Abstract
Background
Dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome are risk factors for cancer, and clinically aggressive CLL cells are believed to rely on lipid metabolism. Statins promote apoptosis and inhibit CLL cell growth in pre-clinical models, and statin use during salvage therapy for CLL may confer a survival advantage.
Methods
To investigate the prevalence of hyperlipidemia and the effect of statin therapy, lipid profiling was performed on 238 consecutive patients presenting to a specialized CLL clinic between January 2012 and February 2014. Demographics, timing of diagnosis and initiation of chemoimmunotherapy was ascertained from clinical records. Prognostic information was obtained from pathology or flow cytometeric reports. The first lipid profile following CLL diagnosis was recorded. RAI stage was determined from blood counts and radiology or clinical examination at the time of lipid profiling. Patients were grouped according to statin therapy (yes/no) and hyperlipidemia.
Results
Of 281 patients reviewed, 238 were evaluable with a lipid profile. 110 patients (46.2%) were either taking statins at the time of their CLL diagnosis (27.3%) or prescribed a statin during the study period (18.5%) and an additional 11 (4.2%) had a diagnosis of dyslipidemia not on therapy. Of the remaining 117 patients, 18 had LDL ³ 3.5mmol/L, giving a total of 139 patients (58.4%) with abnormal lipid profiles. The statin-exposed group was significantly older (median age 69.5 vs 65, p=0.03) and there were a larger proportion of males (68.6% vs. 53.9%, p=0.02). There were no significant differences in RAI staging, cytogenetics, beta-2-microglobulin levels, or CD38 expression between groups. (Table 1)
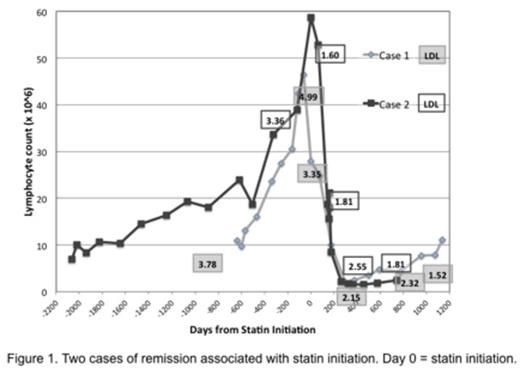
59.7% of all patients were treatment-free by the end of the study period and there were no differences between statin/no-statin groups. Of those requiring treatment, median time to first treatment (TFT) was 48 (IQR, 24-85.3) months. TFT was significantly longer with statins (57.5 (IQR, 32-77) vs. 36 (IQR, 11-100) months, p<0.02. Initiation of statins following diagnosis of CLL was associated with further prolongation of TFT compared to those on statins at diagnosis (74 (IQR, 62-96) vs. 45 (IQR, 30-64) months, p<0.02). Two cases of spontaneous remission were noted with statin initiation. (Figure 1)
Conclusions
There is an increased prevalence of hyperlipidemia in CLL patients (58.4%) compared to the general population (35-39%). Statin therapy is associated with a prolonged TFT despite a significantly older population and a higher proportion of male patients in this group. CLL patients should be screened for hyperlipidemia and statin therapy may be an adjunct to CLL treatment.
Patient Characteristics by Lipid Abnormalities
Time to First Treatment (TFT) by Statin Use
| . | Total N (%) . | No statin N (%) . | Statin Use/Dyslipidemia N (%) . | p -value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 238 | 117 | 121 | |
| Male | 146 (61.3) | 63 (53.9) | 83 (68.6) | 0.02 |
| Median age (Q1, Q3) | 67 (60, 74) | 65 (58, 73) | 69 (63, 76) | 0.01 |
| RAI Stage | 0.64 | |||
| N1 | 178 (74.8%) | 78 (66.7%) | 99 (81.8%) | |
| MBL | 7 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | 71 | 35 | 36 | |
| 1 | 34 | 16 | 18 | |
| 2 | 32 | 10 | 22 | |
| 3 | 20 | 8 | 12 | |
| 4 | 14 | 7 | 7 | |
| Lipid profile (Mean ± Std Dev) | ||||
| HDL (mM) | 1.23 ± 0.47 | 1.33 ± 0.49 | 1.14 ± 0.42 | 0.001 |
| LDL (mM) | 2.55 ± 1.03 | 2.69 ± 0.87 | 2.42 ± 1.16 | 0.05 |
| TC/HDL | 3.92 ± 1.43 | 3.80 ± 1.25 | 4.03 ± 1.57 | 0.21 |
| Non HDL-C (mM) | 3.22 ± 1.14 | 3.29 ± 0.99 | 3.14 ± 1.27 | 0.29 |
| B2M (N = 0.6-2.3 m g/ml) | 0.52 | |||
| Mean ± Std Dev | 3.20 ± 2.14 | 3.19 ± 2.36 | 3.21 ± 1.92 | |
| CD38 status | 0.86 | |||
| Unknown | 74 (31.1%) | 37 (31.6%) | 37 (30.6%) | |
| CD38+ | 33 | 14 | 19 | |
| CD38- | 122 | 62 | 60 | |
| Partial | 9 | 4 | 5 | |
| Cytogenetics2 | 0.32 | |||
| Unknown | 125 (52.5%) | 61 (52.1%) | 63 (52.1%) | |
| 13q- | 62 | 28 | 35 | |
| 11q- | 13 | 6 | 7 | |
| +12 | 20 | 8 | 12 | |
| 17p- | 12 | 7 | 5 | |
| normal | 24 | 15 | 9 | |
| >1 abnormality | 20 | 10 | 10 | |
| . | Total N (%) . | No statin N (%) . | Statin Use/Dyslipidemia N (%) . | p -value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 238 | 117 | 121 | |
| Male | 146 (61.3) | 63 (53.9) | 83 (68.6) | 0.02 |
| Median age (Q1, Q3) | 67 (60, 74) | 65 (58, 73) | 69 (63, 76) | 0.01 |
| RAI Stage | 0.64 | |||
| N1 | 178 (74.8%) | 78 (66.7%) | 99 (81.8%) | |
| MBL | 7 | 3 | 4 | |
| 0 | 71 | 35 | 36 | |
| 1 | 34 | 16 | 18 | |
| 2 | 32 | 10 | 22 | |
| 3 | 20 | 8 | 12 | |
| 4 | 14 | 7 | 7 | |
| Lipid profile (Mean ± Std Dev) | ||||
| HDL (mM) | 1.23 ± 0.47 | 1.33 ± 0.49 | 1.14 ± 0.42 | 0.001 |
| LDL (mM) | 2.55 ± 1.03 | 2.69 ± 0.87 | 2.42 ± 1.16 | 0.05 |
| TC/HDL | 3.92 ± 1.43 | 3.80 ± 1.25 | 4.03 ± 1.57 | 0.21 |
| Non HDL-C (mM) | 3.22 ± 1.14 | 3.29 ± 0.99 | 3.14 ± 1.27 | 0.29 |
| B2M (N = 0.6-2.3 m g/ml) | 0.52 | |||
| Mean ± Std Dev | 3.20 ± 2.14 | 3.19 ± 2.36 | 3.21 ± 1.92 | |
| CD38 status | 0.86 | |||
| Unknown | 74 (31.1%) | 37 (31.6%) | 37 (30.6%) | |
| CD38+ | 33 | 14 | 19 | |
| CD38- | 122 | 62 | 60 | |
| Partial | 9 | 4 | 5 | |
| Cytogenetics2 | 0.32 | |||
| Unknown | 125 (52.5%) | 61 (52.1%) | 63 (52.1%) | |
| 13q- | 62 | 28 | 35 | |
| 11q- | 13 | 6 | 7 | |
| +12 | 20 | 8 | 12 | |
| 17p- | 12 | 7 | 5 | |
| normal | 24 | 15 | 9 | |
| >1 abnormality | 20 | 10 | 10 | |
1stage determined from those untreated at time of lipid profiling
2counted in all pertinent groups if more than one abnormality
Time to First Treatment (TFT) by Statin Initiation
| . | Total (N=238) . | No statin (N=128) . | Statin Use (N=110) . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W&W1 (%) | 142 (59.7) | 74 (58.8) | 68 (61.8) | 0.53 |
| Available TFT data/Total Treated2 | 89/96 | 51/54 | 38/42 | |
| Median TFT (IQR) (mo) | 48 (24, 83) | 36 (11, 100) | 57.5 (32, 77) | 0.02 |
| . | Total (N=238) . | No statin (N=128) . | Statin Use (N=110) . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W&W1 (%) | 142 (59.7) | 74 (58.8) | 68 (61.8) | 0.53 |
| Available TFT data/Total Treated2 | 89/96 | 51/54 | 38/42 | |
| Median TFT (IQR) (mo) | 48 (24, 83) | 36 (11, 100) | 57.5 (32, 77) | 0.02 |
1watch & wait
2could not determine TFT for some patients.
| . | No statin (N=128) . | Statin Started (N=43) . | Statin Previous (N=67) . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W&W1 (%) | 74 (58.8) | 29 (67.4) | 39 (58.2) | 0.55 |
| Available TFT data/Total Treated2 | 51/54 | 13/14 | 25/28 | |
| Median TFT (IQR) (mo) | 36 (11, 100) | 74 (62, 96) | 45 (30, 64) | 0.04 |
| . | No statin (N=128) . | Statin Started (N=43) . | Statin Previous (N=67) . | P-value . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W&W1 (%) | 74 (58.8) | 29 (67.4) | 39 (58.2) | 0.55 |
| Available TFT data/Total Treated2 | 51/54 | 13/14 | 25/28 | |
| Median TFT (IQR) (mo) | 36 (11, 100) | 74 (62, 96) | 45 (30, 64) | 0.04 |
1watch & wait
2could not determine TFT for some
[1]Spaner DE, Lee E, Shi Y, Wen F, Li Y et al. Leukemia 2013; 27:1090-1099.
[2]Chae YK, Trinh L, Jain P, Wang X, Rozovski U et al. Blood 2014; 123: 1424-1426.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal