Key Points
Plasmodium falciparum–generated cytoadherent knobs on infected erythrocytes contain a spiral framework linked to the red cell cytoskeleton.
The findings suggest a structural basis for transmission of shear forces in adhesion of infected cells.
Abstract
Much of the virulence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria is caused by cytoadherence of infected erythrocytes, which promotes parasite survival by preventing clearance in the spleen. Adherence is mediated by membrane protrusions known as knobs, whose formation depends on the parasite-derived, knob-associated histidine-rich protein (KAHRP). Knobs are required for cytoadherence under flow conditions, and they contain both KAHRP and the parasite-derived erythrocyte membrane protein PfEMP1. Using electron tomography, we have examined the 3-dimensional structure of knobs in detergent-insoluble skeletons of P falciparum 3D7 schizonts. We describe a highly organized knob skeleton composed of a spiral structure coated by an electron-dense layer underlying the knob membrane. This knob skeleton is connected by multiple links to the erythrocyte cytoskeleton. We used immuno-electron microscopy (EM) to locate KAHRP in these structures. The arrangement of membrane proteins in the knobs, visualized by high-resolution freeze-fracture scanning EM, is distinct from that in the surrounding erythrocyte membrane, with a structure at the apex that likely represents the adhesion site. Thus, erythrocyte knobs in P falciparum infection contain a highly organized skeleton structure underlying a specialized region of membrane. We propose that the spiral and dense coat organize the cytoadherence structures in the knob, and anchor them into the erythrocyte cytoskeleton. The high density of knobs and their extensive mechanical linkage suggest an explanation for the rigidification of the cytoskeleton in infected cells, and for the transmission to the cytoskeleton of shear forces experienced by adhering cells.
Introduction
Plasmodium falciparum malaria remains one of the leading causes of child deaths globally, with the majority of cases occurring in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. Although chemopreventive and vector control initiatives led to an estimated 42% reduction in mortality rates between 2000 and 2012, the emergence of artemisinin resistance highlights the importance of continued efforts to understand and interfere with the biology of the parasite.1
Of the 5 Plasmodium species capable of infecting humans, P falciparum and P vivax are the most prevalent, with P falciparum causing 90% of malaria-related deaths. P falciparum–infected erythrocytes become cytoadherent, causing erythrocyte sequestration in the microvasculature and avoiding clearance of infected cells by the spleen.2 Much of the virulence of P falciparum malaria has been attributed to this cytoadherence, which impedes blood circulation and results in severe syndromes such as cerebral or placental malaria.2-4
The dominant ligand mediating cytoadherence is PfEMP1, a major variable erythrocyte surface antigen of P falciparum that may interact with a number of different host receptors.2,3,5 Clonal antigenic variation of PfEMP1, encoded by the var multigene family, has been proposed to be responsible for adherence to different tissues, and hence for variations in disease progression.6,7 PfEMP1 isoforms are recognized by antibodies that provide variant-specific immunity to P falciparum.3 One variant, VAR2CSA, which binds to chondroitin sulfate in the placenta, causing pregnancy-associated malaria, has been identified as a vaccine target.8 PfEMP1 is presented on the outside of infected erythrocytes, where it is localized to the surface of membrane protrusions known as knobs.4,9-11 These knobs appear as prominent bumps on the surface of infected erythrocytes, from the early trophozoite stage onward.10,12,13 PfEMP1 is transported to knobs via Maurer's clefts.14 Disruption of genes required for PfEMP1 trafficking to the membrane causes dramatic reductions in cytoadherence.15,16 Loss of the ability to form erythrocyte knobs has been linked with a loss of parasite virulence in primate infections,17 and with reduced cytoadherence in vitro.15,18,19
The formation of the PfEMP1-presenting knobs is dependent on the expression of the parasite-derived knob-associated histidine-rich protein (KAHRP). Erythrocytes infected with KAHRP-negative P falciparum lack knobs and show diminished PfEMP1 presentation and reduced adherence to CD36, ICAM-1, and CSA under flow conditions.18-20 KAHRP is localized with PfEMP1 in knobs,18,21 where it has been shown by immuno-EM to be associated with an electron-dense (as visualized in heavy metal–stained specimens) layer of material under the membrane, as well as in Maurer's clefts.22,23 KAHRP is a 59-72 kDa protein (550-657 amino acid residues depending on the variant) containing an N-terminal signal sequence and a PEXEL (Plasmodium export element) motif that mediate export into the erythrocyte, a 63–amino acid histidine-rich (55%) region, and 2 variable tandem repeat regions.24-26 Expression of KAHRP has been shown to increase the rigidity of infected erythrocytes, thereby further contributing to cytoadherence-associated virulence.27 This rigidifying effect on the cytoskeleton is common to a number of exported parasite proteins.15,27 Use of gene knockout mutants has revealed that in addition to KAHRP, 2 genes, those encoding a PHIST domain protein (PFD1170c) and an Hsp40-like DNAJ Type IV protein (PF10_0381), are also important for knob formation.15 Other parasite proteins that have been shown to associate with knob components, and which may thus form part of the knob structure, include knob-associated Hsp40,28 the PfEMP1 trafficking protein PfEMP3,16,28 the large variable surface antigen SURFIN,29 the 2.5 MDa Pf332 antigen,30 and the PHIST domain protein PFE1605w (LyMP).31,32 PFE1605w is localized at the cell periphery33 and has been shown to be important for cytoadherence but not for knob formation or for surface expression of PfEMP1.31
We have examined the architecture of cytoadherent knobs in P falciparum 3D7-infected erythrocytes. By isolating the erythrocyte cytoskeletons of mature schizonts, we have found a distinctive spiral structure with an electron-dense coat underlying the knob membrane. This knob skeleton is anchored into the surrounding erythrocyte cytoskeleton, which connects to the electron-dense coat. Freeze-fracture scanning electron microscopy (SEM) shows that the arrangement of membrane proteins in the knobs is quite distinct from that in the surrounding erythrocyte membrane, with a structure at the apex that may represent the site of adhesion. We propose that the knob skeleton provides a mechanical linkage between the adhesion site and the cytoskeleton.
Methods
P falciparum culture
P falciparum 3D7 asexual blood stages were maintained in human erythrocytes in RPMI 1640 medium containing Albumax (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), with synchronization using standard methods.34 Human blood was obtained with full consent from the United Kingdom (UK) National Blood Transfusion service and was used within 2 weeks of receipt. Enrichment of mature schizonts was achieved using Percoll (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) as described previously.35
High-pressure freezing and freeze substitution
Mature schizonts were pelleted by centrifugation, mixed in RPMI medium containing brewer’s yeast and dextran as a cryoprotectant, and high-pressure-frozen in aluminum planchettes using an HPM010 high-pressure freezer (BalTec, Reading, UK). This material was freeze-substituted into HM20 resin (Polysciences, Inc., Warrington, PA) containing 0.2% uranyl acetate. Sections of 200-220 nm thickness were cut using an EMUC7 ultramicrotome (Leica Camera AG, Wetzlar, Germany) fitted with a diamond knife, and mounted on carbon-coated copper grids. Grids were then coated with 10 nm protein-A gold (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) as a fiducial marker for tomography.
Preparation of schizont skeletons for negative-stain and cryotomography
Cytoskeletons of schizonts and uninfected erythrocytes were prepared in situ on carbon-coated copper grids as follows. Grids were glow-discharged, coated with 0.01% poly-L-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich) for 30 seconds, washed in water, and blotted dry. Grids for cryotomography were additionally coated with 10 nm colloidal gold fiducial markers (Sigma-Aldrich). Mature schizonts or uninfected erythrocytes in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; ∼20% hematocrit) were applied to the grids, allowed to adhere for 1 minute, and then blotted from the back and washed once in PBS. Grids carrying cells were dipped sequentially into lysis buffer (1 mM Tris pH 4.7, 1 mM KCl, 0.2 mM MgCl2), lysis buffer containing 2% Triton X-100, and then lysis buffer without detergent to wash, for 60 seconds in each solution, passing through the meniscus several times. Grids were then either stained with 2% sodium silicotungstate, pH 7.5, blotted and air-dried, or blotted from the back and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane using a manually operated apparatus.
Immunolabeling
Schizont and uninfected erythrocyte skeletons were prepared on grids as described before, then immunolabeled while still wet before staining or plunge-freezing. KAHRP was detected using monoclonal antibody (mAb) 8922 or mAb 18.2 (anti-KAHRP, obtained from the European Malaria Reagent Repository, donated by Dr. Jana McBride), followed by goat anti-mouse secondary antibody doubly conjugated with 10 nm gold and Alexafluor 488 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Spectrin was detected using antibody ab11751 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), and gold-conjugated secondary antibody described before. Antibodies were diluted in blocking buffer (0.5% cold water fish skin gelatin [Sigma-Aldrich], 1% normal goat serum [Thermo Fisher Scientific], 0.05% Tween-20 in PBS). Grids were incubated for 30 minutes each in blocking buffer, followed by primary antibody solution, then secondary antibody solution. Grids were washed in PBS between steps, and in low salt buffer before negative staining, as described before. For controls, primary antibody was omitted from the second incubation step or replaced with preimmune serum.
Transmission electron microscopy
Images and tomograms of resin-embedded and negative-stained skeletons were collected using an FEI T12 electron microscope with a tungsten filament operated at 120 kV, or an FEI F20 electron microscope operated at 200 kV. A US4000 CCD camera (Gatan, Abingdon, UK) was used for imaging. Dual-axis tomograms were collected using a dual-tilt tomography holder (E.A. Fischione Instruments, Inc., Export, PA).
Cryotomograms were collected from vitrified specimens 100-300 nm thick using a Polara electron microscope operated at 300 kV (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR), equipped with a Quantum energy filter and a K2 direct electron detector (Gatan). Zero-loss filtering was carried out using a 20-eV slit width. Images were collected in electron counting mode with dose fractionation, using 3- to 6-second exposures with 6 to 20 subframes per exposure. Total exposures were 60 to 110 electrons per square Angstrom (e–/Å2) for cryotomograms and 200-270 e–/Å2 for negative-stain dual-axis tomograms. Tomographic tilt-series collection was controlled using Serial EM.36
Image processing
Tomographic reconstruction and subframe alignment were carried out using IMOD.37 Gold beads 5 or 10 nm in size were used as fiducial markers, and some tomograms were aligned by patch tracking. Gold particles in tomographic reconstructions were detected automatically using IMOD findbeads3d, knobs were modeled using 3dmod, and the relative spatial distribution of gold and knobs was calculated using IMOD MTK.37 The average densities of gold beads calculated by MTK for individual tomograms were combined by weighting the tomogram average according to the number of knobs present. Gold beads in images of immunolabeled material were counted automatically using ImageJ. Tomograms were denoised for display using nonlinear anisotropic diffusion (NAD) filtering.
Freeze-fracture scanning electron microscopy
Mature schizonts were concentrated by centrifugation, high-pressure frozen as described before without additional cryoprotectant, then fractured at −110°C and multiaxis rotary-coated at high vacuum with a 4-nm layer of chromium using a BAF060 freeze-fracture system fitted with a VCT100 vacuum cryo-transfer system (BalTec). Samples were imaged under cryo-conditions using a specialized semi in-lens cryo-SEM (JSM-7401F, JEOL [UK] Ltd, Welwyn Garden City, UK) equipped with a cold-source field emission gun, beam deceleration, and an energy filter. Images were collected using low beam landing energy (1.2 kV) at 37000 to 60000× magnification and a working distance of 4 to 5.4 nm.
Database depositions
Representative tomograms have been deposited in the Electron Microscopy Data Bank, with codes EMD-3116, EMD-3117, EMD-3122, and EMD-3123.
Results
Architecture of P falciparum–induced erythrocyte knobs
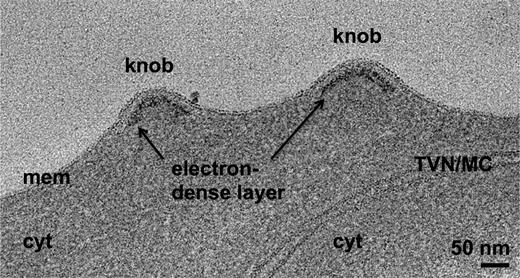
During blood stage development of the parasite, the most evident change to the erythrocyte cell surface is the appearance of the cytoadherent knobs.10,12,13 To characterize knob structure, we processed synchronized late schizonts by high-pressure freezing and freeze substitution and examined sections of this material by EM. Knobs are visible as prominent protrusions on the surface of the erythrocyte membrane (Figure 1), as previously observed.10,18,23,38-45 A layer of electron-dense material approximately 13 nm thick lies under the membrane in the knobs, about 10 nm below the membrane bilayer (Figure 1). It thus occupies a similar position to the erythrocyte cytoskeleton relative to the membrane.46 The electron-dense material follows the shape of the knob in 3 dimensions (3-D), forming cup-shaped structures ranging from 40 to 145 nm in diameter and averaging 50 nm in height (43 knobs examined).
Knobs in the membrane of a P falciparum–infected erythrocyte have an underlying electron-dense layer. Average of 20 slices from a tomogram of a high-pressure-frozen, freeze-substituted schizont, showing knobs in the erythrocyte membrane and underlying electron-dense material. cyt, erythrocyte cytoplasm; mem, erythrocyte membrane; TVN/MC, tubulovesicular network/Maurer's cleft.
Knobs in the membrane of a P falciparum–infected erythrocyte have an underlying electron-dense layer. Average of 20 slices from a tomogram of a high-pressure-frozen, freeze-substituted schizont, showing knobs in the erythrocyte membrane and underlying electron-dense material. cyt, erythrocyte cytoplasm; mem, erythrocyte membrane; TVN/MC, tubulovesicular network/Maurer's cleft.
A spiral structure underlies knobs
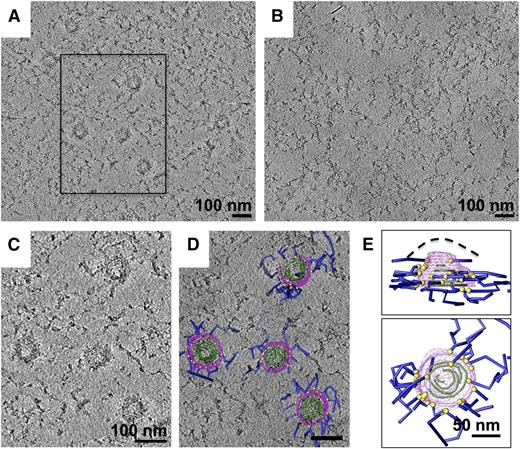
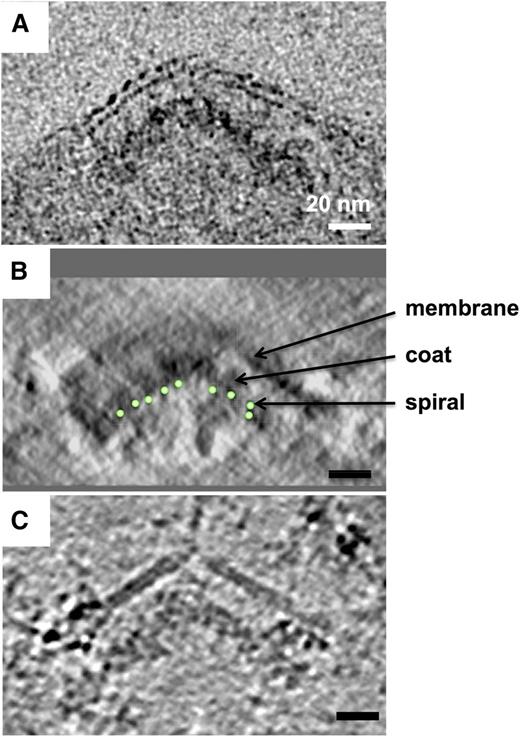
To obtain a more detailed view of the knob structure, we examined detergent-insoluble schizont skeletons by negative-stain EM. Knobs are visible as dark patches in the erythrocyte cytoskeleton, 70 to 100 nm in diameter (Figure 2). When this material is examined by electron tomography, structural components are resolved in 3-D rather than being projected onto a single plane. In the resulting 3-D reconstructions, knobs can clearly be seen to contain spirals made up of a stain-excluding filament 2 to 3 nm wide (supplemental Video 1 available on the Blood Web site). Figure 3A-C shows slices of these spirals at different depths through the knobs. Tracing these structures in 3-D reveals that each knob contains a spiral filament that coils into a shallow cone (Figure 3D-E and supplemental Video 1). Spirals turn anticlockwise as viewed from the cytoplasmic (concave) side (Figure 3D-E and supplemental Figure 2). The spacing between turns of the filament varies from 5 to 12 nm, and the gaps between turns contain a radiating structure with major radial features spaced approximately 4 nm apart (Figure 3A). A layer of more diffuse material, also having a radiating pattern, coats the upper surface of the conical frame formed by the spiral (viewed in different orientations in Figure 3C,F). When viewed from the side, this coating coincides with the cup-shaped structure seen as an electron-dense layer in resin-embedded sections (compare Figure 4A-B). This structure lies between the 2- to 3-nm spiral filament and the membrane, in cases where detergent extraction was incomplete (Figure 4B). The whole spiral-plus-coat structure (which we will refer to together as the “knob skeleton”) is 20 to 50 nm in height, similar to what was seen for resin-embedded material, suggesting that the negative stain procedure did not cause noticeable flattening. Knob density in the cytoskeleton was 11.8 ± 5.1 knobs/µm2, which is similar to that reported for P falciparum strains subjected to long-term in vitro culture as in this study.47
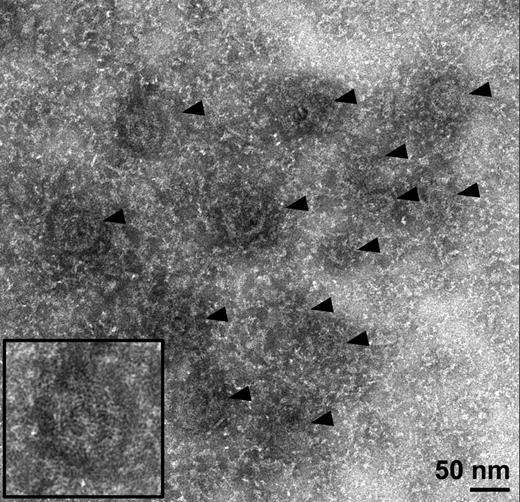
Knobs are visible as dark patches in electron micrographs of detergent-extracted schizont skeletons. Electron micrograph showing several knobs (arrowheads) in a negative-stained schizont skeleton, with surrounding cytoskeletal material. Inset: Twofold enlarged view of the knob at bottom left.
Knobs are visible as dark patches in electron micrographs of detergent-extracted schizont skeletons. Electron micrograph showing several knobs (arrowheads) in a negative-stained schizont skeleton, with surrounding cytoskeletal material. Inset: Twofold enlarged view of the knob at bottom left.
Knobs contain spiral structures seen in sections through 3-D reconstructions. (A-C) Sections (averages of 3-4 slices) taken at different heights through knobs in a tomogram of a negative-stained schizont skeleton, showing a spiral structure. White arrows in (A) indicate some examples of radiating connections between turns; yellow arrows in (C) indicate diffuse coating material with a radiating pattern. (D-E) Handedness and depth of knob spirals: models of 2 adjacent knobs from opposite sides of the skeleton, which have been collapsed onto one another during lysis and staining, viewed face-on (D) and from the side (E). (F) Section through the tomogram tilted to cut through the coating layer of one side of a knob cone, showing coating material over at least 5 turns in curved layers (yellow arrows). Some stain-excluding membrane material (marked in [F] by a dashed line; see Figure 4B) remains after detergent extraction.
Knobs contain spiral structures seen in sections through 3-D reconstructions. (A-C) Sections (averages of 3-4 slices) taken at different heights through knobs in a tomogram of a negative-stained schizont skeleton, showing a spiral structure. White arrows in (A) indicate some examples of radiating connections between turns; yellow arrows in (C) indicate diffuse coating material with a radiating pattern. (D-E) Handedness and depth of knob spirals: models of 2 adjacent knobs from opposite sides of the skeleton, which have been collapsed onto one another during lysis and staining, viewed face-on (D) and from the side (E). (F) Section through the tomogram tilted to cut through the coating layer of one side of a knob cone, showing coating material over at least 5 turns in curved layers (yellow arrows). Some stain-excluding membrane material (marked in [F] by a dashed line; see Figure 4B) remains after detergent extraction.
The electron-dense coating layer lies between the spiral and the membrane. Comparison of side-view sections through knobs in tomograms of schizont material prepared using different methods, showing layered arrangement of spiral, coat layer, and membrane; averages of 10 tomographic slices through the knob apex. (A) High-pressure-frozen, freeze-substituted schizont showing membrane bilayer and underlying electron-dense material. (B) Negative-stained detergent-insoluble schizont skeleton; contrast inverted to match (A) and (C). The path of the spiral coil through the tomogram section is indicated by green circles. Some membrane remains after detergent extraction. View orthogonal to the plane of the tomogram. (C) Schizont skeleton in vitreous ice, showing partially detergent-extracted membrane and underlying electron-dense material. A sharp discontinuity is present at the apex and in the coat layer.
The electron-dense coating layer lies between the spiral and the membrane. Comparison of side-view sections through knobs in tomograms of schizont material prepared using different methods, showing layered arrangement of spiral, coat layer, and membrane; averages of 10 tomographic slices through the knob apex. (A) High-pressure-frozen, freeze-substituted schizont showing membrane bilayer and underlying electron-dense material. (B) Negative-stained detergent-insoluble schizont skeleton; contrast inverted to match (A) and (C). The path of the spiral coil through the tomogram section is indicated by green circles. Some membrane remains after detergent extraction. View orthogonal to the plane of the tomogram. (C) Schizont skeleton in vitreous ice, showing partially detergent-extracted membrane and underlying electron-dense material. A sharp discontinuity is present at the apex and in the coat layer.
Knobs are embedded in the cytoskeleton and have a discontinuity at their apex
To examine the cytoskeleton in the hydrated state, we prepared frozen-hydrated schizont skeletons and imaged these by cryo-electron tomography (Figures 4C and 5 and supplemental Video 3). Cytoskeleton and knobs can be seen clearly in the resulting cryotomograms (Figure 5A,C). It was possible to partially trace the path of the spirals and to identify the coat on the outside of the spiral cone (Figure 5C). The coat coincides with the electron-dense layer in high-pressure frozen material and with the diffuse layer in negative stain (Figure 4). In cases where knobs present clear side views in the resulting cryotomograms, there is a discontinuity at the apex of the knob, with a break in the residual membrane in preparations where detergent extraction was incomplete (Figure 4C). This suggests a difference in membrane properties at this point, which could indicate the presence of specialized transmembrane components. In Figure 5D, a model of the 3-D structure traced from the 3-D reconstruction (see supplemental Video 3) is superposed on a section of the density. Cytoskeletal filaments (blue) connect to the outside of the coat layer (magenta, Figure 5D). Points of contact between the cytoskeleton and coat layer (yellow spheres) are apparent over the whole surface of the coat layer, but most connections occur around the knob base (Figure 5E). No cytoskeletal material can be seen passing underneath the knobs (supplemental Video 3) in tomograms where the 2 apposed layers of the cytoskeleton, arising from the upper and lower cell surfaces, can be adequately distinguished. An antispectrin antibody, recognizing the erythroid spectrin α-chain SH3 domain, labeled the erythrocyte skeleton of schizonts as expected, but labeling was almost completely excluded from regions within 50 nm of the centers of knobs (supplemental Figure 4). This suggests that spectrin, the major erythrocyte cytoskeletal building block, is excluded from the inside of the knobs, which were 70 to 100 nm in diameter. This supports the model described in Figure 5D-E, in which spectrin connects to the outer edges of knobs without passing underneath them. Importantly, outside of the knobs, there is no obvious qualitative difference in cytoskeleton structure between infected and uninfected erythrocyte skeletons (Figure 5A-B).
Knob skeletons make multiple connections to the erythrocyte cytoskeleton. (A) Schizont skeleton with knob skeletons in vitreous ice; average of 50 slices from an NAD-filtered cryotomogram. (B) Uninfected erythrocyte skeleton; average of 30 slices. (C) Enlarged view of the boxed region in (A), average of 30 slices, showing 4 knob skeletons and surrounding cytoskeleton. (D) The same region shown in (B), with superimposed model of knobs and associated material in 3-D. Spiral strands are partially traced as green tubes and the coating layer of the knob skeletons is outlined by magenta contours. Points of connection with the surrounding cytoskeletal material (dark blue tubes) are marked by yellow spheres. (E) Orthogonal views of a model of a typical knob skeleton (top right in C-D). In the side view (top), the estimated location of the cell membrane before detergent extraction, based on Figure 4, is marked by a dashed line. The outer surface of the coat layer has been rendered as a mesh (magenta).
Knob skeletons make multiple connections to the erythrocyte cytoskeleton. (A) Schizont skeleton with knob skeletons in vitreous ice; average of 50 slices from an NAD-filtered cryotomogram. (B) Uninfected erythrocyte skeleton; average of 30 slices. (C) Enlarged view of the boxed region in (A), average of 30 slices, showing 4 knob skeletons and surrounding cytoskeleton. (D) The same region shown in (B), with superimposed model of knobs and associated material in 3-D. Spiral strands are partially traced as green tubes and the coating layer of the knob skeletons is outlined by magenta contours. Points of connection with the surrounding cytoskeletal material (dark blue tubes) are marked by yellow spheres. (E) Orthogonal views of a model of a typical knob skeleton (top right in C-D). In the side view (top), the estimated location of the cell membrane before detergent extraction, based on Figure 4, is marked by a dashed line. The outer surface of the coat layer has been rendered as a mesh (magenta).
KAHRP is in the diffuse layer coating the spiral
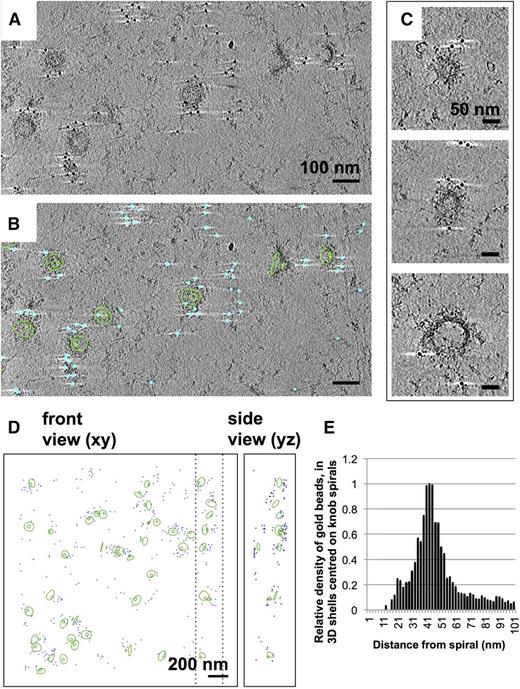
Previous studies have demonstrated that the material underlying knobs contains KAHRP.22,23 To locate KAHRP in the schizont skeletons, we used monoclonal antibodies (mAb) against KAHRP. Labeling was detected by negative-stain and cryo-electron tomography using a gold-conjugated secondary antibody (Figure 6). Skeletons labeled with anti-KAHRP antibody 18.2 (Figure 6A-B) have gold beads clustered over the surface (Figure 6C-D), separated from the spiral by 10 to 60 nm (Figure 6E). Uninfected erythrocyte skeletons showed no labeling under identical conditions (supplemental Figure 5). A similar pattern of labeling was seen using anti-KAHRP antibody 89, which recognizes a different part of the KAHRP sequence (supplemental Figure 6). The epitope for mAb 18.2 is located in residues 282 to 362 of KAHRP, whereas that for mAb 89 lies within residues 424 to 539 (supplemental Figure 6).48 These findings are in agreement with the earlier work and confirm that the knob skeletons contain KAHRP.
Immuno-EM labeling of KAHRP in knob skeletons. (A). Thick section (average of 50 slices) from a cryotomogram of schizont skeleton labeled with anti-KAHRP antibody 18.2 and 10-nm gold-conjugated secondary antibody. (B) The same field of view shown in (A), with 70 slices of a 3-D model overlaid, describing knob spirals by the first and last turn (green contours), and gold beads as cyan spheres. (C) Sections (30 slices each) through individual knobs in a cryotomogram of schizont skeleton labeled with mAb 18.2 and gold-conjugated secondary antibody, showing spiral structure with radiating pattern and gold labeling on the coat layer. Connected cytoskeleton is also visible. (D) Model showing spirals as first and last turn (green contours) and gold label (cyan spheres) in a cryotomogram of schizont skeleton labeled with anti-KAHRP antibody 18.2. Dashed lines mark the boundaries in x of the volume shown in the side view. (E) Chart showing the average density of gold beads at a given radial distance (in 3-D) from knob spirals in 4 cryotomograms of schizont skeletons labeled with KAHRP antibody 18.2 and 10-nm gold-conjugated secondary antibody.
Immuno-EM labeling of KAHRP in knob skeletons. (A). Thick section (average of 50 slices) from a cryotomogram of schizont skeleton labeled with anti-KAHRP antibody 18.2 and 10-nm gold-conjugated secondary antibody. (B) The same field of view shown in (A), with 70 slices of a 3-D model overlaid, describing knob spirals by the first and last turn (green contours), and gold beads as cyan spheres. (C) Sections (30 slices each) through individual knobs in a cryotomogram of schizont skeleton labeled with mAb 18.2 and gold-conjugated secondary antibody, showing spiral structure with radiating pattern and gold labeling on the coat layer. Connected cytoskeleton is also visible. (D) Model showing spirals as first and last turn (green contours) and gold label (cyan spheres) in a cryotomogram of schizont skeleton labeled with anti-KAHRP antibody 18.2. Dashed lines mark the boundaries in x of the volume shown in the side view. (E) Chart showing the average density of gold beads at a given radial distance (in 3-D) from knob spirals in 4 cryotomograms of schizont skeletons labeled with KAHRP antibody 18.2 and 10-nm gold-conjugated secondary antibody.
Membrane proteins are reorganized at knobs
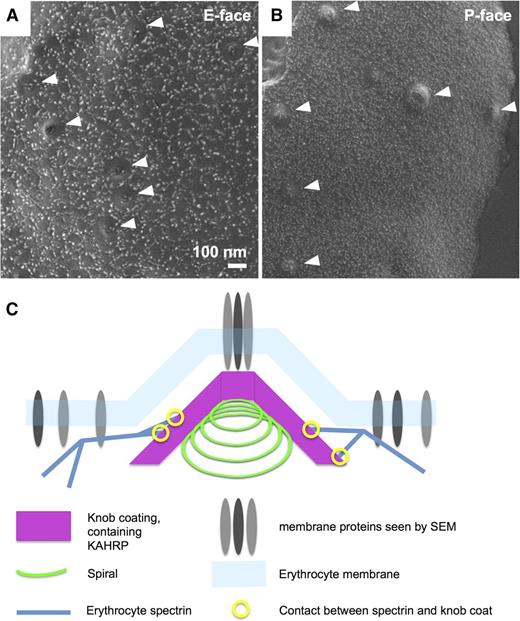
To examine the distribution of proteins in the knob membrane, we used a custom-optimized system combining cryoscanning electron microscopy (cryo-SEM) at ∼2 nm resolution, with freeze-fracture. Freeze-fracture allows examination of the individual leaflets of the membrane bilayer, while this system facilitates visualization over a fractured surface containing many thousands of schizonts at high magnification (Figure 7). Knobs appear as pits in the E-face (the inside of the outer membrane leaflet; Figure 7A) or protrusions in the P-face (the outside of the inner membrane leaflet; Figure 7B). Membrane proteins in the E-face are arranged in a mesh pattern that closely resembles the mesh of the cytoskeleton in dimensions and arrangement; knob protrusions show a circular clearing in this pattern with membrane proteins only remaining at the apex (Figure 7A). The dimensions of individual globular components in the pattern of membrane proteins range between 8 to 25 nm, including the 4-nm chromium coating. Membrane proteins in the P-face are smaller (∼5-10 nm) and appear less organized than in the E-face. However, a circular zone of clearing is also evident around the edges of the knob protrusions, similar to what was seen previously by low-resolution freeze-fracture SEM of the P-face (Figure 7B).19,39 These findings demonstrate that the knob membrane has a distinct distribution of membrane proteins from the surrounding erythrocyte membrane, including a discrete structure at the apex.
Knob membranes have a distinct distribution of membrane proteins. Cryoscanning EM images of freeze-fractured schizont coated with 4 nm chromium, showing erythrocyte membrane proteins. The knobs are clearly recognizable as indentations (A) or protrusions (B). Membrane proteins are visible as small lighter-shaded bumps forming various patterns on the surface. (A) E-face (inside of the outer membrane leaflet). (B) P-face (outside of inner membrane leaflet). Knobs are indicated by white arrowheads. (C) Schematic of the knob structure, showing the spiral with coat layer underlying the erythrocyte membrane, and erythrocyte spectrin connecting to the outside of the coat layer. Membrane proteins are present at the knob apex and in the surrounding erythrocyte membrane, but are otherwise sparse in the knobs.
Knob membranes have a distinct distribution of membrane proteins. Cryoscanning EM images of freeze-fractured schizont coated with 4 nm chromium, showing erythrocyte membrane proteins. The knobs are clearly recognizable as indentations (A) or protrusions (B). Membrane proteins are visible as small lighter-shaded bumps forming various patterns on the surface. (A) E-face (inside of the outer membrane leaflet). (B) P-face (outside of inner membrane leaflet). Knobs are indicated by white arrowheads. (C) Schematic of the knob structure, showing the spiral with coat layer underlying the erythrocyte membrane, and erythrocyte spectrin connecting to the outside of the coat layer. Membrane proteins are present at the knob apex and in the surrounding erythrocyte membrane, but are otherwise sparse in the knobs.
Discussion
We have examined the cytoadherent knobs in P falciparum–infected erythrocytes and have described a knob skeleton, containing a spiral structure, underlying the membrane protrusions (Figures 3 and 4). This structure is described schematically in Figure 7C. Armed with the present data, one can detect hints of the spiral structure in previously published images of purified knobs.49 Our use of 3-D imaging of schizont skeletons facilitated the interpretation of these structures as conical spirals.
The outer coat of the knob skeleton makes multiple connections to the surrounding erythrocyte cytoskeleton (Figure 5C-E and supplemental Video 3). These mechanical linkages suggest a means by which the shear forces involved in cytoadhesion by the knobs under flow conditions could be transmitted to the surrounding cytoskeleton (eg, as discussed in Crabb et al18 ). A spiral support at the point of attachment might function in a springlike fashion to absorb sudden changes in mechanical stress. Intrinsic flexibility in the structure that would support this idea is suggested by the variations observed in spacing between turns of the spiral.
Insertion of KAHRP-containing knobs into the cytoskeleton may also explain the rigidifying effect of KAHRP on the infected erythrocyte.27 Knobs are present at high density on the surface of infected erythrocytes, and the numerous connections between the coat layer and the surrounding cytoskeleton are likely to have a significant impact on cytoskeletal mechanics. In clinical isolates, knob densities can reach up to 4 times what we observed in this laboratory strain.47 These findings support the mechanism proposed in a recent modeling analysis for the rigidifying effect of the knobs on the erythrocyte cytoskeleton.50 Spectrin tetramers are capable of stretching to 194 nm in length,51 which would allow for knob intercalation into the cytoskeleton mesh without further modification. It has been reported that the red cell cytoskeleton is gradually dismantled as the intracellular parasite develops,42,52,53 and it is possible that some cytoskeletal connections are broken during knob formation. However, in this study, which used highly synchronized, mature schizont preparations, no differences in cytoskeletal structure outside of the knobs were observed between uninfected erythrocyte skeletons and those from mature schizonts. These findings are not consistent with the notion of progressive degradation of the cytoskeleton.
Knobs are thought to comprise a complex of the cytoadherent ligand PfEMP1, KAHRP, other parasite-derived proteins, and erythrocyte cytoskeleton components such as spectrin, F-actin, and ankyrin-R.32,54-62 A central fragment of KAHRP containing lysine-rich repeat regions forms electron-dense patches under the membrane in resealed erythrocytes,48 and full-length KAHRP expressed in Escherichia coli forms clusters that associate with spectrin.57 Our immunolabeling (Figure 6) strengthens earlier evidence localizing KAHRP to the electron-dense layer underlying knobs.22,23
The distinctive spiral structure in the knobs (Figure 3) bears a striking resemblance to the structures formed by eukaryotic ESCRT-III proteins involved in ATP-driven intraluminal vesicle budding and membrane scission in mammalian and yeast cells.63-67 ESCRT-III proteins comprise α-helical bundles that assemble into a membrane-associated spiral.63 Although no homology could be detected between ESCRT-III proteins and any of the known components of knobs (supplemental Information 7), it is noteworthy that they both involve spiral structures of very similar appearance in membrane deformation. Only low levels of native ESCRT-III proteins have been detected in erythrocytes.68 By comparison, knobs are present at high density in infected erythrocytes and also contain high concentrations of KAHRP.12 The P falciparum genome encodes 5 homologs of eukaryotic ESCRT-III proteins (PF08_0064, PFI00300w, PFL2090c, PF14_0397, and PF11_0434; supplemental Information 7), all of which are expressed in the blood stages. However, none of these is known or predicted to be exported to the erythrocyte cytoplasm (supplemental Information 7). None of the knob-associated proteins is known to have ATPase activity, as might be expected for ESCRT-III complexes.
The erythrocyte membrane is modified considerably during P falciparum infection by the insertion of parasite-derived proteins, including PfEMP1, as well as by changes in phosphorylation of cytoskeleton-associated proteins.69-72 Phosphorylation of erythrocyte band 3 during infection has been shown to cause uncoupling of this cytoskeleton-organizing transmembrane protein from the cytoskeleton.73 We observed a rearrangement of transmembrane proteins at knobs by high-resolution, freeze-fracture cryo-SEM (Figure 7A-B). This is consistent with a role for knobs in organizing and presenting transmembrane ligands on the erythrocyte surface.18,19 In the E-face, knobs form prominent clearings in a network of membrane proteins, which are absent from all but the knob apex. A discontinuity was also observed at the apex of knobs in cryotomograms, consistent with a difference in the properties of the membrane at this point (Figure 4). Given that PfEMP1 has been clearly localized to the surface of knobs,9,19 and that adhesion appears to occur at the apex of knobs in sections of infected cells adhering to the epithelial surface,19 it seems likely that a PfEMP1-containing adhesive structure is located at the knob apex. Outside of the knobs, the network pattern of membrane proteins seen in the E-face by freeze-fracture SEM suggests that these may be cytoskeleton-associated, possibly band 3 or glycophorins (although there is some evidence that band 3 partitions preferentially with the P-face during fracture of uninfected erythrocytes74,75 ). Altered membrane protein distribution at knobs is less marked in the P-face, although there are clearings around knobs similar to those observed previously by SEM of freeze-fracture replicas.19,39
In conclusion, we have shown that erythrocyte knobs in P falciparum infection contain a highly organized, coated spiral structure underlying a specialized region of membrane (Figure 7C). The application of electron tomography to schizont skeletons has revealed this previously undescribed knob skeletal framework. The observation of multiple connections between the knob skeleton and the erythrocyte cytoskeleton suggests a mechanical explanation for the cytoadherence-enhancing effects of knobs as well as for the reduction in cytoskeletal flexibility caused by knob components. The discovery of these structures suggests new avenues of research to elucidate the roles of individual components of the knob structure in antigen presentation and adherence.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Kirsty MacLellan-Gibson for her assistance; Andrew Osborne, Andrea Nans, Richard Hayward, and Giulia Zanetti for helpful discussions; David Houldershaw and Richard Westlake for computing support; Peter Rosenthal for providing access to some facilities at the Francis Crick Mill Hill Laboratory; and Professor Diane W. Taylor for her kind gift of anti-KAHRP mAb 89. mAb 18.2 was obtained from The European Malaria Reagent Repository (http://www.malariaresearch.eu).
This work was supported by Medical Research Council Project grant G1100013 (H.R.S., M.J.B., R.A.F.); the EU FP7 NoE EviMalAR (M.J.B.); the Wellcome Trust (088497/Z/09/Z) (I.V.); studentship (E.E.C.); equipment grants 101488, 079605, and 086018 (H.R.S., M.J.B., R.A.F.); and the BBSRC (Collaborative Awards in Science and Engineering [CASE] studentship BB/F016948/1 [V.L.H.], equipment grant BB/L014211 [HRS]).
Authorship
Contribution: J.M.W., I.V., R.A.F., M.J.B., and H.R.S. designed the research and wrote the manuscript; J.M.W., V.L.H., F.H., D.K.C., and E.E.C. performed the research and collected data; and J.M.W., V.L.H., I.V., R.A.F., M.J.B., and H.R.S. analyzed and interpreted the data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The PhD studentship for V.L.H. was partly funded by Gatan, but the funders were not involved in planning the research. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for D.K.C. is Electron Bioimaging Centre, Diamond Light Source, Didcot, Oxfordshire, United Kingdom
Correspondence: Helen R. Saibil, Department of Biological Sciences, Birkbeck, University of London, Malet St, London, WC1E 7HX UK; e-mail: h.saibil@mail.cryst.bbk.ac.uk.

![Figure 3. Knobs contain spiral structures seen in sections through 3-D reconstructions. (A-C) Sections (averages of 3-4 slices) taken at different heights through knobs in a tomogram of a negative-stained schizont skeleton, showing a spiral structure. White arrows in (A) indicate some examples of radiating connections between turns; yellow arrows in (C) indicate diffuse coating material with a radiating pattern. (D-E) Handedness and depth of knob spirals: models of 2 adjacent knobs from opposite sides of the skeleton, which have been collapsed onto one another during lysis and staining, viewed face-on (D) and from the side (E). (F) Section through the tomogram tilted to cut through the coating layer of one side of a knob cone, showing coating material over at least 5 turns in curved layers (yellow arrows). Some stain-excluding membrane material (marked in [F] by a dashed line; see Figure 4B) remains after detergent extraction.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/127/3/10.1182_blood-2015-10-674002/4/m_343f3.jpeg?Expires=1769082892&Signature=RdfRncvgK5VgnJalcK2icdBIIcCZMurbr9ZYhsrQwPgYzx17V0wcBZVaqFEfWdzx6EDzSxJUig7hHTp8RguiLMPJ-9QTywWSZHYO9Ehh42a8goaWvXDNF0PEVaZ767jOVhd~5ZfXVHzsmeFq5d443uf6vRAw0STbGKgiPAyCKwiehb~Uj5xN-B~o6SAH~niGm3JveZGta1ImFnkILa~hHXieBAVnq7Adcy0Ep622NTDUWmdRqSWehlO82Sxq4nzLuxjlLYtvEA7jbd8nNXyXU4o5wOlXEVF8547pMeR2KxtHlvUtpyq5VPUOEYfDXc33QaMevJoDj03PVueVU7l4EA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)