Abstract
Introduction: The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) has proved to be an effective targeted therapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). A multicenter phase Ib/II study of ibrutinib in 85 patients with relapsed CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) showed the overall response rate of 71% with an additional 15 to 20% of patients having a partial response with lymphocytosis. A phase II trial of ibrutinib in combination with rituximab in 40 high-risk CLL patients conducted at MD Anderson Cancer Center demonstrated an overall response rate of 95%. However efficacy of ibrutinib in combination with rituximab vs. ibrutinib alone has not been directly compared. A randomized study of ibrutinib vs. ibrutinib+rituximab in patients with relapsed CLL was designed to compare long-term progression free survival rate in two groups (NCT02007044). Here we test a hypothesis that addition of rituximab may abrogate ibrutinib-induced lymphocytosis and accelerate response of other biomarkers, including plasma levels of chemokines CCL3 (MIP-1a) and CCL4 (MIP-1b), which are known to reflect the activation status of CLL cells.
Methods: Patients were randomized to ibrutinib alone (arm A) or ibrutinib plus rituximab arm (arm B). Patients on arm A were treated with ibrutinib 420 mg orally once daily continuously throughout the study. Patients randomized to arm B received ibrutinib starting at day 1 or day 2. Rituximab (375 mg/m2) was administered intravenously on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 (cycle 1), then monthly during cycles 2-6. Study inclusion required previously treated CLL/SLL or treated or untreated high-risk disease (del17p or TP53 mutation). Serial blood samples were drawn at pre-treatment, then weekly during the first month, and monthly until 5/6 months. Plasma levels of CCL3 and CCL4 were measured at pre-treatment, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months and 5 months of follow-up by ELISA. A linear mixed effects model with randomly varying intercepts and slopes was constructed for each absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) measured repeatedly over time using SAS PROC MIXED. Models included an unstructured covariance and the Kenward-Rogers degrees of freedom adjustment to take into account unequally spaced unbalanced data. Models over at least 4 months of measurements included both linear and quadratic components.
Results: Accrual began in December 2013; currently 93 of 208 patients are enrolled. 45 patients (48%) were randomized to arm A and 48 (52%) to arm B.
Median ALC at pre-treatment was similar on both arms (26.28 and 25.14 K/µl). A mixed model with quadratic trend was used to assess the dynamic changes in ALC during the first month of treatment. The model confirmed a curvature pattern for arm A, consistent with lymphocytosis: ALC rose immediately after initiation of treatment and then began to stabilize. In arm B, however, no statistically significant changes in ALC were observed during this initial period.
To appreciate the difference between two treatment arms over a longer time period, changes in ALC were analyzed in the 52 patients who had 4 or more months of follow-up. A mixed model with a quadratic trend demonstrated ALC downward trend for both arms, with a more rapid decrease in arm B (p=0.03 for the linear component; p=0.004 for the quadratic). The curvature in ALC reflecting initial lymphocytosis was clear in arm A, but not arm B. Descriptive analysis suggested that arm B had higher percentage of patients with normal (<5 K/µl) or normalizing (<10 K/µl) ALC following 4 and 5 months of treatment.
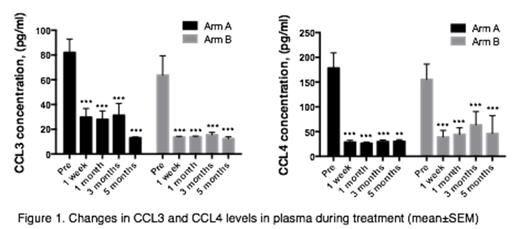
Concentration of CCL3 and CCL4 was significantly reduced after one week of treatment on both arms and remained low (Figure 1). Formal statistical comparison of CCL3 and CCL4 patterns is in process.
Conclusion: In this randomized evaluation of ibrutinib vs. ibrutinib+rituximab an initial analysis suggests that addition of rituximab to ibrutinib abrogates the transient lymphocytosis and is associated with faster clearing of the bloodstream of leukemia cells in patients with relapsed CLL. Significant reduction of CCL3 and CCL4 levels was observed on both treatment arms.
Kipps:Pharmacyclics: Research Funding. O'Brien:Pharmacyclics, Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Burger:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal