Background. Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM) is a rare indolent lymphoma typical of the elderly population, with a median age at diagnosis of 65-70 years and median overall survival of approximately 10 years. Age is the most important prognostic factor in WM, and unrelated mortality significantly impacts survival in elderly patients. The past two decades have witnessed important treatment advances in WM, with the introduction of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies in the early 2000s and of ibrutinib in more recent years.
Less than 10% of WM patients are diagnosed at young age, and few studies have addressed their characteristics and outcome in the era of immunotherapy and targeted therapies. Here we report the presenting features, treatment and outcome of WM patients younger than 55 years diagnosed in 12 Hematologic Centers across Italy between 2000 and 2018.
Patients and Methods. Diagnostic criteria were those established during the second International Workshop on WM (Owen et al, 2003) and were retrospectively applied to patients diagnosed before 2003. The overall survival (OS) observed in the study cohort was compared with the expected survival of the general Italian population matched by sex, age and calendar year. The expected survival estimates were derived from Italian life tables (Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, ISTAT).
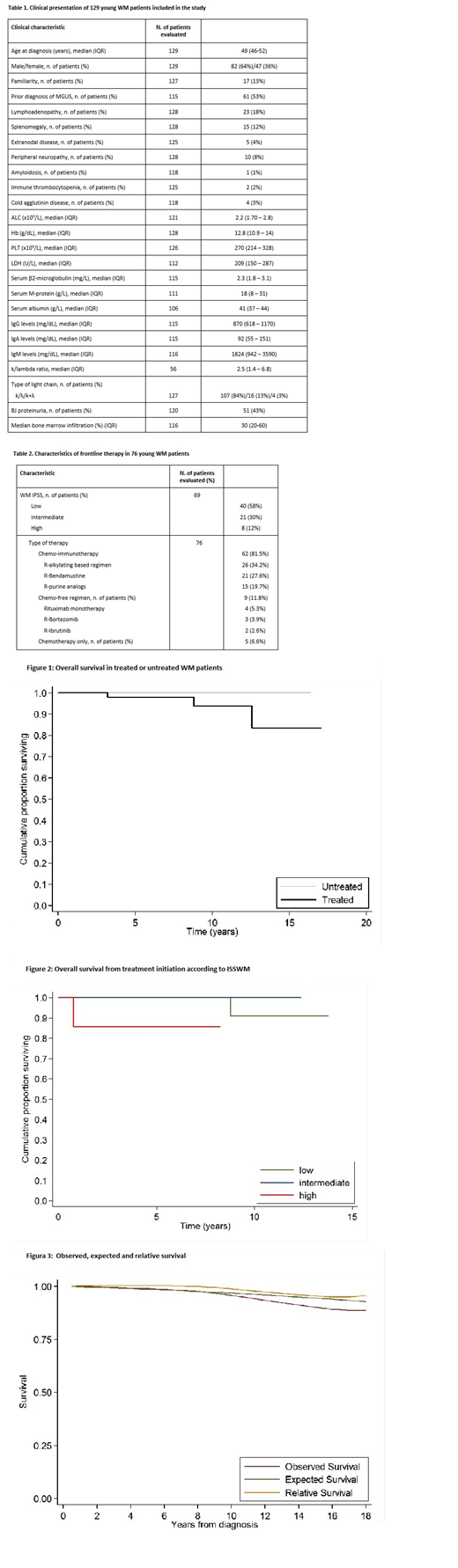
Results. The median age of patients included in the study was 50 years (interquartile range, IQR: 46-52). Their clinical characteristics at diagnosis are reported in Table 1. With a median follow-up of 5.6 years (IQR 3.1-9.1), 76 of 129 patients (59%) have been treated, at diagnosis (n=31, 41%) or after initial observation (n=45, 59%). The median treatment-free survival was 39 months. According to ISS-WM prognostic score, 58% were classified as low risk, 30% as intermediate risk and 12% as high risk. Frontline therapy included Rituximab in 71/76 patients (93%). Rituximab was associated with chemotherapy in 62 patients (82%), whereas 9 patients (12%) received a chemo-free induction. Five patients (7%) received chemotherapy only as first-line therapy (Table 2). The overall response rate (ORR) to induction therapy was 85%, including 39% CR+VGPR. Two patients received Rituximab maintenance for 2 years. The median progression-free survival (PFS) after first-line therapy was 76 months. Four of 76 patients (5%) received an autologous stem cell transplantation at relapse/progression. Overall, 14/76 patients (18%) received ibrutinib as first (n=2) or as subsequent line of therapy (n=12). During follow-up, 4/76 patients (5%) developed a solid cancer (bladder n=2, breast n=1, prostate n=1) and 2 a second hematologic cancer (chronic myelomonocytic leukemia n=1, secondary MDS n=1). Using a competing-risk model, accounting for death from any cause as the competing event, the cumulative incidence of second cancers was 2% at 5 years and 5.8% at 10 years. Three patients have died, 2 due to WM and 1 due to acute myeloid leukemia. The 5-and 10-year OS from diagnosis were 99% and 96% respectively. In a time-dependent survival analysis, considering therapy as a time-dependent covariate, the OS of treated and untreated WM patients was not significantly different (P = 0.162) (Figure 1). Among treated patients, the OS was significantly shorter in high-risk patients as compared with low- and intermediate-risk patients (5-year OS 85.7% versus 100%, P=0.018) (Figure 2). The OS of young WM patients was not significantly reduced as compared with age-, sex- and calendar year- matched general population (P > 0.05) (Figure 3).
Conclusions. The presenting features of young WM patients resemble those typically described in the elderly WM population. Among treated patients, more than half are low-risk according to ISS-WM, confirming age as the most important prognostic factor. More than 90% of patients received Rituximab as part of the upfront treatment, mainly in combination with chemotherapy. Ibrutinib seems to be preferred over autologous stem cell transplantation in the relapsed/refractory setting. The outcome of young WM patients treated in Italy in the contemporary era was excellent in terms of both PFS and OS, with a life expectancy not significantly reduced as compared with the general population.
Varettoni:Gilead: Other: travel expenses; Janssen: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; ABBVIE: Other: travel expenses. Tedeschi:AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen spa: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BeiGene: Honoraria; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; SUNESIS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy. Benevolo:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Del Fabro:Janssen: Consultancy. Luminari:ROCHE: Other: Role as Advisor ; CELGENE: Other: Role as Advisor & Travel Grant; TAKEDA: Other: Travel Grant; GILEAD: Other: Lecturer . Arcaini:Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Celgene, Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Gilead: Other: Travel expenses; Bayer, Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Roche, Sandoz, Janssen-Cilag, VERASTEM: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal