Abstract
Background Acute lymphoblastic leukemias with rearrangements of mixed-lineage leukemia gene (MLL+ALL) frequently develop in infants and have a dismal prognosis. The refractory nature of this leukemia is known to be associated with persistence of high levels of minimal residual disease (MRD). We previously reported that FLT3 ligand (FL) stimulation of MLL+ALL cells, which express FLT3 at high levels, induced quiescence resistant to anti-leukemic agents, to the process of which up-regulation of p27, one of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKIs), was closely attributable. Because a vast amount of FL is secreted from bone marrow stromal cells, it was postulated that this FLT3/FL interaction should contribute, at least in part, to the high levels of MRD in MLL+ALL (Furuichi et. al. Cancer Res 2007). Of interest, in B-cell precursor ALLs other than MLL+ALL, FL stimulated their proliferation. Therefore, we performed the microarray analysis using the MLL+ALL cell line and the ETV6-RUNX1-positive cell line for comparing changes in the gene expression profiles at 24h after FL stimulation, and picked up the transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) as a gene whose mRNA level was conversely regulated between two cell lines. TGFβ1 is a growth inhibitory cytokine for some cancer cells and known to have a potential to induce hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. In the present study, we examined the effects of TGFβ1 and/or FL on MLL+ALL cells particularly in terms of induction of quiescence and chemosensitivity.
Materials and Methods The MLL+ALL cell line KOCL58 (MLL-AF4+) was used throughout the study to examine TGFβ1 mRNA, cell cycle progression, induction of apoptosis, and changes in chemosensitivity in the presence of TGFβ1 and/or FL.
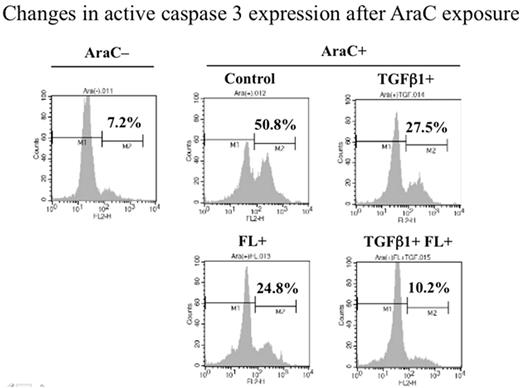
Results1. We first examined changes in TGFβ1 mRNA after FL (20ng/ml) stimulation by real time RT-PCR in KOCL58 cells, and confirmed that TGFβ1 mRNA expression level was significantly increased (1.5 fold at 24h). Of note, when the cells were stimulated with FL and TGFβ1 (10ng/ml), TGFβ1 mRNA expression level was further increased (3.5 fold) between 7 and 24h. 2. We next evaluated the effect of TGFβ1 on proliferation. When KOCL58 cells were incubated with a low concentration of TGFβ1 (0.33ng/ml) in the presence or absence of FL (20ng/m), flow cytometric analysis using the BrdU/PI double staining showed that the G0/G1 population (35.2%; before stimulation) was increased in the presence of TGFβ1 (48.4%) or FL (53.0%), and further in the presence of TGFβ1+FL (75.1%). We also examined expression levels of cell cycle regulating molecules, and found that p27 was significantly increased in the presence of FL and further in the presence of TGFβ1+FL. This p27 up-regulation was due to post-transcriptional mechanism, because p27 mRNA remained unchanged but the half-life of p27 protein was elongated in the presence of FL and/or TGFβ1. 3. To elucidate whether TGFβ1 affects the sensitivity of MLL+ALL cells to a cell cycle dependent anti-leukemic agent AraC, we pre-incubated KOCL58 cells in the presence of TGFβ1 and/or FL for 72h and then exposed to AraC (500nM) for 24h. Flow cytometric analysis using FITC-conjugated Annexin V demonstrated that the Annexin V-negative viable population (%) was decreased by AraC exposure (25.6±1.4%), but it was significantly restored by pre-incubation with FL (39.4±1.7%, P<0.0005) and further by pre-incubation with TGFβ1+FL (49.3±5.9%, P<0.003), although not significantly different by pre-incubation with TGFβ1 alone. Flow cytometric analysis using anti-active caspase 3 antibody also demonstrated that the positive population was increased to 50.8% by AraC exposure, but it was decreased by pre-incubation with either TGFβ1 (27.5%) or FL (24.8%), and further by pre-incubation with TGFβ1+FL (10.2%) (Figure). 4.We performed chmosensitivity experiments to AraC (800nM) using KOCL58 cells adhering to bone marrow stromal cells, which secrete FL and TGFβ1, in the presence of FLT3 inhibitor (CEP701, 5nM) and/or TGFβ-receptor 1 inhibitor (HTS, 5mM), and found that KOCL58 cells adhering to stromal cells showed a marked resistance to AraC (60% increase in Annexin V-negative population), but this restoring effect was partially (~20%) alleviated by each of inhibitors.
[Discussion] TGFβ1 should be involved in the development of MRD in MLL+ALL in synergy with FL, and a combined use of inhibitors against FLT3 and TGFβ1 might be effective for eradicating MRD in MLL+ALL patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal