Abstract
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) promote tumor cell target recognition of adoptively transferred T cellsand clinical studies have shown that autologous T cells transduced with CARs targeting CD19, expressed on normal B cells and several B cell malignancies, are effective against CD19+ malignancies. The potential of donor-derived CD19-CAR T cells to treat relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloHSCT) has been relatively unexplored due to concerns for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and other toxicities. However, recent clinical trials of donor-derived CD19-CAR T cells in allo-HSCT have noted a surprisingly low incidence of GVHD. We studied the GVHD and anti-tumor potential of donor-derived mouse CD19-specific CAR 1928z (m1928z) T cells in preclinical allo-HSCT and lymphoma models.
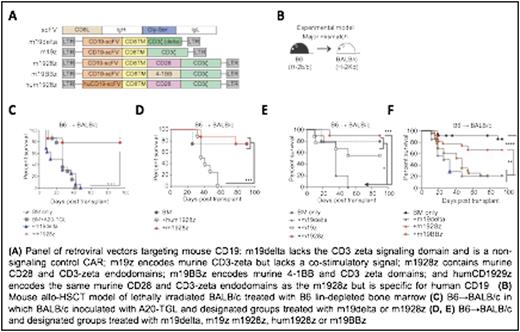
We constructed a panel of retroviral vectors targeting mouse CD19 (Figure 1A) to test various aspects of CAR stimulation and co-stimulation and generated T cells expressing these constructs. We then used these constructs in mouse allo-HSCT models comprising BALB/c recipients and B6 donors (Figure 1B).
A20 lymphoma-inoculated BALB/c recipients of B6 BM treated with donor B6 m1928z T cells had significantly higher tumor-free survival and improved survival compared to m19delta treated recipients (Figure 1C, P < 0.0001). Adoptive transfer of B6 m1928z T cells caused significantly less GVHD compared to B6 m19delta T cells (P < 0.001) in BALB/c recipients of B6 BM confirming that m1928z T cells cause less GVHD. We explored the requirement of CAR signaling for attenuated GVHD using hum1928z (P < 0.001) (anti-human CD19-CAR, non reactive in mice) T cells and noted significantly worse survival and GVHD scores in mice as compared to with m1928z indicating that CAR signaling was necessary for this protection (Figure 1D). We also examined the importance of co-stimulation and noted increased GVHD mediated by m19z T cells (P < 0.05) (CAR with no co-stimulation) (Figure 1E) and m19BBz (P < 0.01) (CAR with 4-1BB co-stimulation) (Figure 1F) indicating that CD28 co-stimulation was also vital for attenuated GVHD. To study the effect of concurrent TCR and CAR signaling in vitro, we used T cells engineered to co-express 1928z CAR and OT-1 TCR in a cold-target inhibition killing assay and noted that activation of the T cells through 1928z can impair lytic activity mediated by TCR. To elucidate the consequence of concurrent TCR and CAR activation, we studied the TCR signaling pathway and found increased phosphorylated PKCa, pERK1/2, pS6, pSTAT1, pSTAT3, and pSTAT5 in donor m1928z T cells compared to m19delta T cells, indicating a hyperactivated state. In order to further study the effect of concurrent stimulation of alloreactive TCR and m1928z CAR, we utilized B6 ABM-RAG1 knockout (ABM) T cells, which express monoclonal TCR specific to I-Abm12 expressed on B6.C-H2bm12 (BM12) mice. In accordance with our previous findings, we observed significantly less GVHD in allo-HSCT BM12 recipients of ABM m1928z T cells versus m19delta T cells (P < 0.0001). We performed global transcriptional analysis of ABM m1928z T cells and m19delta harvested from adoptively transferred BM12 recipients of B6 BM and differential upregulation of Bim, Bid, FasL and Apaf1 in m1928z T cells. Phenotypic analysis of these cells also showed increased PD-1 and Fas expression, consistent with post-stimulatory programmed cell death
In conclusion, we show that donor m1928z T cells mediate strong GVT effects with decreased GVHD. Following adoptive transfer, alloreactive m1928z T cells (but not m19BBz) undergo progressive loss of effector function and proliferative potential, and eventual deletion, which significantly decreases graft-versus-host activity. The non-alloreactive m1928z T cells present in bulk donor T cell populations retain significant anti-lymphoma activity. Our findings support the administration of donor 1928z T cells to prevent relapse of CD19+ malignancies after allo-HSCT and provide mechanistic insight into recent clinical trial results demonstrating that allogeneic CD19-specific 1928z CAR T cells promote anti-lymphoma activity while causing minimal GVHD.
Davila:Adaptive Biotechnologies: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celyad: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sadelain:Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal