Abstract
Introduction: Cytogenetic abnormalities occur frequently in patients with myelofibrosis (MF) and carry significant prognostic value. A variety of cytogenetic abnormalities have been reported with variable incidence. While the prognostic significance of more common cytogenetic abnormalities is well documented, the prognostic significance of less common abnormalities are difficult to discern due to limiting cohort size. Further, the specific phenotype associated with various cytogenetic abnormalities is less clear. We reviewed our institutional experience in an effort to describe the spectrum of chromosomal abnormalities, assess their correlation with clinical features, and validate their prognostic impact in a cohort of MF patients.
Methods: This was a single institution, retrospective study of all patients with a diagnosis of MF who were seen at our center between 2/2001 - 6/2016.We reviewed cases of myelofibrosis in the Moffitt Cancer Center database. Definitions of primary myelofibrosis (PMF), post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis (post-ET MF) and post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis (post-PV MF) were according to World Health Organization 2016 criteria and the International Working Group for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms, Research and Treatment, respectively. Cytogenetic analysis was documented with preference to date of diagnosis. Overall survival was measured from time of cytogenetic analysis.
Results: We identified 312 eligible. Cytogenetic data were available in 278 of 312 (89%) patients. The cohort was 59% male with a median age of 70 years at time of first presentation. PMF comprised 76% of cases with post-PV MF and post-ET MF accounting for 9% and 15% of cases respectively. Cytogenetic analysis was performed within 3 months of diagnosis in 63% and over a year after diagnosis in 24% of patients.
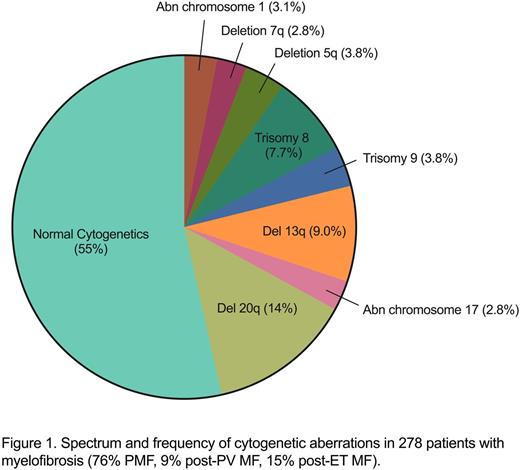
Cytogenetic spectrum and frequency is shown in Figure 1. Normal diploid karyotype was present in 55%. The most common cytogenetic abnormality was a deletion of the long arm of chromosome 20 (del 20q), occurring in 39 (14%) cases. Del 20q occurred as an isolated abnormality in 26/39 cases. When occurring in conjunction with other structural abnormalities, it was most often associated with trisomy 9 (6/39). A deletion of the long arm of chromosome 13 (del 13q) was the second most common chromosomal aberration, occurring in 26 (9%) of cases and usually presenting as the sole abnormality (15/26). An extra copy of chromosome 8 (trisomy 8) occurred in 21 (8%) cases and often occurred in conjunction with other cytogenetic abnormalities (11/21). Less common cytogenetic abnormalities included trisomy 9, deletion 7q and deletion 5q, occurring in less than 4% of cases. Monosomal and complex karyotypes accounted for 10% and 8.3% of cytogenetics, respectively.
We then assessed relationships between cytogenetic abnormalities and clinical and pathologic features. Del20q was associated with a lower IPSS score (r = -0.18, p = 0.0006). Deletion 13q was associated with older age at presentation (r = 0.14, p = 0.007). Prevalence of trisomy 8 was highest in post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis (r = 0.14, p = 0.03) and associated with increased peripheral blast percentage (r = 0.16, p < 0.0001). Deletion 5q was associated with decreased hemoglobin (r = -0.13, p = 0.04), transfusion dependence (r = 0.20, p = 0.0009) and conversion to blast phase (r = 0.23, p = 0.0001).
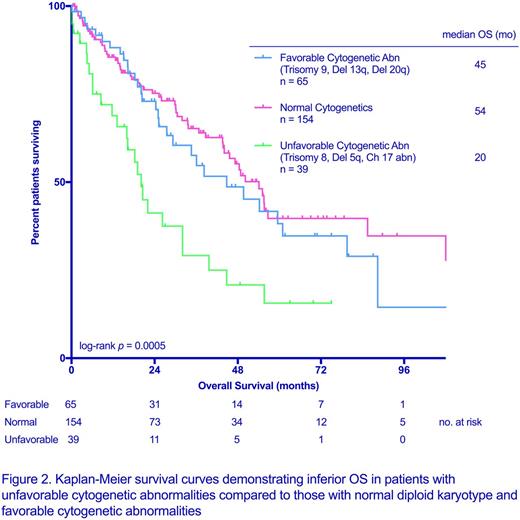
Patients with del 20q, del 13q, and trisomy 9 had median overall survival (OS) comparable to patients with a normal karyotype (45 vs 54 months, respectively, p = 0.69). Patients with unfavorable cytogenetic profiles (del 5q, trisomy 8, and chromosome 17 abnormalities) had significantly worse OS when compared to patients with normal diploid karyotype (20 vs 54 months, p = 0.0002) (figure 2). In multivariate regression analysis, controlling for DIPSS, deletion 5q (HR: 0.34 [0.15-0.78]; p = 0.01) and trisomy 8 (HR: 0.35 [0.17-0.73]; p = 0.005) were significantly associated with inferior overall survival.
Conclusions: Cytogenetic abnormalities in myelofibrosis provide significant prognostic discrimination in patients with myelofibrosis. Our findings validate the prognostic value of cytogenetics and raise possible heretofore unrecognized clinical associations.
Lancet:Novartis: Consultancy; Biopath Holdings: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Consultancy; Quantum First: Consultancy; ERYtech: Consultancy; Pfizer: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Kalo Bios: Consultancy; Baxalta: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy. Sweet:Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Pfizer: Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Komrokji:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal