Abstract
Introduction:SIMPLICITY (NCT01244750) is an ongoing observational study of CP-CML pts in routine clinical practice receiving first-line (1L) imatinib (IM) prior to 2010 (retrospective) or 1L IM, dasatinib (DAS) or nilotinib (NIL) since 2010 (prospective) in the US and Europe.
Methods: This analysis was designed to identify baseline characteristics associated with TKI switching in pts pooled from the prospective and retrospective cohorts. Pts were characterized as 'early switchers' (who discontinued 1L TKI and switched to a second-line [2L] TKI within 3 months of TKI initiation) or 'late switchers' (who discontinued 1L TKI and switched to a 2L TKI between 3 and 12 months after TKI initiation). A comparator group of 'non-switcher' pts did not discontinue 1L TKI within 12 months of TKI initiation; 'early non-switchers' did not switch 1L TKI within the first 3 months and 'late non-switchers' did not switch 1L TKI between 3 and 12 months after TKI initiation. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify factors associated with early vs. late switching (gender, age at diagnosis ≥65 years, 1L TKI, region, reason for discontinuation).
Results: By March 07 2016, 1494 pts were enrolled at 197 sites in 7 countries. Within 12 months of initiating 1L TKI 238 pts (16%) had switched to 2L TKI. Of switchers, 31% and 69% were early and late, respectively. Of the overall cohort, 1189 pts were early non-switchers and 1146 were late non-switchers. Most early switchers received IM as 1L TKI (49%), followed by NIL (32%) and DAS (19%); most late switchers received IM (56%), followed by DAS (26%) and NIL (18%). Fewer early non-switchers than switchers received IM as 1L TKI (43%), followed by NIL (28%) and DAS (28%); fewer late non-switchers than switchers received IM (44%), followed by DAS (28%) and NIL (28%). Most switchers were female; a higher proportion of female switchers was early vs. late (63% vs. 52%, respectively). In comparison, 43% of pts in both non-switching groups were female. Median ages of early and late switchers were 54 (interquartile range [IQR]: 46-68) and 58 (IQR: 46-69) years, respectively; median ages of early and late non-switchers were 56 (IQR: 46-68) and 56 (IQR: 45-67) years, respectively.
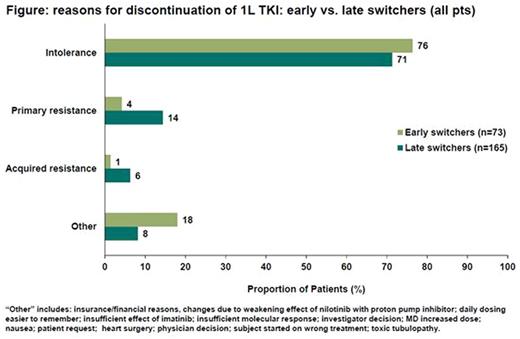
Logistic regression analysis showed that pts who switched due to intolerance had greater odds of switching early compared with those who switched due to resistance (odds ratio = 3.49; 95% confidence interval: 1.11-10.98; p=0.0323). Among the 238 pts who switched 1L TKI, the main reason for 1L TKI discontinuation was intolerance (early switchers: 76%; late switchers: 71%; Figure).
The most common intolerances leading to changes in early and late switchers varied by 1L TKI. Most common for IM early switchers (n=26) was general disorders/administration site conditions (including fatigue, edema, pain) and skin/subcutaneous disorders; for IM late switchers (n=53), gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, general disorders/administration site conditions and skin/subcutaneous disorders. Most common for DAS early switchers (n=10) was GI disorders; for DAS late switchers (n=36), respiratory/thoracic/ mediastinal disorders. Most common for NIL early switchers (n=19) was GI disorders; for NIL late switchers (n=25), GI disorders, general disorders/administration site conditions and skin/subcutaneous disorders.
TKI resistance less commonly contributed to 1L TKI discontinuation. Primary and acquired resistance were seen in higher proportions of late than early switchers (Figure). In late switchers, primary resistance was a more common reason for discontinuation in IM pts vs. DAS pts or NIL pts (22%, 5% and 4%, respectively). Acquired resistance was only reported as a reason for discontinuation in IM-treated pts (early switchers: 0.3%; late switchers: 11%).
Conclusions: Of pts switching or discontinuing 1L TKI in the first 12 months of therapy, around one third switched within the first 3 months; compared with late switchers and non-switchers these pts were more likely to be younger and female. TKI intolerance was the main reason for switching and was significantly associated with early switching. Resistance was a less common reason for changing TKI therapy and was seen more frequently after 3 months and among pts treated with IM. More research is necessary to make definitive conclusions about comparisons between TKI groups, given the small numbers of pts in the TKI cohorts and the non-controlled nature of the trial.
Goldberg:COTA Inc: Employment; Novartis: Consultancy; Neostem: Equity Ownership; Pfizer: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Michallet:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Astellas Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria. Hehlmann:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; German CML-Group: Research Funding. Zyczynski:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Foreman:ICON Clinical Research: Employment. Calimlim:ICON Clinical Research: Employment. Paquette:Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy; Ariad: Consultancy. Gambacorti:Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding. Cortes:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squib: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding. Zagorska:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Rong:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment. Mauro:BMS: Consultancy; Ariad: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal