Introduction: Evading Natural Killer (NK) cell-mediated immunosurveillance is key to the development of Multiple Myeloma (MM). Recent attention has focused on the role of hypersialylation in facilitating immune-evasion of NK cells. Abnormal cell surface sialylation is considered a hallmark of cancer and we have implicated hypersialylation in MM disease progression. Certain sialylated glycans can act as ligands for the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) receptors expressed by NK cells (Siglec-7 and Siglec-9). These ITIM motif-containing inhibitory receptors transmit an inhibitory signal upon sialic acid engagement. We hypothesized that desialylation of MM cells or targeted interruption of Siglec expression could lead to enhanced NK cell mediated cytotoxicity of MM cells.
Methodology: MM cells were treated with the sialidase neuraminidase prior to co-culture with primary NK (PNK) cells. MM cells were treated with 300µM 3Fax-Neu5Ac (sialyltransferase inhibitor) for 3 days prior to co-cultures with PNK cells. PNK cells were expanded, IL-2 activated (500U/ml) overnight, or naïve (resting). Primary MM samples/MM cell lines were screened with Siglec-7/9 chimeras (10µg/ml). PNK (IL-2 activated) cells were stained with anti-Siglec-7 and anti-Siglec-9 antibodies. Siglec-7 was targeted for knockout (KO) using the CRISPR/Cas9 system, a pre-designed guideRNA and the MaxCyteGT transfection system. MM cells were treated with 10µg/ml of Daratumumab prior to co-culture with expanded PNK cells.
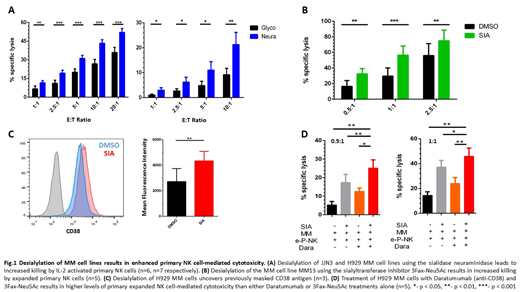
Results: Using recombinant Siglec-7/9 chimeras a panel of MM cell lines (MM1S, RPMI-8226, H929, JJN3 and U266) were shown to express ligands for Siglec-7 and Siglec-9 (>85%, n=3). Primary MM cells isolated from BM of newly diagnosed (n=3) and relapsed patients (n=2) were also shown to express Siglec-7 ligands (72.5±17.5%, 36.5% respectively). PNK cells express Siglec-7 and Siglec-9 (94.3±3.3% and 61±8.8% respectively, n=6). Desialylation of the MM cell lines JJN3 and H929 using neuraminidase significantly enhanced killing of MM cells by healthy donor (HD) derived PNK cells (expanded, IL-2 activated and naïve, n=7) at multiple effector:target (E:T) cell ratios. Furthermore, de-sialylation of JJN3 and H929 using neuraminidase resulted in increased NK cell degranulation (CD107α expression), compared to a glycobuffer control (n=7).
De-sialylation, using 300µM 3Fax-Neu5Ac, resulted in strongly enhanced killing of MM1S by expanded HD-derived PNK cells at multiple E:T ratios (n=5, p<0.01 at 0.5:1, p<0.001 at 1:1, p<0.01 at 2.5:1). Furthermore, CD38 expression on H929 MM cells significantly increased after treatment with 300µM 3Fax-Neu5Ac for 3 days (p<0.01, n=3). In a cytotoxicity assay, expanded PNK cell-mediated antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) of H929 MM cells pre-treated with Daratumumab (anti-CD38 moAb) and 3Fax-Neu5Ac was significantly higher than H929 cells pre-treated with Dara (p<0.05 at 0.5:1, p<0.01 at 1:1) or 3Fax-Neu5Ac (p<0.01 at 0.5:1, p<0.01 at 1:1) alone (n=5).
Using CRISPR/Cas9, over 50% complete KO of Siglec-7 was observed on expanded PNK cells, yet did not result in enhanced NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against either H929 or JJN3 (n=7). Siglec-9 KO using CRISPR/Cas9 is ongoing.
Discussion: Hypersialylation of MM cells facilitates immune evasion and targeted removal of sialic acid strongly enhances the cytotoxicity of NK cells against MM. However, to date the role of Siglecs remains inconclusive. Nevertheless, our data suggest that targeted desialylation is a novel therapeutic strategy worth exploring in MM. In particular, upregulation of CD38 provides a strong rationale for combinatory strategies employing targeted desialylation with CD38 moAbs such as Daratumumab, with the goal of maximizing ADCC.
Sarkar:Onkimmune: Research Funding. O'Dwyer:Onkimmune: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; GlycoMimetics Inc: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal