Abstract
Background: MCL is B-cell neoplasm diagnosed predominantly among older men. (R)CHOP-like regimens demonstrated high response rate, but the event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) are disappointingly short - 16-20 months and 3-4 years, respectively. An addition of high-dose AraC (12 g/m2) to the upfront therapy and autoSCT have significantly improved outcomes but remain feasible largely for younger and medically fit patients. Based on the activity and good tolerance of gemcitabine-oxaliplatin combinations in relapsed and refractory MCL patients, we developed an alternative first-line regimen for patients who are not candidates for R-HD-MTX-AraC (R-HMA). We presented an initial data of our pilot protocol at ASH 2012 (#2043). According to the protocol patients who had renal insufficiency and/or experience prohibitive toxicity following the first course of R-EPOCH, were assigned to receive R-EPOCH/R-GIDIOX regimen, while others were treated with R-EPOCH/R-HMA regimen. Both arms received consolidative autoSCT followed by R-maintenance.
Aim: Assess toxicity and efficacy of R-DA-EPOCH/R-HMA and R-DA-EPOCH/R-GIDIOX in untreated MCL patients eligible for autoSCT.
Patients and Methods: 47 untreated MCL patients from 6 centers were enrolled in prospective study between May 2008 - Sep. 2013; stage II-IV; ECOG 0-3; median age 55 years (29-64); M/F 76%/24%; MIPIb: 28% low, 33% intermediate and 39% high risk. Following 1st R-EPOCH patients were assigned to receive either R-DA-EPOCH/R-HMA or R-DA-EPOCH/R-GIDIOX regimen. In the absence of hematological toxicity gr. 4, severe infections and renal failure patients received R-HMA (R 375 mg/m2 d1, MTX 1000 mg/m2/24 hours d 2, AraC 3000 mg/m2 q 12 hrs d 3-4). Patients who experienced at least one of the complications above received R-GIDIOX (R 375 mg/m2 d 1, gemcitabine 800 mg/m2 d 2 and 5, oxaliplatin 120 mg/m2 d 3, irinotecan 100 mg/m2 d 4, dexamethasone 10 mg/m2 IV d 2-6, ifosfamide 1000 mg/m2 d 2-6). Subsequently these courses were alternating with R-DA-EPOCH in each arm of the protocol. Patients who achieved CR after the first cycle (2 courses), received additional 2 cycles, (for a total 6 courses). Patients without CR after 2 cycles of therapy received 2 more cycles, for total of 8 courses, unless they progressed on therapy. Those patients who achieved PR/CR/CRu underwent autoSCT (BEAM-R). Response the therapy was assessed by Cheson's criteria (2007). Patients with residual PET+ tumor after autoSCT were consolidated with local radiotherapy. Post-transplant R- maintenance was administered for 3 years (R-375 mg/m2 every 3 months). Patients were analyzed on an intent-to-treat basis.
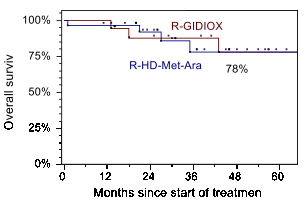
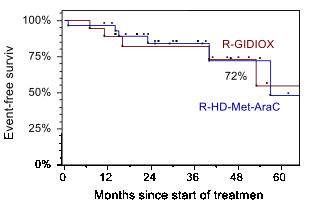
Results: 29/47 patients were treated on R-HMA arm (Arm1) (median 51years; MIPIb: 35,7% low, 28,6% intermediate and 35,7% high risk) and 18/47 patients were on R-GIDIOX arm (Arm2) (median 60 years; MIPIb: 16,7% low, 38,9% intermediate and 44,4% high risk). There was 1/29 induction death after first R-HMA course (acute renal failure and septic shock). 1 of 18 patients had disease progression before autoSCT in Arm2. 28/29 patients from Arm1 achieved CR/CRu (96,6%). In Arm 2 OR and CR/CRu rates were 94,4% (17/18) and 77,8% (14/18), respectively. Main non-hematological toxicity of R-GIDIOX was asymptomatic elevation of transaminases (gr. 1-2 and 3-4 in 65,5% and 6,9% of courses respectively), while leukopenia gr. 4 occurred in 74,1% of courses (median 5 days, range 1-13), thrombocytopenia gr. 4 -39,7% courses. 45/47 patients underwent autoSCT: 28/29 in Arm1 and 17/18 in Arm2. The sources of stem cells were PBSC in 39/45 patients (86,7%) and BM in 6/45 (13,3%) patients with PBSC collection failure following R-HMA (3/28) or R-GIDIOX (3/17). With median follow-up of 31 months (range 11-76), the estimated 4-year OS and EFS remain identical in both groups: 78% (SE 12%) and 72% (SE 18%), respectively.
Conclusions: Combination of R-DA-EPOCH/R-GIDIOX followed autoSCT and R-maintenance is well tolerated and produces EFS/OS similar to those seen with more toxic regimen utilizing R-HD-MTX-AraC. Equal outcomes were observed despite higher proportion of high risk patients treated with non-HD-AraC regimen. We conclude that R-GIDIOX can be an alternative component of induction regimen for those patient with MCL who are not candidates for intensification with high-dose AraC and MTX.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal