Abstract
Introduction: DAC is a hypomethylating agent FDA approved for the treatment of advanced myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML).Despite its clinical activity, the duration of response is limited and prognosis at relapse is poor. In pre-clinical studies, we identified potent epigenetic effects of ATO alone and in combination with DAC, and also found that carboplatin (Carbo) can enhance gene reactivation in combination with DAC. We therefore initiated a randomized phase 2 clinical trial (NCT02188706) to compare the safety and efficacy of DAC in combination with either Carbo or ATO as compared to single agent DAC in patients with MDS/CMML and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Here we present updated results for the MDS/CMML cohort.
Methods: Patients with MDS/CMML INT-1 were randomized to one of three regimens: DAC 20 mg/m2 days 1-5, (DAC), DAC as above and Carbo AUC 5 on day 8 (DAC/Carbo), or DAC as above and ATO 0.15 mg/kg days 1-5 (DAC/ATO). We used adaptive randomization based on response rate which started after 10 patients were equally randomized to each arm. Cycles were scheduled every 28 days for a minimum of 4 cycles. Dose reductions/delays were allowed based on response and tolerability. Patients remained on treatment as long as they continued to benefit without toxicity. The primary endpoint was the composite response rate: the complete response (CR: complete response, mCR: marrow complete response and CRi: complete response with incomplete blood count recovery) and partial response (PR) rates using the modified IWG 2006 criteria. Secondary endpoints included median overall survival (OS) and safety. DNA methylation changes were measured using LINE1 bisulfite/pyrosequencing.
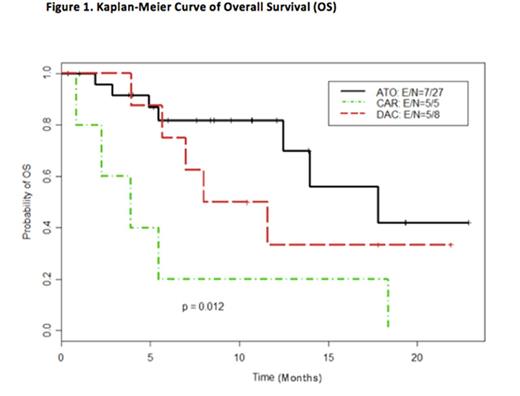
Results: As of July 2016, 42 patients (MDS = 40, CMML=2) have been enrolled on study. Median age was 71 years (range, 35 to 84 years). There was no statistically significant difference in patients' characteristics between the three arms. Median number of cycles for the treatment arms was 4 (range, 1-15). Response data was evaluable for 36 patients (8 on DAC alone, 5 on DAC/Carbo and 23 on DAC/ATO). Composite responses were seen in 3/8 patients on DAC (37.5%), 0/5 patients on DAC/Carbo (0%, p=0.23 compared to DAC alone) and 12/23 patients on DAC/ATO (52.2%, p=0.69 compared to DAC alone). Median OS among MDS/CMML patients receiving DAC/ATO (17.8 months) was improved compared to the DAC/Carbo (3.9 months) and DAC (9.8 months) arms (p=0.01) [Figure 1]. There was not a significant difference in high-grade (≥ grade 3) toxicity between the three arms, with grade 3 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia as the most common side effects. DNA methylation analysis showed equivalent demethylation in all the arms, suggesting that the epigenetic effects of ATO were independent of DNA methylation, which was consistent with pre-clinical studies.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate higher response rates and a significant survival benefit with the combination of DAC and ATO in comparison to DAC alone in patients with MDS/CMML.
Kropf:Celgene: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy. Fung:Amgen: Consultancy; Genzyme: Consultancy. Kantarjian:ARIAD: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer Inc: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Issa:Astex Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Teva Pharmaceutical Industries: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal