Abstract
Background: the Registro Italiano Trombocitemie (RIT) was activated mainly to evaluate the diagnosis and therapy appropriateness in the thrombocythemic patients with Ph-negative myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) observed in the adhering centers.
Objective: to evaluate how the diagnostic and therapeutic approach changed in the RIT patients diagnosed with thrombocythemic MPN in the last two decades.
Methods: the RIT centers registered by a web-based system during the years 2005-2014 their thrombocythemic MPN patients, and semesterly updated their follow-up data. For patients diagnosed before 2005, the data on diagnosis and prior follow-up were retrospectively collected. The diagnostic process and the initial treatment (started into the first year after diagnosis) were comparatively analyzed in the patients diagnosed before and after 2005.
Results: the RIT centers registered 2629 patients. 2388 of them, object of this analysis, were diagnosed between1995 and 2014: 1098 (46%) in the decade 1995-2004 (Group I), and 1290 (54%) in the decade 2005-2014 (Group II).
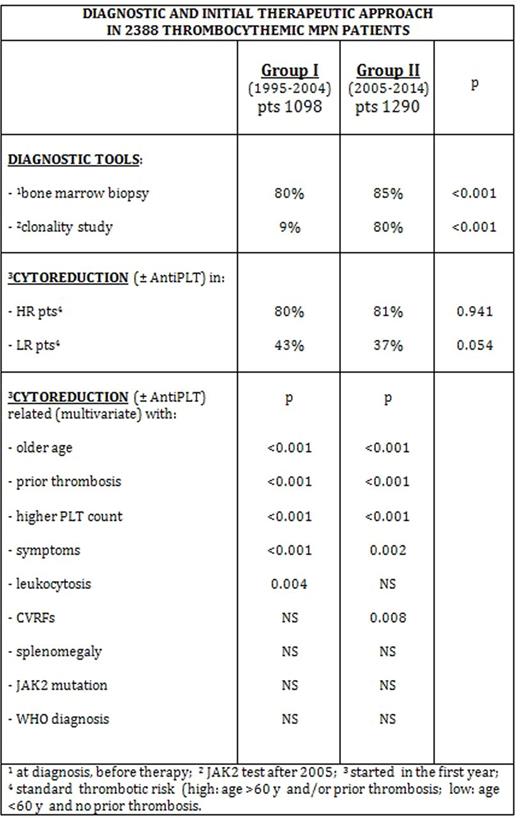
The diagnostic process in the patients of Group II and Group I included bone marrow biopsy (BMB, performed into 1 year and before any cytoreduction): 85% vs 80%, p <0.001; clonality tests (JAK2 and/or others): 80% vs 9%, p<0.001; cytogenetic evaluation: 55% vs 57%, p 0.58; abdominal echography: 46% vs 41%, p 0.016.
The patients of Group II, as compared with those of Group I, showed a similar gender distribution (M/F ratio 0.61 vs 0.65, p 0.452), and had at diagnosis: a higher age (median 60 vs 57 years, p <0.001; age >60 years in 50% vs 45% of cases, p <0.01); a similar rate of prior thrombosis (19% vs 19%), prior hemorrhage (3% vs 4%), CVRFs 69% vs 66%), splenomegaly (25% vs 25%), and hepatomegaly (22% vs 24%); a lower rate of disease-related symptoms (36% vs 40%, p 0.04); a higher rate of comorbidities (55% vs 51%, p 0.03).
Moreover, they had: a lower platelet (PLT) count (median 737 vs 775 x 109/L, p <0.001; <600 x 109/L in 22% vs 14% of cases, p <0.001); a similar white blood cell (WBC) count (median 8.6 vs 8.5 x 109/L; >10 x 109/L in 28% vs 26% cases); a similar median levels of hematocrit (HCT %, in females 41.4 vs 41.0; in males 44.7 vs 44.6) and hemoglobin (Hb g/dL, in females 13.8 vs 13.6; in males 15.0 vs 14.9). The BMB, revised according to the WHO 2008 criteria, showed a not different distribution (p 0.21) of ET (64% vs 61%), ep-PMF (16% vs 17%), PMF (3% vs 2%), PV (4% vs 4%), and U-MPN (13% vs 16%. The JAK2 V617F mutation in patients of Group II (at diagnosis) and of Group I (after diagnosis) was found in 62% and in 58% of tested cases (p 0.054), respectively. The patients at high standard thrombotic risk were 58% vs 52%, p 0.004.
In the patients of Group II and Group I the distribution of the treatment started into the first year was significantly different (p<0.001): AntiPLT 29% vs 24%, CYT 13% vs 16%, CYT+AntiPLT 49% vs 46%, CYT ± AntiPLT 62% vs 62%, AntiPLT ± CYT 78% vs 69%.
The treatment CYT ± AntiPLT was started in the patients at high standard thrombotic risk with a rate of 81% vs 80%, respectively, and in the patients at low standard thrombotic risk in 37% vs 43% of cases, respectively.
The initial treatment CYT±AntiPLT was related, in multivariate analysis, both in patients of Group II and Group I, with older age (>60 and 40-60 vs <40 years, p <0.001), higher PLT count (>1000 and 700-1000 vs <700 x 109/L, p <0.001), prior thrombosis (p <0.001), symptoms (p <0.001). Noteworthy, no relationship was found with JAK2 mutation, and WHO diagnosis.
Conclusion: in the studied thrombocythemic MPN patients the real-life diagnostic approach was improved after 2005 not only due to the routine use of JAK2 tests, but also due to the higher rate of BMB done (85% vs 80%).
The appropriateness of the cytoreductive treatment (CYT±AntiPLT started into one year from diagnosis) remained high in patients at high standard thrombotic risk (over 80% of cases were treated). Concomitantly, the inappropriate use of the cytoreductive drugs in patients at low standard thrombotic risk appreciably decreased (from 43% to 37% of cases). Moreover, it has to be remarked that the therapeutic approach was significantly influenced not only by older age and prior thrombosis, but also by thrombocytosis (PLT count >700 x 109/L), disease-related symptoms, and inconstantly by leukocytosis and CVRFs.
Gugliotta:SHIRE Co.: Honoraria. Gugliotta:Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal