Abstract
Background: Carfilzomib (Car, 2012), pomalidomide (Pom, 2013), and panobinostat (Pano, 2015) were approved for the treatment of rrMM patients after failure of at least two prior standard therapies. There is limited real-world data on utilization of these medications, health care resource utilization (HCRU) and costs in patients with rrMM at the US population level. This study aimed to describe treatment pattern, HCRU, and costs in rrMM patients who received at least two prior therapies using a large administrative claims database.
Methods: This was a retrospective database analysis using the Truven Health MarketScan Commercial and Medicare Database. Patients (pts) were included if they were diagnosed with MM between Jan 1, 2006 and May 31, 2015, were ≥18 yrs, had no claim for stem cell transplant, and had ≥6 mos continuous enrollment before and ≥1 mos after the 1st MM diagnosis (index date) and treatment initiation (TI). Only patients who had ≥6 mos continuous enrollment after TI were included in HCRU and cost evaluation. If two or more drugs started within 90 days, they were considered as 1 regimen. End of a line of therapy (LOT) was defined when a new treatment was introduced or there was a treatment gap >90 days or end of follow-up, whichever occurred first. Third line of therapy (3L) was identified following 2 prior lines of therapy. Time to next treatment (TTNT) was defined from initiation of the LOT to initiation of subsequent LOT. Duration of treatment (DOT) and TTNT were estimated based on Kaplan-Meier method. Regimens were classified into 6 mutually-exclusive categories, including bortezomib (Bor), lenalidomide (Len), Pom, Car, thalidomide (Thal), and Other based therapies. HCRU and cost (per patient per month, PPPM) were calculated. The total costs included inpatient costs, outpatient costs and pharmacy costs.
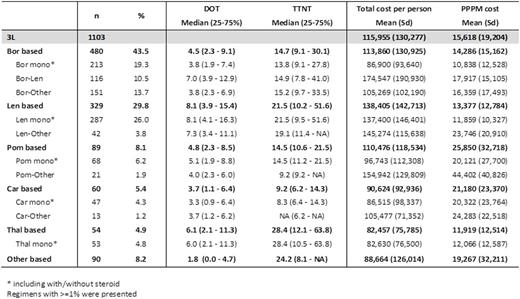
Results: A total of 9,960 pts were identified with initiation of 1L therapy. Median age was 67 yrs. And 57.4% were male. During an average of 20.0 mos follow-up post TI, 3,282 (33.0%), 1,103 (11.1%) and 400 (4%) pts initiated 2L, 3L, and 4L therapies, respectively. During 3L therapy, Bor (43.5%, including 10.5% for Bor-Len) and Len based regimens (29.8%) were most commonly observed. Median DOTs ranged from Car (3.7 mos) to Len (8.1 mos) based regimens. Median TTNT from short to long was Car, Pom, Bor, Len, Other, and Thal based regimens. On average, each patient with rrMM had 4.5 outpatient visits, 0.1 inpatients visits, 0.1 ER visits and 0.004 hospice care visits per month. The average PPPM costs were $14,286, $13,377, $11,919, for Bor, Len, Thal based regimens and $25,850 and $21,180 for Pom and Car based regimens, respectively.
Conclusions: Although novel agents were added to rrMM treatment, Bor and/or Len based regimens remained the most commonly used therapies in 3L setting. Compared to Bor, Len and Thal based therapies, PPPM costs were higher for Pom and Car based regimens. These data could be useful for treatment consideration and economic evaluation.
Shao:Merck & Co., Inc.: Employment. Monberg:Merck & Co.: Employment. Cao:Merck & Co.: Employment. Zhou:Merck & Co.: Employment. Zhong:Merck & Co., Inc.: Employment. Marinello:Merck & Co., Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal