Abstract
Introduction: Relapses after front-line therapy for Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia (BL) are unfrequent, and there is scarce information about the best rescue strategy for these patients. The objective of this study was to evaluate the incidence of relapse, salvage treatment and prognosis after relapse in patients with BL treated with two consecutive Spanish protocols.
Patients and methods: Retrospective study of patients diagnosed with BL in 40 Spanish hospitals betwen January 1997 and October 2014 treated with first line chemotherapy according to protocols PETHEMA LAL-3/97 (specific chemotherapy without rituximab) and BURKIMAB (rituximab plus specific chemotherapy). The demographic, clinical and biological characteristics were collected at the time of diagnosis and at relapse, as well as the salvage treatment and outcomes.
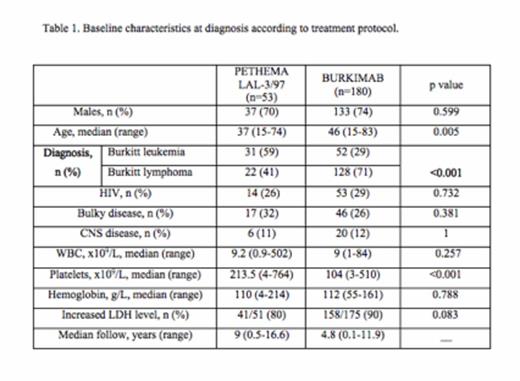
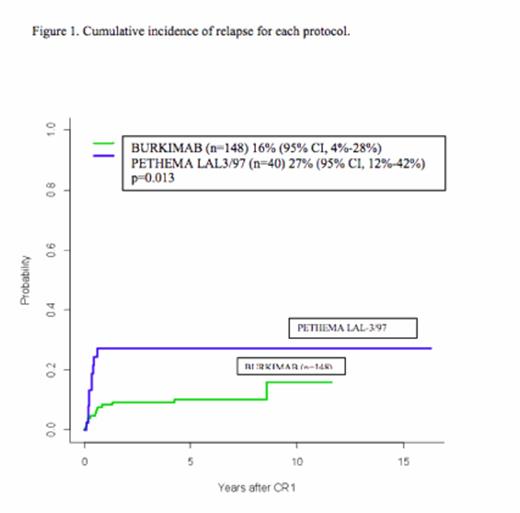
Results: 233 patients were diagnosed with Burkitt lymphoma (n=150) or leukemia (n=83) and received first-line therapy according to PETHEMA LAL-3/97 (n=53) and BURKIMAB (n=180) protocols. Baseline characteristics at diagnosis are described in Table 1. A total of 26 patients relapsed, 11 (28%) treated with PETHEMA LAL-3/97 protocol and 15 (10%) with BURKIMAB protocol (p=0.009). The cumulative incidence of relapse at 10 years was 27% (95% CI, 12%-42%) in PETHEMA LAL-3/97 protocol vs.16% (95% CI, 4%-28%) in BURKIMAB protocol (p= 0.013) (Figure 1). Time to relapse was shorter in PETHEMA LAL-3/97 protocol (median of 3.7 months) vs. BURKIMAB protocol (6.3 months), but it was not significant (p=0.506). No differences were observed in relapse incidence between Burkitt leukemia and Burkitt lymphoma in PETHEMA LAL-3/97 protocol (6/31 vs. 5/22, p=1) and BURKIMAB protocol (7/41 vs. 8/107, p=0.124). Out of 15 patients in whom rescue treatment strategy was evaluable, 12 received chemotherapy with high-dose methotrexate and/or cytarabine (4 of the them followed response, CR in 2, followed by SCT in the 2 patients achieving PR [autologous in one and allogeneic SCT in the other]), and the remaining 3 patients received DA-EPOCH-R (n=1, achieving CR), R-ICE (n=1, no response) and paliative care (n=1). At the time of the analysis, only 3 patients are alive. Median overall survival after relapse was 3 months (95% CI, 0.9-5.1) for PETHEMA LAL-3/97 relapsed group and 3.6 months (95% CI, 0.1-7.1) for BURKIMAB relapsed patients group.
Conclusions: Patients with Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma treated with specific immunochemotherapy have lower probability of relapse compared with those treated with specific chemotherapy without rituximab. In our series, the most frequent regimens administered for the treatment of relapsed patients were based in high-dose methotrexate and/or cytarabine. The prognosis of relapsed Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma is poor, independently of the type of rescue therapy. Supported by grants RD12/0036/0029 (RTICC, FEDER), Instituto Carlos III, Spain.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal