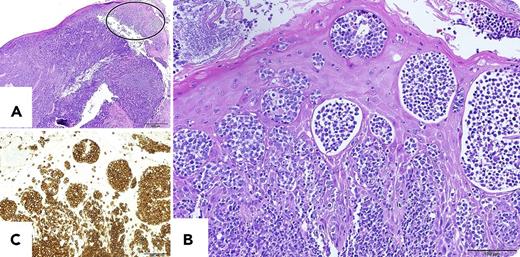
A 69-year-old Japanese man was admitted to our hospital for examination of a sore throat during the past 3 months. Physical examination showed swelling of the right tonsil and right cervical lymph nodes. Hematoxylin and eosin imaging of the tonsil biopsy showed diffuse infiltration of medium-sized atypical lymphoid cells (panel A; bar: 500 μm). Interestingly, the atypical lymphoid cells infiltrated into the squamous epithelia covering the tonsil and formed aggregates (panel A, closed ellipse). Shown in higher magnification (panel B; bar: 100 μm), they reminded us of Pautrier microabscesses observed in primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma such as mycosis fungoides (MF) or cutaneous infiltration of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL). Immunohistochemically, these atypical lymphoid cells were positive for CD3 (panel C; bar: 100 μm), CD4, and FoxP3, and negative for CD20 and CD8. Together with monoclonal integration of human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 provirus, a diagnosis of ATLL was made.
We have recently experienced another case of Pautrier-like microabscesses in the tonsil by non-ATLL peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Both cases had no cutaneous lesions. Tonsil infiltration of MF is reported to form Pautrier-like microabscesses. To our knowledge, this is the first report of Pautrier-like microabscesses in noncutaneous squamous epithelia by non-MF peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
A 69-year-old Japanese man was admitted to our hospital for examination of a sore throat during the past 3 months. Physical examination showed swelling of the right tonsil and right cervical lymph nodes. Hematoxylin and eosin imaging of the tonsil biopsy showed diffuse infiltration of medium-sized atypical lymphoid cells (panel A; bar: 500 μm). Interestingly, the atypical lymphoid cells infiltrated into the squamous epithelia covering the tonsil and formed aggregates (panel A, closed ellipse). Shown in higher magnification (panel B; bar: 100 μm), they reminded us of Pautrier microabscesses observed in primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma such as mycosis fungoides (MF) or cutaneous infiltration of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL). Immunohistochemically, these atypical lymphoid cells were positive for CD3 (panel C; bar: 100 μm), CD4, and FoxP3, and negative for CD20 and CD8. Together with monoclonal integration of human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 provirus, a diagnosis of ATLL was made.
We have recently experienced another case of Pautrier-like microabscesses in the tonsil by non-ATLL peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Both cases had no cutaneous lesions. Tonsil infiltration of MF is reported to form Pautrier-like microabscesses. To our knowledge, this is the first report of Pautrier-like microabscesses in noncutaneous squamous epithelia by non-MF peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
For additional images, visit the ASH Image Bank, a reference and teaching tool that is continually updated with new atlas and case study images. For more information, visit http://imagebank.hematology.org.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal