Abstract
Median age of CML patients at diagnosis is reported to be around 66 years. Few data about the characteristics and outcome of patients younger than 40 years are available, and the clinical trials of dasatinib and nilotinib as first line treatment were not stratified by age.
We retrospectively analyzed 251 young patients with CML in chronic phase from 12 different Italian Institutions, diagnosed between October 2001 and October 2016. Up to 2011 all patients were treated frontline with imatinib while from January 2011 onwards with imatinib or a second generation TKI (nilotinib or dasatinib), based on clinical judgment. At diagnosis median age was 32,6 years [interquartile range (IQR) 27,6- 36,9]; 143 (57%) were male.
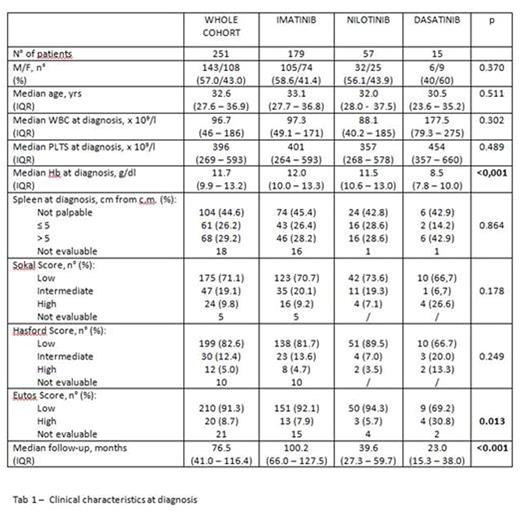
Splenomegaly was found in 129 out of 233 evaluable patients, in 29,2% of the cases spleen was palpable >5 cm below the costal margin. The risk score was low in most of the cases (low risk Sokal 71%, low risk Eutos 91,3% vs high risk Sokal 9,8%, high risk Eutos 8,7%). Clinical features of the patients in treatment with different inhibitors are summarized in table 1. There were two main statistically significant differences in the group of patients treated with dasatinib: a higher proportion of high risk (30,8%) according to Eutos score and a lower median Hb level at diagnosis (8,5 gr/dL). These features probably reflected the trend of using dasatinib in patients with a more aggressive disease, as this drug was shown to be more potent since the first in vitro studies.
Out of 251 patients 179 were treated with imatinib, 57 (22%) with nilotinib, 15 (5,9%) with dasatinib.
Median follow up of the whole cohort was 76,5 months (IQR 41- 116); as expected, the follow up was longer in the imatinib group compared to the nilotinib and dasatinib groups (100 months vs 39,6 and 23,0 respectively).
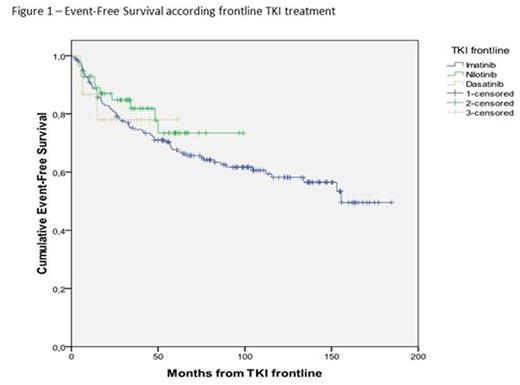
In the whole cohort, the cumulative incidence of Complete Cytogenetic Response (CCyR) and Major Molecular Response (MMolR) were 90,4% and 75,7% respectively; a deep molecular response (negative nested PCR, MR4.0, MR4,5) was achieved by 52.2% of patients, without differences among the 3 groups. Primary resistance occurred in 12,4% of patients, without differences among the 3 groups: secondary resistance occurred in 15.9% of patients, with a higher rate in the imatinib group (19,5%) as compared with nilotinib (7,0%) and dasatinib (6,7%) (p=0.047). Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity was observed in 6.0% of patients, without differences among the 3 groups. Blast transformation occurred in 7 out of 251 patients (2,8%), all in the imatinib group, after a median time from the diagnosis of 31 months (range 4-110). The 4-year cumulative Event-Free Survival (EFS) and Overall Survival (OS) were 72,4% (95%CI 66,7 - 78,5) and 98,1% (95%CI 96,4 - 99,8) respectively, without differences among the 3 groups. All deaths were related to blast transformation in imatinib group.
In conclusion, as expected in a younger population, response to treatment and OS were excellent. However, the 4-year EFS was lower than expected, in spite of the presence of patients with predominantly low risk score. Furthermore, while the higher rate of secondary resistance in the imatinib group probably reflects the longer follow-up, it is worth of note that no statistically significant difference was observed between imatinib and 2nd generation TKI groups in terms of OS and EFS.
Breccia:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Ariad: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal