex 20 mg D 1+2, 4+5, 8+9, 11+12; and RAD of len 25 mg D1-21; IV adriamycin 9 mg/m² D1-4; dex 40 mg D 1-4 + 17-20. MethodsThis is a secondary analysis of a phase 2 and a phase 3 study. We hypothesized MM disease response (and in turn, renal recovery) would be best with VRD. GFR was estimated by the MDRD IV or CKD-Epi formulas. The increase (and decrease, respectively) of renal function expressed by "GFRpost induction- GFRscreening" was tested for significance (p<.05) by an averaging process. In addition to absolute values, we performed slope analysis of changes in eGFR over time. ResultsThe safety set included 883 patients, 811 of whom received three induction cycles plus restaging and were eligible. 395 patients had received VCD; 214 VRD; and 202 RAD, with similar median ages of 54, 56 and 55 yrs, respectively. Baseline body mass index, heart rate and systolic/diastolic blood pressure were well balanced between groups. Proportion of ISS III pts was around 15% with all regimens. 8.1% of VCD pts, 12.6% of VRD and 10.9% of RAD pts all had baseline eGFR <50 ml/min (group I). eGFR rates of > 50 ml/min and ≤ 70 ml/min (group II) were observed in 11.6 % of VCD pts, 29.9% of VRD and 25.2 % of RAD pts, respectively. 78.2% of VCD pts, 56.1% of VRD and 63.9% of RAD pts had a baseline eGFR of > 70 ml/min (group III; p<.0001, chi-square-test). Evaluating MM PInd response by IMWG and EBMT criteria, 85.1% of VCD pts, 91.1% of VRD pts and 90.6% of RAD pts all achieved >PR (p=.0387). In the whole cohort, proportion of patients in eGFR group I had decreased from 10.0 to 3.0% (p<.001). The respective values were 1.8% post VCD, 5.6% post VRD and 2.5% post RAD (p<.0001). A downgrade of at least one GFR group occurred in 1.8% after VCD, 8.4% after VRD and 6.4% after RAD, respectively (distribution of group changes: p=.0030). In eGFR slope analysis (baseline vs PInd), median value was +3.8 mL/min(/1.73m²)/month in VCD pts, +0.7 mL/min(/1.73m²)/month in VRD and +2.1 mL/min(/1.73m²)/month in RAD patients (p=.0714). Next, we used three categories for incremental slope changes: < 0 ml/min(/1.73m²)/month; ≥ 0 ml/min(/1.73m²)/month and ≤ +2 ml/min(/1.73m²)/month; and > +2 ml/min(/1.73m²)/month, respectively. 25.7% of VCD, 29.4% of VRD and 23.3% of RAD pts fell into the <0 ml/min(/1.73m²)/month categories. An incremental change of >+2 ml/min was achieved by 55.2% of VCD vs 42.1% of VRD treated pts, respectively (Figure 1; p<.0001). ConclusionsIn our cohort of 811 NDMM pts, 10 % presented with <50 ml/min baseline eGFR. This proportion decreased significantly to 3.0% PInd. The different MM response across induction protocols was obviously not reflected by a concordant rate of renal recovery. Significantly more VCD vs VRD-treated patients achieved a positive eGFR slope of > +2 ml/min(/1.73m²)/month. It is tempting to speculate that either the difference between SQ and IV btz, differential effects of len and cyclophosphamide on kidney function or non-MM related factors account for these unexpected and discordant renal and MM responses. Kidney-specific AEs, urine protein studies and comorbidities will be presented.
Mügge:Celgene: Research Funding; Celgene, Janssen: Honoraria. Schreder:Janssen, Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria. Schaefer-Eckart:Pfizer, Janssen, Celgene: Honoraria. Metzler:Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria. Hertenstein:RS Media: Research Funding. Maschmeyer:Gilead, Janssen Cilag, Astra Zeneca; BMS, Merk-Serono: Honoraria. Salwender:Janssen Cilag: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Celgene: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; AMGEN: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Sanofi: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: Travel grants; Oncopeptides: Honoraria, Other: Travel Grants. von Lilienfeld-Toal:Celgene, Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Honoraria. Straka:Celgene, Janssen, AMGEN: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Knop:Janssen, AMGEN, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Lenalidomide, adriamycin, dexamethsone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal