The bone marrow (BM) niche, is an extrinsic regulator of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) (Morrison and Scadden 2014). The niche can drive disease and loss of HSPC function (Raaijmakers et al., 2010; Kode et al., 2014; Dong et al., 2016). Of particular interest, deletion in specific niche cells of the small RNA processing enzymes, Dicer1 and Angiogenin (Ang1) resulted in hematopoietic transformation (Raaijmakers et al., 2010) and loss of HSC quiescence (Goncalves et al., 2016), respectively. We tested mechanisms by which small non-coding RNAs (sncRNA) from niche cells might contribute to HSPC regulation.
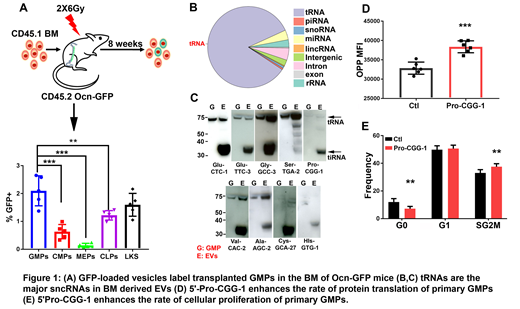
The transfer of cytoplasmic contents from specific mesenchymal subsets to wild type (WT) transplanted hematopoietic cells was evaluated by GFP. Osteoblastic cell reporter mice (Ocn-GFP, Col1-GFP) transferred 40-fold more GFP to HSPC than mesenchymal stem cells (Nes-GFP) or osteoprogenitors (Osx-GFP). GFP cannot transfer through gap junctions, however 100nM extracellular vesicles (EVs) labeled with the endocytic marker TSG-101 and GFP were found in Ocn-GFP bone marrow plasma. Granulocyte macrophage progenitor (GMPs) cells were the major hematopoietic recipients of osteoblast derived EVs (Fig. 1A).
Small RNA analysis of mouse BM EVs demonstrated >85% were tRNA (Fig. 1B) while Northern blot (NB) revealed both tRNAs and stress induced RNAs (tiRNAs) (Fig. 1C). tRNAs were evident in EVs and in EV generating and recipient cells, while tiRNAs were highly enriched in EVs compared to cells (Fig. 1C). Extracellular vesicle recipient and non-recipient GMPs (GMP[GFP+] and GMP[GFP-]) respectively demonstrated a 2-fold enrichment in reads mapping to tRNAs in GMP[GFP+]. Principle component analysis demonstrated that the two populations are distinct in their tRNA content. In addition, twelve specific tRNAs were present at a significantly higher levels in GMP[GFP+].
Gene expression analysis of GMP[GFP+]and GMP[GFP-] revealed an enrichment of protein translation and cell cycle related functions in GMP[GFP+] which were validated using an in vivo protein translation assay and cell cycle analyses. Synthetic oligos corresponding to the sequence of top ten tiRNAs that are enriched in GMP[GFP+] were transfected into primary GMPs. 5'-Pro-CGG-1 and 5'-Cys-GCA-27 increased the rate of protein translation and cellular proliferation in transfected GMPs (Fig. 1D-E). The physiologic relevance of EV transfer was assessed using two stress states, systemic Candida albicans infection and low dose gamma irradiation. The frequency of GMP[GFP+] increased in both states in concert with increased cell proliferation.
Therefore, EV transfer of sncRNAs from niche to hematopoietic progenitors in vivo is a rapid means of conveying information between cells. It alters progenitor protein translation and proliferation in a manner responsive to stress. The transfer of 5'tiRNA EV from specific niche cells to specific hematopoietic cells is an additional mechanism for niche regulation of blood cell production.
Sykes:Clear Creek Bio: Equity Ownership, Other: Co-Founder. Scadden:Clear Creek Bio: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Magenta Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Fog Pharma: Consultancy; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; LifeVaultBio: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Editas Medicine: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bone Therapeutics: Consultancy; Novartis: Other: Sponsored research; Fate Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Red Oak Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal