Abstract
Expression levels of miR-29 family members (i.e. miR-29a, miR-29b, & miR-29c) are deregulated in various neoplastic diseases, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), known to affect DNA-methylation profiles by targeting epigenetic modifiers, & have been shown to be important for normal hematopoietic stem cell function. Mir-29 is organized in two distinctively regulated bi-cistronic clusters: the miR-29a/b-1 cluster & the miR-29b-2/c cluster.
Here we evaluated the biological associations & clinical impact of the differential expression of pre-miR-29a/b-1 & pre-miR-29b-2/c clusters in AML.
We analysed121 AML patients (pts) (median age 63 years [y], range 37-75 y) who have been consolidated with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation following non-myeloablative conditioning (nma-HCT; Fludarabin 30 mg/m2 on day -4 till -2 & 2 Gy total body irradiation) between 2000 & 2014 with pretreatment bone marrow material (BM) available. Disease status at nma-HCT was first (CR1 62%) or second complete remission (CR2 18%) or CR with incomplete peripheral recovery (CRi 20%). The mutation status (mut) of the ASXL1, CEBPA, DNMT3A IDH1, IDH2, NPM1, & TP53 gene & the FLT3-ITD & EVI1 expressionstatusas well as common surface marker expressions were assessed at diagnosis. European LeukemiaNet (ELN) classification was favorable (25%), intermediate-I (23%), intermediate-II (21%), adverse (27%) or unknown (4%). Pretreatment pre-miR-29a/b-1 & pre-miR-29b-2/c clusters expressionin bone marrow (BM)was measured by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction & normalized to 18S. The median normalized gene expression defined high & low pre-miR-29a/b-1 & pre-miR-29b-2/c clusterexpressers. Median follow-up was 4.4y for pts alive.
At diagnosis a high pre-miR-29a/b-1 expression did not associate with clinical characteristics. High pre-miR-29a/b-1 expressers were less likely to be TP53 mut (p=.01). Pts with high pre-miR-29b-2/c expression at diagnosis had higher BM blast counts (p=.01), were more likely to have a normal cytogenetics (CN, p=.03) & were less likely to be TP53 (p=.004) or ASXL1 mutated (p=.03).
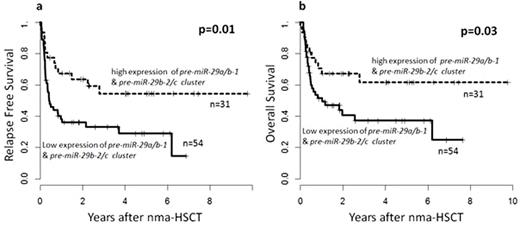
When we combined the expression status information of the two miR-29 clusters we found that AML blasts of pts with high expression of both clusters were less likely to be CD34 (p=.05) or CD117 (p=.04) positive & more likely to be CD11b positive (p=.05). These pts more often had CN-AML (p=.04) & better ELN genetic risk (p=.03). High expressers of both miR-29 clusters were also more likely to be DNMT3A mut (p=.01) & less likely to be EVI1 positive (p=.007). Noteworthy, none of the pts with high expression of both clusters had a TP53 (p=.16) or ASXL1 mutation (p=.08). Pts with a high expression of both miR-29 clustershad a significant longer relapse free survival (RFS, p=.01, Figure 1a) & overall survival (OS, p=.03) compared to pts with low expression of one or both miR-29 clusters.
In conclusion, high expression of pre-miR-29a/b-1 & pre-miR-29b-2/c associated with different clinical & genetic characteristic at AML diagnosis. High expressers of both clusters were more often DNMT3A mutated, a gene targeted by miR-29. Furthermore, none of these patients harbored TP53 mutations, a gene known to be indirectly activated by miR-29 family members. These findings provide new insights into the miR-29 associated AML biology, which may contribute to the observed impact on AML pts outcomes. While we observed a trend for better survival for each miR-29 cluster, pts with high expression of the pre-miR-29a/b-1 & the pre-miR-29b-2/c clusterhad significantly longer RFS & OS.
Poenisch:Mundipharma: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal