Abstract
Background
Sustained treatment-free remission (TFR) has been reported in 40-60% of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase (CML-CP) after discontinuation of imatinib or dasatinib following at least 1-2 years of deep molecular response (MR). We investigated safety and efficacy of discontinuing nilotinib treatment after 2 years of sustained MR4.5 (BCR-ABL1IS ≤ 0.0032%) on nilotinib in patient for whom MR4.5 was achieved by prior treatment with imatinib or nilotinib.
Methods
The Stop Nilotinib (NILSt) trial was a single-arm multicenter phase 2 study in Japan. CML-CP patients who obtained MR4.5 by treatment with imatinib or nilotinib were enrolled, and were further treated with nilotinib for 2 years. The patients who maintained MR4.5 during those 2 years were eligible for discontinuation of nilotinib. After treatment discontinuation, maintenance of MR4.5 was monitored by quantitative RT-PCR every month during the 1st year and every 2 months during the 2nd year. Nilotinib was reintroduced in patients who lost MR4.5. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who maintained MR4.5 at 1 year after the discontinuation. This study is registered, number UMIN000007141.
Results
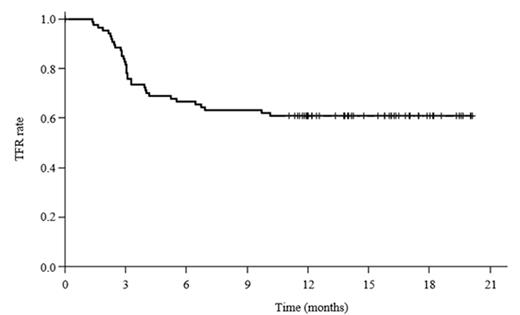
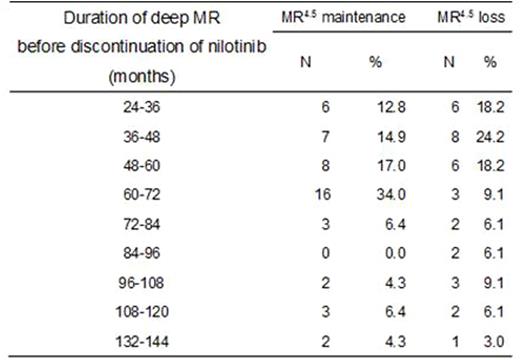
112 patients were enrolled between April 11, 2012 and November 30, 2012, and were treated with nilotinib for 2 years. 90 of those patients maintained MR4.5 during the entire 2-year period and were eligible to discontinue treatment, among which 87 patients actually discontinued nilotinib to intend a treatment-free remission period. Median follow-up after the discontinuation was 13.4 months (range 4.8-20.1). At 1 year, 53 patients (58.9%, 90% CI 49.7-67.7) maintained MR4.5, whereas 34 patients experienced loss of MR4.5 mostly within 6 months after the discontinuation (Figure 1). Thirty-two of those 34 patients (94.1%) regained MR4.5 2.2 months (median, 95% CI 1.5-2.6) after reintroduction of nilotinib. The following parameters did not significantly predict the probability of MR4.5 at 1 year after the discontinuation: age, sex, Sokal, Hasford, EUTOS scores, history of IFN-a therapy, total duration of imatinib or nilotinib therapy, time to MR4.5, or trough concentrations of nilotinib in sera. Notably, the percentages of patients maintaining MR4.5 for one year without treatment did not improve significantly with longer duration of prior MR4.5 on treatment; even some patients with a duration of prior deep MR on treatment exceeding 10 years experienced loss of MR4.5 after treatment discontinuation (Table 1). The rates of all grade (grade 3/4 in parentheses) cardiovascular events were 5.5% (2.7%), fluid retention were 14.1% (0%), and musculoskeletal pain were 9.7% (1.8%) during the 2-year treatment periods.
Conclusion
Nilotinib can be discontinued without relapse in more than half of the patients who maintained MR4.5 for at least 2 years. However, relapse occurred after the discontinuation following even more than 10 years of sustained deep MR in the rest of the patients. This suggests that the period of deep MR after which nilotinib can be discontinued without relapse is considerably long, if any, in a substantial proportion of patients. Biomarkers to detect such patients are awaited. Furthermore, additional strategies may be required to safely discontinue nilotinib as early as possible in such patients, in order to avoid serious adverse events caused by prolonged administration.
Kaplan-Meier estimates of TFR after discontinuation of nilotinib
Kaplan-Meier estimates of TFR after discontinuation of nilotinib
Rates of MR4.5 maintenance at 1 year after discontinuation of nilotinib in relation to the duration of deep molecular response before the discontinuation
Rates of MR4.5 maintenance at 1 year after discontinuation of nilotinib in relation to the duration of deep molecular response before the discontinuation
Kawaguchi:Novartis: Honoraria. Kuroda:Janssen: Honoraria; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding. Nakamae:Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis Pharma KK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel/accommodation/meeting expenses, Research Funding. Matsumura:Bristol-Myers Squibb Company: Honoraria; Novartis Pharma K.K: Honoraria; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer Japan Inc.: Honoraria. Kanakura:Bristol Myers: Research Funding; Alexionpharma: Research Funding; Nippon Shinyaku: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Eisai: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Shionogi: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin: Research Funding; Fujimotoseiyaku: Research Funding; Toyama Chemical: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal