Abstract
Lysosomal-associated protein transmembrane 5 (LAPTM5) encodes a transmembrane protein in lysosomal, which is specifically expressed in hematopoietic system. Autophagy, a lysosomal degradation pathway, is now emerging as an importance prosurvival or prodeath factor in response to some chemotherapy. In our previously study, we found the expression of LAPTM5 is closely related with acute lymphocytic leukemia, but exactly role of this gene in acute leukemia(AL) was unknown. To investigate the association of LAPTM5 with autophagy, we overexpressed LAPTM5 in K562 cells, and the results showed LAPTM5 significantly decreased autophagy activity, which measured by testing the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II and LC3-II dots using western blotting and imaging flow cytometry, respectively(Figure 1 and 2). Moreover, PCR array was performed to detect the changes of 92 genes regulating autophagic activity in LAPTM5 overexpressed cells, and 73 autophagy-related genes were found downregulated. Finally, the overexpression of LAPTM5 significantly reduced the pH value in lysosomal, which was very essential for autophagy-mediated degradation activity (Figure 3). Taken together, these results suggest that LAPTM5 decreased autophagy activity though downregulation of pH value in lysosomal. Therefore, LAPTM5 might represent a potential target modulating autophagy activity to increase sensitivity to chemotherapy in treatment of AL.
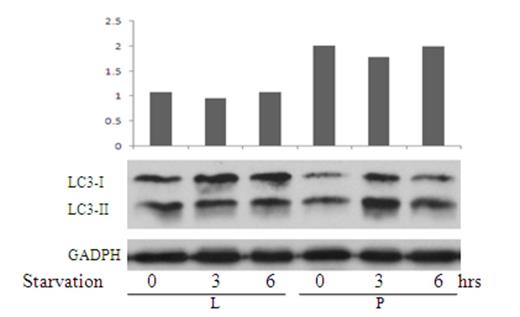
LAPTM5 gene suppressed K562 cells' autophagy activity. K562 cells transfected with LAPTM5(L) and empty vector (P) were cultured in HBSS conditional media for 6 hrs. On the time point of 0hrs, 3hrs and 6hrs, transfected cells were collected and run Westernblot with the antibody of LC3-II and LC3-I. The ratio of LC3-II/LC3I which represented the extent of autophagy activity decreased in K562/LAPTM5 (L).
LAPTM5 gene suppressed K562 cells' autophagy activity. K562 cells transfected with LAPTM5(L) and empty vector (P) were cultured in HBSS conditional media for 6 hrs. On the time point of 0hrs, 3hrs and 6hrs, transfected cells were collected and run Westernblot with the antibody of LC3-II and LC3-I. The ratio of LC3-II/LC3I which represented the extent of autophagy activity decreased in K562/LAPTM5 (L).
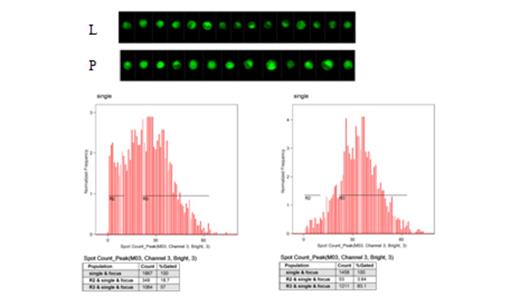
Autophagy activity of K562 transfectants were detected by Flow. K562 cells transfected with LAPTM5(L) had less fluorescent spots than that of K562 transfected with empty vector (P).
Autophagy activity of K562 transfectants were detected by Flow. K562 cells transfected with LAPTM5(L) had less fluorescent spots than that of K562 transfected with empty vector (P).
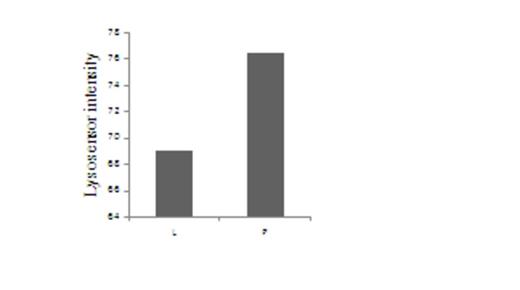
Lysosomal acid decreased in K562 cells transducted with LAPTM5(L). Lysosomal was marked by LysoSensor™ Green DND-189£¨50 nM£©and run Flow cytometry. Fluorescent intensity represented pH value. More intensity means lower pH value.
Lysosomal acid decreased in K562 cells transducted with LAPTM5(L). Lysosomal was marked by LysoSensor™ Green DND-189£¨50 nM£©and run Flow cytometry. Fluorescent intensity represented pH value. More intensity means lower pH value.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal