Abstract
Introduction: Novel therapies are urgently needed in pediatric Burkitt lymphoma (pBL) where the survival for relapsed disease is less than 20%. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is molecular chaperone that protects proteins from proteolytic degradation including oncogenic signaling complexes. The clinical development of broad-spectrum Hsp90 inhibitors has previously been limited by suboptimal target inhibition and off-target toxicities. PU-H71 is a next-generation Hsp90 inhibitor that preferentially targets tumor enriched (te-Hsp90), the functionally distinct pool of Hsp90 present in tumor cells. PU-H71 is not toxic to normal B-cells and has demonstrated pre-clinical efficacy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, but has not been studied in Burkitt lymphoma. In the current study, we evaluated te-Hsp90 as a potential therapeutic target in pediatric Burkitt lymphoma.
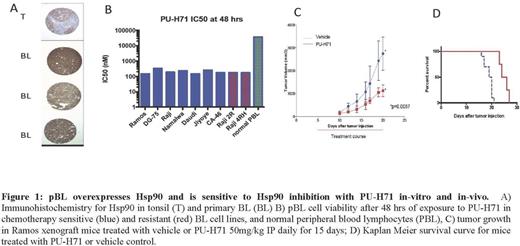
Methods and Results: To evaluate overall Hsp90 protein expression in primary pBL tumors we performed immunohistochemistry on a tissue microarray. Fifty-three of 59 cases (90%) demonstrated high levels of Hsp90 expression defined as >90% tumor cell positivity (Fig. 1A). To evaluate the sensitivity of pBL to te-Hsp90 inhibition we performed in-vitro viability assays with the ATP-based CellTiter-Glo¨ in a panel of pBL cell lines (Ramos, DG-75, Raji, Namalwa, Daudi, Jiyoye, CA-46, Raji 2R, Raji 4RH) and in-vivo studies with a Ramos xenograft model of pBL. pBL cells were sensitive to inhibition by PU-H71 with IC50s in the low nanomolar range (151-337nM, Fig 1B). The Raji 2R and Raji 4RH pBL cell lines with acquired resistance to chemotherapy (Czuczman et al, Clin Cancer Res 2008) were also sensitive to PU-H71 (IC50 175-181nM). In contrast, normal peripheral blood lymphocytes were resistant (IC50 >37,000nM). In pBL xenograft studies, PU-H71 decreased tumor volume (p<0.01, Fig. 1C) and prolonged survival (p<0.01, Fig. 1D).
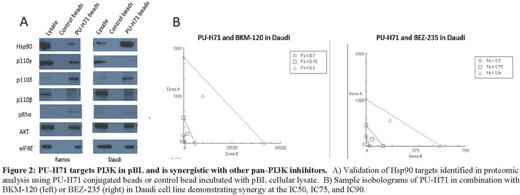
To evaluate the targets of PU-H71 in pBL we performed high affinity capture followed by proteomic analysis using mass spectrometry. Cellular lysates from pBL cell lines were incubated with PU-H71 conjugated agarose beads and the cargo was subject to tandem mass spectrometry. Data was analyzed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis¨. PI3K and mTOR signaling were among the top networks identified. Given the data supporting a crucial role for PI3K in BL (Sanders et al, Cancer Cell 2012), we further investigated protein targets in this pathway. We found a significant number of proteins in the mTOR (p<0.0001) and PI3K (p<0.0001) signaling pathways including ERK, mTOR, and multiple isoforms of PI3K (p110-β; p110-γ, p110-δ). PI3K targets were validated by pull-downs with PU-H71 conjugated beads (Fig 2A).
To investigate the activity of PI3K inhibition in pBL we evaluated a panel of PI3K inhibitors in pBL. Agents with a narrow spectrum of PI3K isoform inhibition such as idelalisib (p110δ inhibition) and IPI-145 (p110 δ and γ inhibition) did not have activity in pBL. In contrast, agents that broadly target PI3K/mTOR such as BEZ235 (pan PI3K and mTOR inhibition) and BKM120 (pan PI3K inhibition) demonstrated activity (IC50 35nM-2602nM). Based on this we concluded that PI3K inhibition is effective in pBL only when multiple components of the pathway are targeted. We hypothesized that PU-H71 will therefore synergize with PI3K inhibitors through dual targeting of PI3K signaling. To test this we evaluated the combination of PU-H71 + BKM-120 and PU-H71 + BEZ235 in four pBL cell lines (Ramos, Namalwa, Daudi, DG-75). The combined response at 48-72 hours was evaluated using the Chou-Talalay method. Both combinations were synergistic in 3 of 4 cell lines with a combinatorial index at the IC50 of <1 (CI 0.44-0.79, Fig. 2B).
Conclusion: Our work demonstrates that Hsp90 is over-expressed in primary pBL tumors and that te-Hsp90 inhibition with PU-H71 is toxic to pBL in-vitro and in-vivo. The oncoprotein targets of Hsp90 in pBL include multiple components of the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway, highlighting the importance of this pathway in pBL. The anti-lymphoma activity of PU-H71 is synergistic with pan-PI3K inhibition as well as dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition. Overall this work provides support for te-Hsp90 as a therapeutic target in BL and suggests the potential for combination therapy with PU-H71 and inhibitors of PI3K/mTOR.
Cesarman:Weill Cornell Medical College: Patents & Royalties: applied for patent for 6-ETI.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal