Abstract
Introduction: Modern chemoimmunotherapy cures the majority of patients (pts) with newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCL). The paradigm for pts who relapse has been salvage chemotherapy followed by autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation (auto-HCT) when chemosensitive disease. This approach is often also applied to pts with primary treatment failure (PTF), although this group is heterogeneous and outcomes of HCT in this population have not been well described.
Methods: Fifteen US academic medical centers contributed pts to the REgistry of diFfuse large B cell lymphoma with prImary treatmeNt failurE (REFINE) collaboration. REFINE retrospectively captured patient, disease and treatment characteristics and response as assessed by treating center. Eligible pts were ≥ 18 years diagnosed with DLBCL during 2008-2015, who received upfront therapy including anthracycline and CD20-directed antibody and developed one of 3 patterns of PTF: relapse < 6 months following CR (early relapse- ER); only partial remission (PR) or stable disease (SD) with upfront therapy (residual disease-RD); progressive disease (PD) while receiving upfront therapy (primary progression-PP). Pts with HIV infection, primary CNS lymphoma or lymphoma transforming from a more indolent histology were excluded.
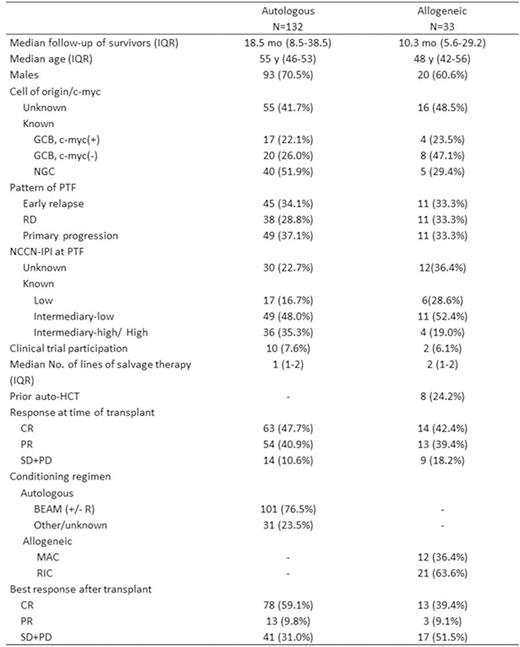
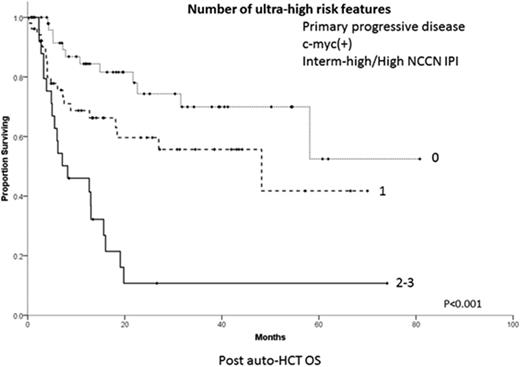
Results: Among 331 cases included in REFINE, patterns of PTF were ER in 95 (28.7%), RD in 92 (27.8%) and PP in 144 (43.5%) pts. Salvage therapy was administered to 94.6% of pts. We analyzed the 157 (47.4%) PTF pts who subsequently underwent HCT, 132 auto-HCT and 33 allo-HCT (8 after failure of auto-HCT) (Table). Nearly half of pts were in CR at transplant, after 1-2 lines of salvage therapy. Among all pts receiving auto-HCT, 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) from time of transplant was 38.4% (95% C.I. 29.6-47.2%) and overall survival (OS) 54.9% (95% C.I. 44.9-64.9%). Two-year OS from auto-HCT was affected by pattern of PTF: 71.3% for ER, 55.0% for RD and 41.7% for PP (P=0.05). OS at 2-years was 23.7% for auto-HCT pts with germinal center B (GCB)type,c-myc(+) (by FISH) tumors vs. 66.7% for GCB, c-myc (-), vs. 67.8% for non-germinal center (NGC) (P=0.01). Auto-HCT pts with intermediate-high/high NCCN-IPI at time of PTF had 2-year OS of 28.6% vs. 66.0% for intermediate-low and 80.9% for low risk (P<0.001). In multivariate analysis, PP pattern, c-myc(+) status and intermediate-high/high NCCN-IPI at time of PTF, hereforth called ultra-high-risk (UHR) fetures, negatively affected survival. Auto-HCT pts with no UHR features had 2-year OS of 74.3%(95% C.I. 60.0-88.6%)vs. 59.6% (95% C.I. 44.5-74.7%)for pts with 1 vs. 10.7% (95% C.I. 0-24.4%)for pts with 2-3 features (Figure, P<0.001). Among pts who underwent allo- HCT, 2-year PFS and OS were 20.5% (95% C.I. 6.4-34.6%)and 32.7% (95% C.I. 13.1-52.3%)respectively. Failure of allo-HCT was primarily due to disease progression, with only one death occuing due to HCT complications.
Conclusions: Pts with DLBCL experiencing PTF and 2 or more UHF features have dismal outcome after auto-HCT and should be targeted for experimental modalities of cellular therapy. Outcomes of allo-HCT in DLBCL with PTF are poor, due to rapid and fatal relapses.
Costa:Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding. Reddy:INFINITY: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; KITE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GILEAD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Karmali:Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Chavez:Janssen: Speakers Bureau. Calzada:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding. Barta:Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Celgene, Merck, Seattle Genetics: Research Funding. Flowers:Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Mayo Clinic: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; ECOG: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; NIH: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Millenium/Takeda: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding. Fenske:Seatle Genetics: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Millennium/Takeda: Research Funding. Cohen:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millennium/Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Infinity: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding. Hamadani:Takeda: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal