Abstract
Introduction: Hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD)/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome (SOS) is a serious complication of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) that is triggered, at least in part, by conditioning regimen-induced sinusoidal endothelial cell injury. VOD is thus commonly, but not exclusively, associated with myeloablative conditioning (MAC). The incidence of VOD in reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) HSCT was ≈2% in a single center series (Carreras et al. BBMT 2011), and risk factors for VOD in RIC HSCT remain poorly defined.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review to confirm all cases of VOD among patients undergoing RIC HSCT at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Brigham and Women's Cancer Center between January 2007 and June 2017. Diagnosis of VOD was based on modified Seattle or Baltimore criteria and/or liver biopsy or RUQ ultrasound in conjunction with fluid retention/ascites and hepatomegaly/RUQ pain. Diagnosis dates for all VOD cases were confirmed and clinico-laboratory values collected in the 10 days preceding the diagnosis. The same data were collected for a randomly selected control non-VOD RIC cohort, calculated from the median day of VOD onset derived from the cases. Acute kidney injury was defined as an absolute increase in creatine by 0.3 mg/dL or a relative increase of > 50% within a 48-hour period. Increased platelet transfusion requirement was defined as requiring a platelet transfusion on 2 consecutive days in the 7 days prior to VOD diagnosis, excluding transfusions for procedures. Incidence of VOD at D50 was calculated using a competing risk framework. Cox regression was used to identify significant features for predicting VOD. Survival was compared to a concurrent cohort of 76 patients with VOD after MAC HSCT recently published from our center (Roeker et al. BBMT 2018).
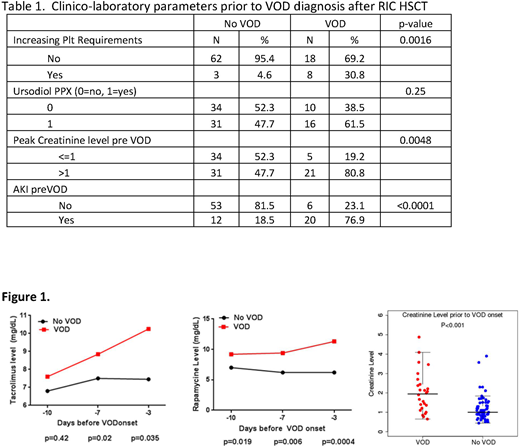
Results: A total of 1492 patients underwent RIC HSCT, of whom 1070 (67.8%) received sirolimus (Sir) with tacrolimus (Tac) as part of the GVHD prophylaxis, and 1217 (82%) received intravenous busulfan(Bu) 3.2 or 6.4mg/kg with fludarabine(Flu) as conditioning. Twenty-six developed VOD (median day of diagnosis = d+26, range 5-48 days), for a cumulative incidence of 1.6% (95%CI 1.1%-2.4%). The median bilirubin at diagnosis was 1.1 mg/dL(range 0.6-5.2). Only 5 (19.2%) patients had a bilirubin of ≥2.0 mg/dL on the date of VOD diagnosis, although total bilirubin peaked at ≥ 2 mg/dL in 17 of 26 (65.4%). VOD was mild/moderate in 16 and severe in 10 patients. Sixteen had received ursodiol as VOD prophylaxis. Defibrotide was used as treatment in 17 cases. The 2-year overall survival (OS) was 54% from VOD onset. VOD was associated with increased risk for NRM (HR 4.02, 95% CI 2.1-7.7, p<0.0001), but not OS (HR 1.53, 95% CI 0.9-2.6, p= 0.11), PFS (HR 1.42, 95% CI 0.9-2.4, p= 0.17) or relapse (HR 0.68, 95% CI 0.3-1.5, p= 0.35). Compared to patients who developed VOD after MAC, OS at 2 years after VOD was better in RIC patients (54% vs. 28%, p=0.04). Use of ursodiol was not associated with any reduction in VOD incidence. In the multivariable model, the only significant risk factor for VOD was use of Sir with Tac for GVHD prophylaxis (HR 3.2, 95% CI 1.26-12.17). Among RIC Bu/Flu patients who received Tac/Sir based GVHD prophylaxis, 18/877 (2.1%) developed VOD, compared to 1/351 (0.28%) in RIC Bu/Flu patients without Sir, p <0.01. To assess clinico-laboratory predictors of VOD patients in the 10 days prior to VOD diagnosis, we compared the 26 VOD cases to 65 randomly selected control RIC patients. The groups were well matched with regards to baseline characteristics. In the 10 days prior to VOD diagnosis (or D+26 for controls), VOD patients were significantly more likely to develop acute kidney injury, peak creatinine >1, increasing platelet transfusion requirements, and increasing Tac and Sir trough levels (Table 1, Fig 1).
Conclusions: The incidence of VOD in this large modern cohort of 1492 RIC HSCT patients was 1.6%, and was associated with the use of Sir with Tac. Onset of VOD in RIC patients was delayed (median D+26 vs. D+14) and 2 yr-OS is superior compared to MAC patients. Only 19% of the RIC VOD cases met the bilirubin threshold for Baltimore and Seattle criteria at diagnosis, suggesting that the rise in bilirubin is a later event in these RIC VOD cases, whereas increasing platelet transfusion requirements, sudden rise in Tac and Sir levels, elevated serum creatinine and acute renal injury appear to be early clinical predictors.
Nikiforow:Kite Pharma: Consultancy. Antin:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Richardson:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Soiffer:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ho:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal