Abstract
BACKGROUND: Patients (pts) with CLL/SLL are at high risk for infections, and pts with genetically high-risk disease are at increased risk for early disease progression and death. Lenalidomide, an oral immunomodulatory agent with demonstrated activity in treatment-naïve CLL/SLL, can potentially restore immune system dysfunction associated with CLL/SLL. We present results from an NCI/CTEP-sponsored, randomized phase 2 study (NCI 8834) of low-dose lenalidomide designed to assess the ability of lenalidomide to restore immune synapse response and humoral immunity, as well as delay progression of asymptomatic, genetically high-risk, early-stage CLL/SLL.
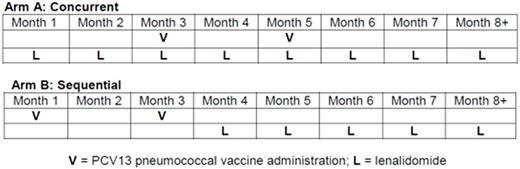
METHODS: Pts with genetically high-risk CLL/SLL (unmutated IGHV, deletion(17p)/(11q), and/or complex abnormal karyotype) were eligible if they were treatment-naïve, did not meet IWCLL 2008 criteria for initiating therapy, age ≥ 18 but < 80 years, ECOG ≤ 2, no history of autoimmune cytopenia, no venous thromboembolic event ≤6 months prior, and adequate end-organ function. Pts were randomized to receive lenalidomide either concurrent with (Arm A) or sequential to (Arm B) 2 doses of 13-valent protein-conjugated pneumococcal vaccine (Prevnar-13) administered 2 months apart (see figure). Lenalidomide was dosed at 2.5 mg/day during the first 28-day cycle to reduce risk for tumor flare and increased to 5 mg/day for the second and subsequent cycles as tolerated. Treatment continued for at least 24 cycles in the absence of disease progression or irreversible Grade ≥ 3 adverse event (AE). Anti-pneumococcal antibody titers, the primary endpoint of the study, were measured in each arm at 1 and 2 months after the second dose of vaccine and every 6 months thereafter. Secondary endpoints included clinical response, IWCLL 2008 response after 24 cycles, and progression-free survival (PFS).
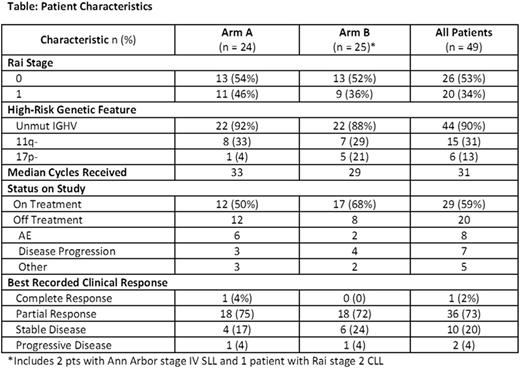
RESULTS: 49 pts were randomized. Median age at enrollment was 59 (range 40-70) years, median time from diagnosis 1.26 (range 0.15-9) years, and ECOG = 0 in 96%. Baseline clinical and genetic risk factors were similar between the 2 arms (see table). In general, AE were mild and manageable. Gr ≥3 AE were uncommon and included (in ≥10% pts): neutropenia in 10 (20%) and hypophosphatemia in 6 (12%). The most common treatment-emergent Gr 1/2 AEs included neutropenia in 27 pts (55%), diarrhea in 26 (53%), rash in 25 (51%), and thrombocytopenia in 23 (47%). Gr 1/2 infections were reported in 17 (35%), but only 1 Gr 3 infection (pneumonia) was observed. Gr 1/2 tumor flare was observed in 2 pts (4%). There were no thromboembolic events. Seroprotection against 7 pneumococcal serotypes (1, 3, 4, 5, 14, 19F, and 23F) was measured 4 weeks after the second dose of vaccine. All but 4 pts (3 in Arm A, 1 in Arm B) achieved seroprotection against ≥1 serotype, and the median number against which seroprotection was achieved was 3 (range: 0-7) in both arms. Mean IgG/IgM/IgA levels at baseline were 722/109/49, and improved to 820/136/51 and 947/197/59 after 12 and 24 cycles of treatment, respectively. Disposition of study patients and treatment responses are summarized in the table; after median 31 cycles received, 59% of patients remain on treatment. 75% of patients achieved a clinically assessed disease response, and of the 34 patients that completed IWCLL response assessment after 24 cycles of therapy (including CT scans and bone marrow biopsy), 9 achieved a PR, 23 SD, and 2 PD. Median PFS has not yet been reached; 1 year PFS was 88% (95%CI 74-94), 2 year PFS was 78% (63-88), and estimated 3 year is PFS 72% (95%CI 56-83).
CONCLUSIONS: Low-dose lenalidomide can be administered to asymptomatic, genetically high-risk, early-stage CLL patients with modest toxicity and high rates of durable clinical response. Some anti-pneumococcal vaccine response was achieved by nearly all treated patients on both schedules. Lenalidomide effectively prevented and/or reversed the expected progression of hypogammaglublinemia, which may explain the low incidence of infection, and near absence of severe infection, observed here.
Jones:Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Awan:Novartis Oncology: Consultancy; Innate Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Andritsos:Hairy Cell Leukemia Foundation: Research Funding. Woyach:Morphosys: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding. Lozanski:Stemline Therapeutics Inc.: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Beckman Coulter: Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal