Abstract
Background: Obinutuzumab (GA101; GAZYVA/GAZYVARO; G) is a glycoengineered type II anti-CD20 antibody with significant activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In the CLL11 study, infusion-related reactions (IRRs) were more common and more severe with G plus chlorambucil (Clb) than with rituximab plus Clb in CLL patients (pts) with coexisting conditions, and seen most frequently after the first G infusion. GREEN (NCT01905943) is an ongoing Phase 3b study investigating the safety and efficacy of G alone or in combination with chemotherapy in CLL pts. The primary endpoint is safety (adverse event [AE] profile). We report an exploratory analysis of the effectiveness of three different approaches to reduce IRRs during or after G administration.
Methods: Enrolled pts were aged ≥18 years (y) with documented CLL, an ECOG PS of 0-2, and adequate hematologic function. Pts received G 1000mg i.v., alone or with chemotherapy, on Day (D) 1, 8, and 15 of cycle (C) 1, and D1 of C2-6 (six 28-day cycles), with the C1D1 dose administered over 2 days as follows: Cohort 1, 25mg + 975mg infused at 12.5mg/hour (h) and 25mg/h, respectively; Cohort 2, 100mg (25mg/h) and 900mg (50-400mg/h) with oral dexamethasone 20mg or equivalent 12h pre-dose; Cohort 3 (recruited after independent analysis of Cohorts 1 and 2), doses and infusion rates as in Cohort 1 with pre-medication scheme as in Cohort 2. All three cohorts also received i.v. corticosteroids 1h pre-dose on D1. Administered regimens included G alone for any pt or G combined with chemotherapy: fludarabine and cyclophosphamide for fit pts only (CIRS ≤6 and CrCl ≥70ml/min); Clb for unfit pts only (CIRS >6 and/or CrCl <70ml/min); or bendamustine (B) for any pt. Pts refractory to previous G monotherapy had to receive G with chemotherapy. IRRs were defined broadly as any AE occurring during or within 24h of G infusion and considered related to G. Pts with high tumor burden (bulky lymphoadenopathy ≥10cm, or ≥5cm and <10cm with peripheral blood lymphocyte count ≥25x109/l) were considered high risk for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). The data cut-off for the analysis was March 25, 2016.
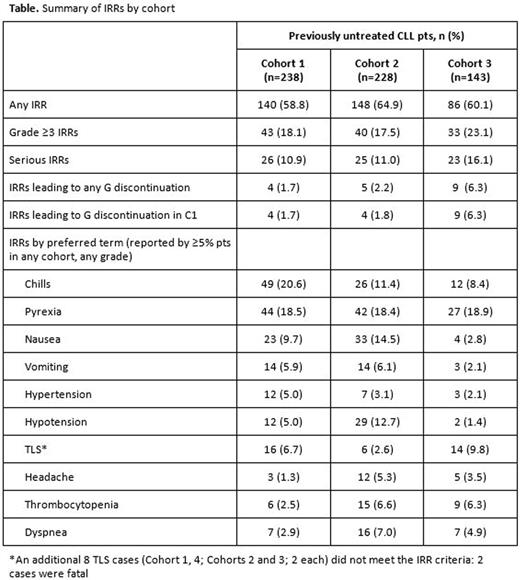
Results: A total of 622 first-line (1L) pts were analyzed; 609 were evaluated by Cohort (1, 238; 2, 228; 3, 143). Median age was 66.0y in Cohort 1 (61.8% at-risk for TLS), 64.5y in Cohort 2 (54.4% at-risk), and 64.0y in Cohort 3 (49.7% at-risk); approximately 54% of pts in each cohort were fit. Baseline demographic and disease characteristics were similar across cohorts. Median time on G treatment was 20.4 weeks (wks) in Cohort 1, 20.3 wks in Cohort 2, and 8.3 wks in Cohort 3; 62.6%, 46.5%, and 53.1% of pts, respectively, received G-B. Median observation time was 23.4, 15.5, and 3.4 wks, respectively. The frequency of all IRRs was similar across cohorts, but grade 3-4 IRRs, serious IRRs, and IRRs leading to discontinuation were more frequent in Cohort 3 than Cohorts 1 and 2 (Table). There were no grade 5 IRRs. All 44 TLS cases (36 classified as IRRs) were grade 3-5 and 23 were serious (5 [2.1%], 5 [2.2%] and 8 [5.6%] in Cohorts 1, 2, and 3, respectively); 29/44 (66%) were identified from laboratory findings alone. Of grade 3-4 and serious IRRs, TLS was the most frequent AE in 1L pts. TLS (as an IRR) was more frequent in Cohort 3 (9.8%) than in Cohorts 1 (6.7%) or 2 (2.6%), but cytokine-related IRRs, e.g. chills, gastrointestinal events (nausea and vomiting), and blood pressure events (hypertension and hypotension) were less frequent in Cohort 3 than Cohorts 1 and 2 (Table). In Cohort 3, most grade 3-4 IRRs (73%) occurred >5h after the C1D1 dose; in Cohorts 1 and 2, most occurred within 5h of dosing (60% and 58%, respectively). Treatment-emergent AEs were reported by 95.0% of all enrolled 1L pts (n=622; grade ≥3 AEs, 71.5%; serious AEs, 46.3%; AEs leading to G discontinuation, 13.5%). Of 29 deaths (4.7%) in 1L pts, 9 (1.4%) were related to G.
Conclusions: The frequency of all IRRs was similar across the three cohorts, but the highest frequencies of grade ≥3 and serious IRRs, most notably TLS, were seen in Cohort 3 (most stringent IRR reduction measures). In contrast, rates of some cytokine-related IRRs were lowest in this cohort. Sequential recruitment may have resulted in over-reporting of IRRs, particularly TLS, in Cohort 3: updated definitions of patients at risk of TLS and additional risk mitigation measures were communicated to investigators in January 2016 in the early stages of recruitment to this cohort.
Bosch:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Foà:Pfizer: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Ariad: Speakers Bureau. Leblond:Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Tumyan:Roche, Takeda: Consultancy. Gresko:Roche: Employment. Robson:F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Employment. Stilgenbauer:Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants, Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Hoffmann-La Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel grants , Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal