Abstract
Introduction
The phagocytic activity of macrophages is regulated by activating ("eat") and inhibitory ("do not eat") signals. Under normal physiologic conditions, the ubiquitously expressed cell surface antigen CD47 suppresses phagocytosis by binding to signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) on macrophages. It is hypothesized that overexpression of CD47 by cancer cells enables immune evasion. Blockade of CD47 results in phagocytosis of cells bearing "eat" signals and primes effective anti-tumor T cell responses. TTI-621(SIRPαFc)is a soluble recombinant fusion proteinconsisting of the CD47 binding domain of human SIRPα linked to the Fc region of human IgG1designed to both: 1) block the CD47 "do not eat" signal, and 2) engagemacrophage Fcγ receptors with IgG1 Fc to enhance phagocytosis and antitumor activity.In vitro, TTI-621 binds to normal human cells, platelets, a wide range of human primary tumor cells and cell lines, but only minimally to human erythrocytes. TTI-621 selectively promotes macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of hematologic and solid tumors over that observed with normal monocytes, and exhibits antitumor activity in xenograft mouse models.
Methods
A first-in-human, phase 1, open label, multicenter study (NCT02663518) is ongoing to evaluate the safety and tolerability, and to identify the maximum tolerated dose of TTI-621 in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory lymphomas using a 3+3 dose-escalation design. Once the optimal dose has been determined in the dose-escalation phase, multiple expansion cohorts will be enrolled comprising pts with various relapsed/refractory hematologic malignancies. Assessments include peripheral receptor occupancy, serum cytokine levels, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity.
Eligible pts are adults with advanced, measurable, hematologic malignancies, who have progressed on standard anticancer therapy or for whom no other approved therapy exists. Pts are required to have baseline hemoglobin ≥10 g/dL, platelets ≥75 x 109/L, and be transfusion- and growth factor-independent. Pts with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, high-grade lymphoma, and acute promyelocytic leukemia are excluded.
TTI-621 is administered IV once weekly at protocol-defined doses. Treatment may continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Results
Eleven pts (6M/5F, age 21-72 years) have been enrolled as of the data cut-off date of 28 July 2016. Lymphoma diagnoses included Hodgkin (N=4), diffuse large B cell (DLBCL) (N=4), follicular (N=2), and mantle cell (N=1).
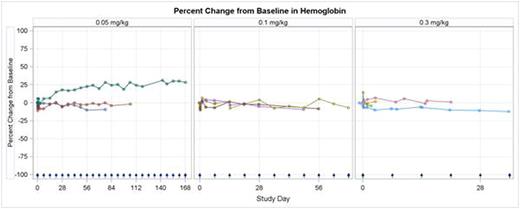
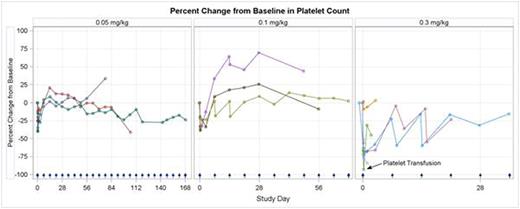
Treatment has been reasonably well tolerated by pts in the 0.05 mg/kg (N=3), 0.1 mg/kg (N=3), and 0.3 mg/kg (N=5) dose cohorts. The majority of pts experienced mild to moderate infusion-related events. Hemoglobin levels have remained stable or improved with treatment. Transient, dose-dependent decreases in platelets and leukocytes occurred in the hours following infusion in all pts without clinical sequelae. The 0.3 mg/kg dose was associated with reversible, dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) in 2 of 5 pts: one pt with G3 elevated ALT/AST and G4 platelet count, and a second pt with G4 platelet count who was transfused. Dosing at 0.2 mg/kg is now being explored. Aside from the DLTs and 2 non-DLT G3 platelet count (all in 0.3 mg/kg cohort), treatment-related adverse events have been ≤G2. CD47 receptor occupancy increased with each cohort, peaking at the end of infusion and remaining detectable 24 hrs after the 1st infusion in Cohort 3. Macrophage-associated cytokines, including MIP-1α and MIP-1β, increased during the 4 hrs after infusion. Six pts continue to receive weekly infusions of TTI-621; one pt with DLBCL and another with FL have experienced progression-free intervals of 161 and 70 days, respectively.
Conclusions
TTI-621 has been reasonably well tolerated. Pts retained stable hemoglobin levels consistent with minimal drug binding to erythrocytes. Manageable, dose-dependent thrombocytopenia was likely due to increased phagocytic clearance of platelets. TTI-621 binds to CD47+ cells in a dose-dependent manner, potently yielding increases in cytokines associated with augmented phagocytic activity. Enrollment continues at the 0.2 mg/kg dose level; updated data will be provided at the meeting.
Ansell:BMS, Seattle Genetics, Merck, Celldex and Affimed: Research Funding. Chen:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Millenium: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding. Flinn:Janssen: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; RainTree Oncology Services: Equity Ownership. O'Connor:Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Spectrum: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Mundipharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Mundipharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding. Johnson:Trillium Therapeutics: Employment. Irwin:Hoffmann La Roche: Employment, Equity Ownership; Trillium Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Petrova:Trillium Therapeutics Inc: Employment, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties. Uger:Trillium Therapeutics: Employment, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties. Sievers:Seattle Genetics: Employment, Equity Ownership; Trillium Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership; MEI Pharma: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal