Abstract
Introduction :Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) expression is a major modulator of sickle cell disease (SCD) severity. Hydroxyurea improves SCD clinical manifestations in part through its ability to induce HbF synthesis which decreases the HbS polymer formation. However, the distribution of HbF is heterogeneous in red blood cells (RBCs) from SCD patients. In the hypothesis of an HbF "threshold" for inhibiting the HbS polymerization, accurate measurement of the HbF content in RBC is an important issue. Several techniques have been developed to quantify HbF. Nevertheless, these technics are qualitative, or semi quantitative, allowing only to detect the RBCs containing a mild/high HbF level, called "F-cells".
Methods : we developed a simple and accurate method to quantify the HbF in each single RBCs and to evaluate the HbF distribution in SS RBCs during a 6 month Hydroxyurea therapy, as a proof of concept. RBCs adults carrying hereditary persistence of HbF (HPFH), β-Thalassemia or db-Thalassemia, were collected. Pancellular homogenous HbF distribution was controlled by flow cytometry. The mean amount of HbF (MCHbF) was calculated from the %HbF determined by HPLC and the mean corpuscular haemoglobin (MCH). The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) after HbF staining by a monoclonal antibody was quantified by flow cytometry and normalized using quantitation beads.
RBCs from homozygous SCD patients were collected before treatment (D0), between 15 days and 3 months (D15-M3) and after 6 months of HU treatment (M6). RBCs were frozen at -80°C. Non-inclusion criteria were vaso-occlusive crisis, blood transfusion within 3 months preceding the enrolment, and on-going pregnancy. After thawing, RBCs were analysed by flow cytometry after HbF staining.
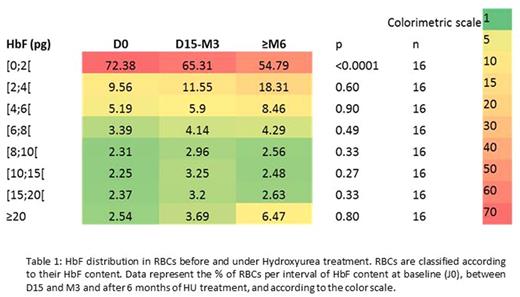
Results : Homogenous HbF distribution was proven by flow cytometry in 12 adults with HPFH, δβ thalassemia or β thalassemia. A linear regression between MCHbF and MFI, on 11 different experiments, was performed and provided an equation allowing the quantification of HbF (pg) by RBC (R²=0.94; p<0.0001). A mathematical model calculated the 95% confidence interval. Sixteen homozygous SCD adults were included for the study on HbF distribution under HU. RBCs containing 0 to 2 pg of HbF (table 1) decrease by 25% after 6 months of HU (p<0.0001) whereas a non-significant increase in the other categories of HbF by RBC was found.
Conclusion : This simple technique, based on flow cytometry, could represent a new important tool in sickle cell and thalassemia diseases to better quantify the HbF expression and then better evaluate patient's pronostic and therapeutic effects.
Galactéros: Addmedica: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Bartolucci: Addmedica: Research Funding; GBT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Fondation Fabre: Research Funding; Novartis US: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal