Abstract
Introduction: Ibrutinib is an oral Bruton Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor, approved for the treatment of symptomatic Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia (WM). MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations affect progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with WM. In some cases, ibrutinib dose reductions are needed for the management of toxicity. However, it remains unclear if ibrutinib dose reductions adversely affect PFS in WM patients.
Methods: We evaluated 217 consecutive patients with the clinicopathological diagnosis of WM who were symptomatic and received treatment with ibrutinib. We analyzed relevant clinical features and their association with the risk of dose reduction, using logistic regression models, as well as PFS using Cox proportional-hazard regression models. Time to events was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. p<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: All 217 patients were initiated on ibrutinib monotherapy at the approved dose of 420 mg by mouth (PO) once daily (QD). At a median follow-up of 26 months (95% CI 22-31 months), 159 patients (73%) continued ibrutinib without dose-reduction, while 58 (27%) patients had a decrease in their ibrutinib dose. There was no difference in follow-up between those with and without dose reduction. Of the 58 patients that dose reduced, 45 (78%) were reduced to 280 mg daily; 12 patients (21%) were reduced to 140 mg daily, and 1 (2%) to 140 mg every other day.
The median time to ibrutinib dose reduction from 420 mg PO QD to 280 mg PO QD was 155 days (95% CI 89-282 days), and median time to dose reduction from 280 mg PO QD to 140 mg PO QD was 55 days (95% CI 24-260 days). Reasons for ibrutinib dose reduction included cytopenia(s) (n=13; 24%), arrhythmia (n=9; 17%), musculoskeletal discomfort (n=8; 15%), constitutional symptoms (n=6; 11%), skin changes/rash (n=5; 9%), mouth sores (n=4; 7%), gastrointestinal symptoms (n=3; 6%), infections (n=3; 6%), bleeding (n=2; 4%) and transaminase elevation (n=1; 2%). Patients in whom ibrutinib dose reduction was needed were more likely to be older than 65 years (76% vs. 47%; p<0.001), had higher International Prognostic Scoring System for WM (IPSSWM) at ibrutinib initiation (IPSSWM 1, 2 and 3 were 19%, 23% and 58% vs. 24%, 39% and 37%, respectively; p=0.03), and were more likely to have attained a major response (93% v. 69%; p<0.001) than patients in whom ibrutinib dose was not reduced.
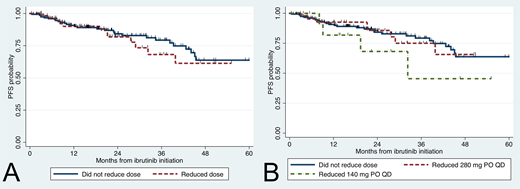
There were no differences in baseline characteristics including sex, hemoglobin levels, platelet counts, beta-2-microglobulin levels, serum IgM levels, bone marrow involvement, previous treatment, MYD88 and CXCR4 mutational status and time from WM diagnosis to ibrutinib initiation between those with and without dose reduction. Regression analyses showed higher odds of dose reduction occurring in patients >65 years (OR 3.6, 95% CI 1.8-7.1; p<0.001) and those who had attained a major response (OR 6.0, 95% CI 2.1-17.5; p=0.001). The median PFS for the entire group was not reached, and the 3-year PFS rate was 76% (95% CI 68-83%). Factors associated with a worse PFS were platelet count <100 K/uL (HR 3.9, 95% CI 1.8-8.7; p=0.001) and CXCR4 mutations (HR 3.0, 95% CI 1.5-6.0; p=0.001). Expression of mutated MYD88 (HR 0.01, 95% CI 0.00-0.09; p<0.001) and attainment of major response (HR 0.23, 95% CI 0.12-0.43; p<0.001) were associated with a better PFS. Importantly, those who experienced a reduction in their ibrutinib dose showed no significant difference in PFS (HR 1.19, 95% CI 0.61-2.35; p=0.61; Figure 1A). There were no differences between patients who reduced to 280 mg PO QD (HR 1.0, 95% CI 0.5-2.2; p=0.99) or 140 mg PO QD (HR 1.9, 95% CI 0.7-5.5; p=0.22) versus those without dose reduction (Figure 1B).
Conclusion: Ibrutinib dose reduction occurred in 27% of patients with WM, at a median time to dose reduction of 155 days. Patients older than 65 years and those with major responses were more likely to have a dose reduction. With a median follow-up time of 26 months, ibrutinib dose reduction did not significantly impact PFS.
Castillo:Millennium: Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy. Hunter:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Treon:Johnson & Johnson: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; BMS: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal