Abstract
Acute erythroid leukemia (AEL) is a distinct subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) characterized by predominant erythropoiesis. Currently, only few studies using next-generation sequencing were reported in AEL. To decipher the somatic mutation spectrum and discover disease-driving genes responsible for the pathogenesis of AEL, we performed whole exome-sequencing (WES) in 6 AEL and validating using targeted next generation sequencing (NGS) and Sanger sequencing in 58 AEL.
From August 2003 to October 2014, a total of 158 patients fulfilling the WHO criteria for AEL were identified, comprising 91 males and 67 females. Median age was 50 years. These patients were further subclassified into 3 groups: 37 AEL after MDS, 108 de novo AEL, and 13 AML with myelodysplasia-related changes.
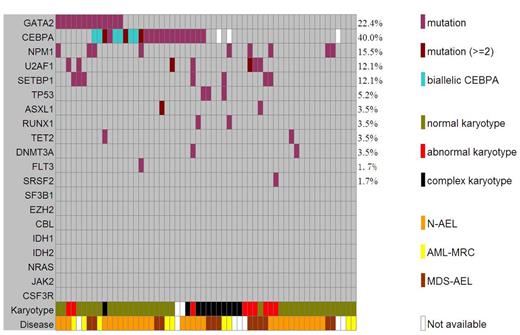
In total, we identified 52 genes with somatic mutations in at least 2 patients, including CEBPA in 4 patients and GATA2 in 2 patients. We identified high frequencies of mutations in CEBPA (40.0%, 22/55; about 1/4 are biallelic mutations), GATA2 (22.4%, 13/58), NPM1 (15.5%, 9/58), SETBP1 (12.1%, 7/58), and U2AF1 (12.1%, 7/58), followed by TP53 (5.2%, 3/58), RUNX1 (3.5%, 2/58), TET2 (3.5%,2/58), ASXL1 (3.5%, 2/58), DNMT3A (3.5%, 2/58), SRSF2 (1.7%, 1/58) and FLT3 (1.7%, 1/58). We did not detect alterations of some of commonly mutated genes associated with AML, including IDH1, IDH2 and RAS. The results are summarized in Figure 1. To further identify the prevalence of GATA2 mutations in hematologic malignancies, we amplified and sequenced the entire coding region of GATA2 gene in 253 non-AEL AML, 40 chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis (CML-BC), 55 B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), and 38 T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). We detected GATA2 mutations in 5.5% of non-AEL AML, 15% of CML-BC, and none of B-ALL or T-ALL.
The GATA2 mutations in AEL are mainly localized in ZF1 domain (P304H, D309E, A318V/T, G320S/D, L321P, and R330X) and TAD domain (Q20H). To find out the implications of GATA2 mutations in the leukemogenesis of AEL, we overexpressed the mutants of GATA2 (P304H, L321P, and R330X) in 293T cells and demonstrate that GATA2 mutant led to reduced transcriptional activity. Whereas overexpression of GATA2 mutants in mouse myeloid progenitor cell line, 32D, has no effect on the proliferative or colony formation abilities, it caused increased expression of erythroid-related antigen Ter-119 (Figure 2), b-globin and bh1-globin. Furthermore, 32D cells transfected with GATA2 mutants showed increased positivity than control cells by Benzidine staining.
Taken together, our findings demonstrate that the mutatome of AEL is different from other types of AML. AEL is associated with a high frequency of mutations in GATA2 and CEBPA. GATA2 mutations resulted in a decrease of transcriptional activity and erythroid development of mouse myeloid progenitors, suggest an important role of GATA2 mutations in AEL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal