Abstract
Background: Bortezomib-containing combination chemotherapy regimens are effective in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), although there are limited data on toxicity in the front-line setting for indolent NHL when combined with reduced-dose vincristine-containing chemotherapy. Our group (Sinha et al, Cancer 2012) reported outcomes from a phase I study of bortezomib combined with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, modified vincristine, and prednisone (VR-CHOP) and found a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of bortezomib (V) of 1.6mg/m2 with vincristine capped at 1.5 mg with an overall response rate (ORR) of 100%. Herein we report the results of our phase II study of this regimen.
Patients and Methods: Eligible patients had untreated indolent NHL (small lymphocytic lymphoma [SLL], marginal zone lymphoma [MZL], or follicular lymphoma [FL] grades 1-3) meeting standard criteria for treatment or with FL international prognostic index (FLIPI) ≥3. Patients received V administered at a dose of 1.6mg/m2 on days 1 and 8 as well as rituximab (R) 375mg/m2, cyclophosphamide 750mg/m2, doxorubicin 50mg/m2, and vincristine 1.4mg/m2 (capped at 1.5mg/dose) on day 1 and prednisone 100mg on days 1-5 of a 21-day cycle. Patients received at least 6 cycles and up to 8 cycles of therapy at the discretion of the treating physician. Patients who achieved a complete response (CR) after induction were assigned to receive maintenance R 375mg/m2 every 12 weeks for 2 years while patients with a partial response (PR) or stable disease received R 375mg/m2 along with V 1.6mg/m2 (VR), both administered weekly for 4 weeks every 6 months for up to 2 years. Response was assessed by Cheson 1999 criteria, and toxicity assessed by CTCAE version 3.0. One FL patient discontinued study therapy after cycle 2 when a central pathology review revised the diagnosis to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. This patient was not included in the efficacy analysis but is included in the safety reports. CR rate and ORR were determined at the conclusion of induction therapy, and progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were evaluated by the Kaplan-Meier method from the date of study entry.
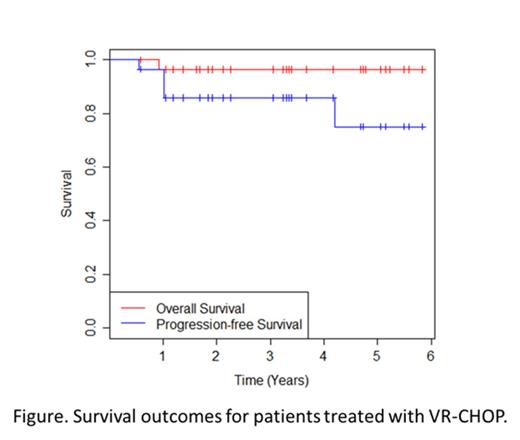
Results: Thirty patients received at least 1 treatment of VR-CHOP, including 16 males and 14 females. The median age was 58 (range: 31-71), and histologies included MZL (n=5), SLL (n=4), and FL (Grade 1, n=7; Grade 2, n=12; Grade 3, n=2). FLIPI score for patients with FL were 1 (n=2), 2 (n=4), 3 (n=12), and 4 (n=3). Twenty-nine were evaluable for response, including 19 patients with CR and 10 patients with PR at the conclusion of induction therapy (CR rate of 66%; ORR of 100%). For 20 evaluable patients with FL, the CR rate was 75%. Twenty-five patients proceeded with maintenance therapy, including 6 patients who received VR and 19 patients who received R alone. Three patients with PR to induction converted to CR after maintenance with VR. Four patients received no maintenance due to refusal/lost to follow-up (n=2), toxicity (n=1), and progression (n=1). Three patients with PR received only R due to neuropathy. Four patients have relapsed or progressed on therapy, including 1 patient prior to starting maintenance, 2 patients during VR maintenance, and 1 patient who achieved a PR but was receiving R maintenance. One additional patient progressed after completing R maintenance. With a median follow-up of 39 months, 3-year PFS rate is 85.8%, and the 3-year OS rate is 96.4% (Figure). Grade ≥3 peripheral neuropathy was noted in 2 patients (7%), while grade 1-2 neuropathy occurred in 17 patients (57%). Grade 3-4 hematologic toxicities included neutropenia (n=14, 47%), thrombocytopenia (n=3, 10%), anemia (n=1, 3%), and febrile neutropenia (n=1, 3%). Eight patients experienced additional grade 3 non-hematologic toxicities, including the following which occurred in more than 1 patient: vomiting (n=3, 10%), abdominal pain (n=2, 7%), fatigue (n=2, 7%), hyperglycemia (n=2, 7%), hypokalemia (n=2, 7%), and nausea (n=2, 7%).
Conclusion: VR-CHOP is highly efficacious in the front-line setting for management of patients with untreated indolent NHL, and toxicities are expected and manageable. Incidence of grade 3 peripheral neuropathy is low with incorporation of a decreased dose of vincristine, and the PFS compares favorably with previously reported outcomes in FL and indolent NHL for R-CHOP, R-Bendamustine, and R-CHOP plus maintenance R.
Cohen:Janssen: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Off Label Use: Bortezomib is not currently approved for follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, or small lymphocytic lymphoma and is being evaluated in combination with a standard induction regimen.. Kaufman:Millennium: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Nastoupil:TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Genentech: Honoraria; Janssen: Research Funding. Lechowicz:Millennium: Consultancy. Lonial:Millennium, Celgene, Novartis, BMS, Onyx: Consultancy, Research Funding. Flowers:Gilead, Spectrum, Millennium, Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene, Prescription Solutions, Seattle Genetics, Millennium (unpaid), Genentech (unpaid) : Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal