Abstract
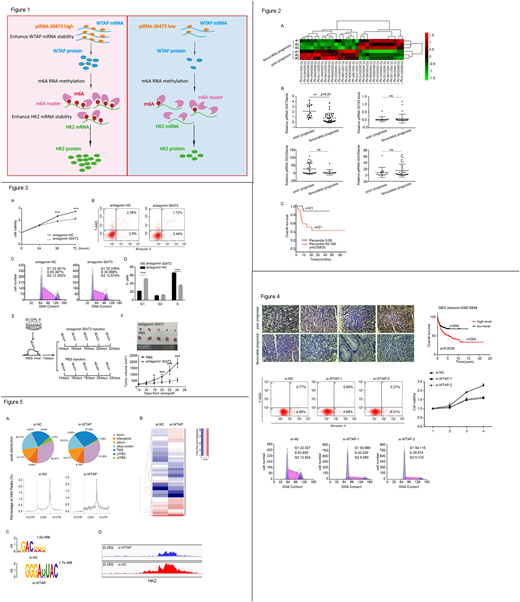
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant modification on eukaryote messenger RNA (mRNA), functions in various fundamental bioprocesses. However, the role of m6A in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) remains poorly understood. Here, we reported that piRNA-30473, which expression supported the aggressive phenotype of DLBCL and was correlated with poor prognosis, was a potent regulator of m6a modification through targeting m6a methyltransferase WTAP (Figure 1).
Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), a novel class of small non-coding RNAs, have been documented to be involved in the epigenetic regulation of cancer. A cohort of 42 patients with newly diagnosed DLBCL, uniformly treated and followed, was studied. We show that piRNA-30473 was significantly upregulated in high-risk DLBCL patients compared to low-risk DLBCL patients by microarray assay on 6 samples, further confirmed by qPCR analysis on 42 samples (Figure 2). Moreover, silencing of piRNA-30473 expression reduced proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest, but not apoptosis in SU-DHL-8 and Toledo lymphoma cells. In "human-in-mouse" xenograft DLBCL models, injection of antagomir-30473 into mice led to a significant reduction in tumor volume compared with control(Figure 3).
Our data further indicated that the combination of piRNA-30473 signature with the National Comprehensive Cancer Network International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) and cytogenetics status had a better prediction for PFS and OS than those without the piRNA-30473 signature in the univariate and multivariate analyses by an AUC analysis with cross-validation.
Silencing of piRNA-30473 diminished global m6A level in SU-DHL-8 and Toledo cells and decreased m6a methyltransferase WTAP in mRNA and protein levels. We further identified that piRNA-30473 enhanced WTAP expression through direct binding to its 3' UTR. Consistently, WTAP knockdown decreased the global m6A level and induced cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition in SU-DHL-8 and Toledo cells. Moreover, Silencing of piRNA-30473 displayed decreased cell proliferation, which could be abrogated by WTAP overexpression. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that high WTAP levels in DLBCL patients were correlated with OS by analyzing the gene expression profiling of DLBCL patients from GEO database (GSE10846) (Figure 4).
Next, we mapped the m6A methylomes of siCtrl and siWTAP SU-DHL-8 cells by m6A sequencing (m6A-seq) with independent biological replicates. The RGACH motif (R = G/A; H = A/C/U) were identified to be highly enriched within m6A sites in the SU-DHL-8 cells. M6A peaks in siCtrl and siWTAP SU-DHL-8 cells were abundant in coding sequences (CDSs), 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), and near stop codons. Remarkably, 85% m6A-Hyper transcripts identified from siCtrl SU-DHL-8 cells turned into m6A-Hypo in siWTAP SU-DHL-8 cells, with approximately 66% of the Hypo-down and 65% of Hypo-up transcripts became Hyperup and Hyper-down, respectively, which might be genuine targets of WTAP. Eleven genes listed in Table 2 showed a significant change between siCtrl and siWTAP SU-DHL-8 cells in m6A peak levels, and abundance of the corresponding mRNA transcript, and were also significantly positively or negatively correlated with WTAP in expression in four datasets of large cohorts of DLBCL. Collectively, our data demonstrate that an enzyme hexokinase II (HK2), which was reported to be a key metabolic driver of the DLBCL phenotype, were functionally important targets of WTAP. WTAP-mediated regulation of HK2 depended on its m6A demethylase activity and the m6A modifications in the target mRNA transcripts (Figure 5).
In summary, our finding demonstrate that piRNA-30473 were significantly associated with both PFS and OS in the univariate analysis, and were still statistically significant after adjusting for NCCN-IPI, and adverse cytogenetics in the multivariate analysis. Moreover, we provide compelling evidence demonstrating that WTAP, which was downregulated by piRNA-30473, played a critical oncogenic role in DLBCL, through enhancing m6A levels in mRNA transcripts of its critical target gene HK2 and thereby triggering corresponding signaling cascades. Our study highlights the functional importance of the m6A modification machinery in DLBCL, and provides profound insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis by revealing a previously unrecognized mechanism of gene regulation in DLBCL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal