Abstract
Background:
Despite advances in treatment, Multiple Myeloma (MM) remains incurable. The PI3K/AKT pathway is activated in MM cells in > 50% of cases due to factors such as bone marrow (BM) microenvironmental signaling and hyperactivation following treatment with proteasome inhibitors (PI). Multiple small-molecule inhibitors have been developed to target PI3K/AKT or mTOR kinases, but the efficacy of these drugs is likely to be compromised by the stimulation of compensatory signaling pathways. The redundancy of signaling pathways provides back-up mechanisms allowing escape from targeted inhibition. One such compensatory pathway is that driven by PIM kinases, which produce parallel oncogenic signals to AKT and mTOR and share several downstream molecular targets. As with PI3K/AKT, the BM microenvironment plays a major role in PIM activation and other factors increasing PIM levels include hypoxia and PI treatment. PIM1 and particularly PIM2 are known to be highly expressed in MM and play important roles in regulating MYC-driven transcription, apoptosis, cytokine signaling, cell proliferation and protein translation. Combinations of separate PI3K and PIM inhibitors have shown evidence of synergy in MM cell lines and animal models and a PIM kinase inhibitor has recently shown activity in relapsed/refractory MM. Given this background we wished to evaluate the activity of a novel family of kinase inhibitors capable of inhibiting not only PIM kinases but also PI3K/AKT (dual inhibitors) and PI3K/AKT/mTOR (triple inhibitors).
Methods:
We evaluated the in-vitro activities of a single pan-PIM (pPIMi), dual PIM/PI3K (IBL-202) and triple PIM/PI3K/mTOR (IBL-301) inhibitor in MM cell lines: MM1.S, NCI-H929, RPMI8226 and KMS11, which is known to be PIM2 dependent, alongside the pan-PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 and the pan-PIM inhibitor AZD1208. IBL-202 and IBL-301 are optimized lead compounds and are low nanomolar pan-PIM/PI3K and pan-PIM/PI3K/mTOR inhibitors respectively. These dual and triple inhibitors show excellent kinase selectivity profile against a panel of 456 kinases. Cell viability was assessed using the Cell-Titre Glo assay and apoptosis determined by Annexin-V/PI staining. Co-culture experiments were performed with HS-5 stromal cells. Combination treatment was performed with bortezomib and IBL-202 to assess synergy.
Results and discussion:
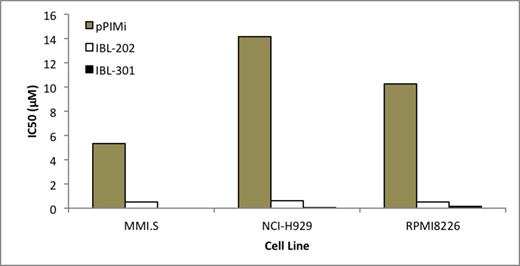
IBL-202 and IBL-301 were significantly more potent than pPIMi in all MM cell lines tested (figure 1). IBL-202 and IBL-301 caused a loss in cell viability 50% and 70%, respectively, greater than pPIMi alone. IBL-202 and IBL-301 induced 50-80% and 80-100% cell death, respectively .v. 10% for pPIMi after 48 hrs, p<0.001. The Pim2 dependent MM cell line KMS11 showed a loss in cell viability following treatment with IBL-202 and IBL-301 up to three times greater than either of the PIM kinase inhibitors or GDC-0941. IBL-202 treatment caused a 90% reduction in cell viability at a dose of 5µM and IBL-301 was equally effective at a concentration of just 1µM. GDC-0941(5µM) caused a loss of approximately 30% in cell viability whereas cells remained entirely resistant to pPIMi and AZD1208 at concentrations up to 10µM (p< 0.001). IBL-202 in combination with bortezomib was synergistic in MM cell lines (CI<1).
While co-culture with HS-5 cells protected MM cell lines against bortezomib-induced cell death, it promoted the apoptotic effect of both IBL-202 and IBL-301 with an increase in Annexin V positive cells from 15% to 40%. This suggests that micro-environmental stimulation could potentially induce synthetic lethality in the presence of these inhibitors. We observed strong induction of PIM2 in MM1.S cells following co-culture. Mechanistically, cells respond to dual and triple inhibitors with cell cycle arrest, marked apoptosis and strong down-regulation of biomarkers. The dual and triple inhibitors are optimized with respect to their in vitro ADME properties and have excellent oral bioavailability. In-vivo IBL-301 has been well tolerated, with no signs of toxicity even 20 times above the efficacious dose in a transgenic (KRASV12NSCLC) mouse model. Testing of IBL-202 in a relevant MM mouse model is planned in the near future.
Conclusions:
IBL-201 and IBL-301 show promising activity in MM cellular models with increased potency compared to inhibitors targeting PIM or PI3K alone and warrant further evaluation in this disease.
O'Neill:Inflection Biosciences: Employment, Equity Ownership. O'Dwyer:Inflection Biosciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal