Abstract
Background: NLPHL is a relatively uncommon subtype of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) accounting for about 5-6% of all HL cases. It has unique clinico-pathological, morphologic and immunohistochemical features with CD20-positive "lymphocyte predominant cells". Although long-term survival is better than in classical HL, frequent relapses are common and progression/transformation to aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) may occur. Whilst HDC auto-SCT is considered as standard of care for relapsed/refractory classical HL, data on HDC auto-SCT in relapsed/refractory NLPHL is sparse. Here, we report a registry study of HDC auto-SCT for NLPHL using the EBMT database, representing the largest sample analyzed to date.
Design: Eligible were patients with NLPHL18 years or older who underwent a first auto-SCT between 2003 and 2013, and were registered with the EBMT. Patients with NLPHL transformed to DLBCL were not eligible. The primary objective was 5-year progression-free survival (PFS). Baseline patient, disease and transplant data were collected from EBMT MED-A standard forms. Centers with potentially eligible patients were contacted to provide additional treatment and follow-up details with a copy of written diagnostic report for central review. Statistical analysis was descriptive and employed log rank comparisons for univariate assessment of the impact of baseline characteristics on survival endpoints.
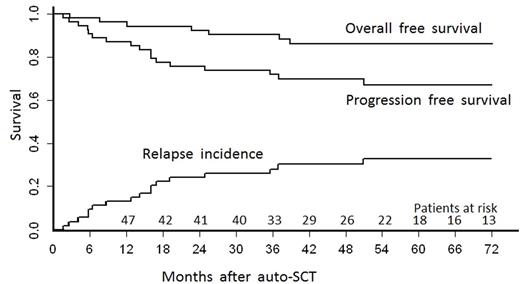
Results: We identified 92 patients who met the inclusion criteria with full data including a written diagnostic pathology report available. Of these, 36 patients were excluded after histopathology report review (17 classical HL, 2 NHL, 17 no sufficient information). The final sample comprised 56 patients. There was a predominance of male patients with a male:female ratio of 88%:12%. Median age was 36 (interquartile range (IQR) 29-50) years. Most patients (65%) had advanced stage (III-IV) at diagnosis and one third had B-symptoms. Prior to HDC auto-SCT, 71% patients had 2, 20% had 3, and the remainder had more than 3 lines of treatment (median: 2 lines). Rituximab was used in 62% of patients. The median time from diagnosis to HDC auto-SCT was 21 (IQR 14-51) months. Disease status prior to HDC auto-SCT was complete remission (CR) in 54% and partial remission (PR) in 43%. Most commonly used HDC was BEAM (84% patients), with additional rituximab in 13%. With a median follow-up of survivors of 5 (IQR 3.6-6.6) years, 5-year PFS and overall survival were 67% (95%CI 55-82) and 86% (95%CI 77%-96%), respectively. The 5-year incidence of relapse was 32% (95%CI 20-46). There were no transplant-related deaths. Univariate comparisons considering age, time from diagnosis to transplant, number of pre-treatment lines and rituximab use during induction, salvage and/or HDT failed to identify significant predictors of PFS or OS endpoints.
Conclusions: This study, the largest reported thus far on HDC auto-SCT in NLPHL, shows that two thirds of patients remain free of disease 5 years after HDC auto-SCT. In contrast with the usual characteristics of patients with NLPHL, those included in this series had high-risk disease with B-symptoms and advanced stage at diagnosis, and half the patients had HDC auto-SCT less than 2 years after diagnosis. This study demonstrates that patients with NLPHL and adverse features can benefit from HDC auto SCT at relapse.
Montoto:Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Research Funding. Masszi:Janssen-Cilag: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Moraleda:Pfizer: Research Funding. Bloor:Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; GSK: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Meissner:Amgen: Other: Travel Support; Takeda: Other: Travel Support; Celgene: Other: Travel Support; Teva: Other: Travel Support. Dreger:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal