Abstract
BACKGROUNDThe combination of ATRA and anthracycline-based chemotherapy has traditionally been regarded as the gold standard for induction and consolidation in previously untreated APL patients (pts), with ATO usually reserved for relapse. Recent data in Sanz low-risk (LR) and intermediate-risk (IR) APL indicate ATRA + ATO is superior to ATRA + chemotherapy (N Engl J Med 2013), but the optimal therapy for high-risk (HiR) pts remains unclear. In an attempt to improve anti-leukemic efficacy whilst limiting reliance on anthracyclines for all risk categories of APL, the ALLG incorporated ATO into an ATRA + reduced chemotherapy backbone, and the results of an interim analysis with a median follow-up of 2 years (yr) have been published (Blood 120:1570, 2012). Herein, we report results of the protocol-specified final analysis, conducted when all surviving pts had been followed for at least 2 yr after completion of consolidation.
METHODS As published, APML4 protocol treatment comprised: (i) induction with ATRA (45 mg/m2 d1-36), IDA (12 mg/m2 d2,4,6,8), ATO (0.15 mg/kg d9-36), prophylactic prednisone (1 mg/kg d1-10) and aggressive hemostatic support; (ii) consolidation with ATRA and ATO (continuous in cycle 1, intermittent in cycle 2); (iii) 2 yr oral maintenance with ATRA, 6-mercaptopurine and methotrexate. Between 2004-2009, 124 evaluable pts were accrued, and median follow-up by the censor-reversing Kaplan-Meier method in this final analysis is 4.2 yr.
RESULTS Median age was 44 (3-78) yr, median white cell count was 2.4 x 109/L (0.1-85.8), and median platelet count 22 x 109/L (2-173). Risk groups were 33 LR, 67 IR, 23 HiR, 1 unknown. FLT3 mutations were present in 44%, and 11% had ≥ 2 additional cytogenetic abnormalities (2+ACA). There were 4 (3.2%) deaths during induction (myocardial infarction d1, cerebral hemorrhage d3 and d7, cerebral edema and seizures d30). Grade 3-4 non-hematological adverse events included differentiation syndrome in 14%, and frequent but reversible biochemical hepatic and gastrointestinal toxicity. Q-Tc prolongation > 500 msec occurred in 14%, but there were no cases of ventricular arrhythmias or torsades de pointe. Significant neurological and cutaneous toxicity were infrequent.
After induction, 118 pts (95%) achieved hematological complete remission; 112 commenced consolidation, and all were in molecular remission after cycle 2. A total of 5 relapses and 3 deaths have occurred post-induction, but none of the deaths were attributable to protocol therapy. Severe adverse events were less common during the chemotherapy-free consolidation cycles, especially cycle 2. The frequency of grade 3-4 neutropenia was 62% in cycle 1 and 27% in cycle 2, but there was no grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia.
The following table lists event-free survival (EFS), disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS) and cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR):
| . | All pts . | LR . | IR . | HiR . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . |
| EFS | 92% | 90% | 97% | 97% | 93% | 89% | 83% | 83% |
| DFS | 97% | 95% | 100% | 100% | 97% | 93% | 95% | 95% |
| OS | 94% | 94% | 97% | 97% | 96% | 96% | 87% | 87% |
| CIR | 3% | 5% | 0% | 0% | 3% | 7% | 5% | 5% |
| . | All pts . | LR . | IR . | HiR . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . | 2 yr . | 5 yr . |
| EFS | 92% | 90% | 97% | 97% | 93% | 89% | 83% | 83% |
| DFS | 97% | 95% | 100% | 100% | 97% | 93% | 95% | 95% |
| OS | 94% | 94% | 97% | 97% | 96% | 96% | 87% | 87% |
| CIR | 3% | 5% | 0% | 0% | 3% | 7% | 5% | 5% |
In univariate analysis, 2+ACA predicted for inferior DFS (P = .04), whereas age > 70 was associated with increased risk of early death (ED, P = .02), inferior EFS (P = .0002), and inferior OS (P = .001). Neither Sanz risk category nor FLT3 mutation status was significantly correlated with these outcome endpoints (all P > .05). In multivariate analysis, the significant associations of 2+ACA (P = .04 for DFS) and age > 70 (P = .0002 for EFS, P = .005 for OS) were retained. In addition, Sanz risk category was correlated with EFS (P[trend] = .003) and OS (P[trend] = .02).
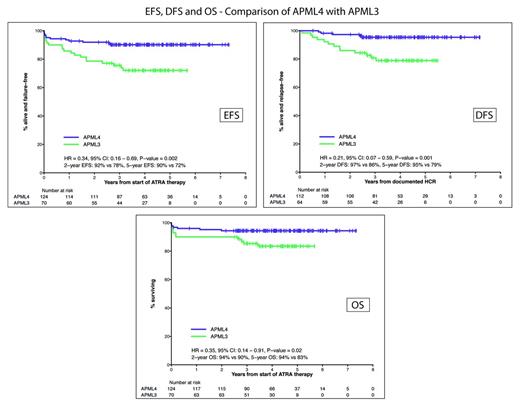
When compared with our previous ALLG APML3 trial (ATRA + IDA for induction and consolidation without ATO; Haematologica 2012), treatment with APML4 was associated with substantial and statistically significant improvements (see Figure) in EFS (P = .002), DFS (P = .001) and OS (P = .02). The significance of trial assignment was retained in multivariate analysis when APML3 and APML4 data were combined.
CONCLUSIONS APML4 is a potent anti-leukemic regimen with manageable toxicity and a low ED rate. EFS and OS remain impressive with mature follow-up, and were influenced primarily by advanced age and Sanz risk category. The CIR was 5%, and was only associated with 2+ACA. Our results support the inclusion of ATO in induction and consolidation as front-line therapy for APL whilst simultaneously limiting cumulative anthracycline exposure.
Off Label Use: Arsenic trioxide is currently only registered in the US, Europe and Australia for the treatment of relapsed APL. This report includes its use in the initial treatment of APL.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal