Abstract
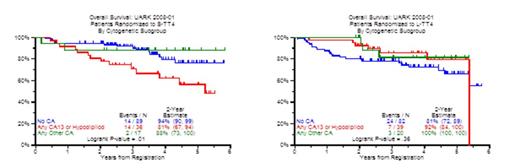
In recognition of the lack of progress in GEP70 high-risk CMM, we decided in 2008 to assign low and high risk patients to TT4 and TT5, respectively. In TT4, we elected to examine in a phase 3 trial, to determine whether L-TT4 was associated with lesser toxicity by reducing induction prior to and consolidation cycles after tandem transplants from 2 cycles each in S-TT4 to 1 cycle in L-TT4. To compensate for potentially reduced efficacy by this strategy in L-TT4, the transplant regimen was altered from a single melphalan dose of 200mg/m2 (MEL200) to a fractionated 50mg/m2/d x 4d (MEL50x4) schedule in L-TT4 with the addition of bortezomib and thalidomide (VTD) to exploit synergism between MEL50x4 and VTD. Two-hundred eighty nine patients were randomized (S-TT4, n=145; L-TT4, n=144) and stratified by ISS stage, presence of metaphase cytogenetic abnormalities (CA). With a median follow-up of 38.9m in both arms, 115 and 110 patients remain alive on S-TT4 and L-TT4, respectively. Two-year overall survival (OS) estimates are 90% and 87%; the corresponding PFS estimates are 84% and 80%. At the time of analysis, 91 and 92 achieved CR status, with 2-year CR duration estimates of 87% and 82% (P=0.06). Causes of death (COD) were divided into MM-related mortality (MRM), treatment-related (TRM) and “other/indeterminate” (OIM); at 2y, the relative COD estimates for the 3 groups were 2.1%/6.2%/1.4% for S-TT4 and 5.6%/5.6%/2.1% for L-TT4 (P=0.886/0.735/0.378). Grade 3 or higher non-hematological toxicities were similar between the 2 arms (GI: 39%/32%; Cardiac :22%/20%, infection: 8%/9%). Next we analyzed S-TT4/L-TT4 outcomes in the context of [anm1] metaphase cytogenetic abnormalities (CA). As depicted in Figure 1, a reversal of the CA implications in the 2 arms were observed. With S-TT4, both OS and PFS were inferior in with the chromosome 13 abnormalities or hypodiploidy (with patients having no CA or other CA (virtual all hyperdiploidy) having superior outcome (OS: P=0.01, PFS: P=0.06). With L-TT4, patients with no CA seemed to fare worse in terms of OS and PFS, but the differences did not reach statistical significance. There was a trend towards shorter 2-yr CR duration with L-TT4 visa S-TT4 (82% vs 87%, p=0.06) 2-Year estimate of time to relapse from CR was 8.1% in S-TT4 versus 11.5% in L-TT4 (p=0.07). Overall, the early results of this randomized study suggest that toxicities were similar on both arms. Trends for shorter CR duration and time to relapse from CR were seen in L-TT4. S-TT4 seems to benefit patients with no CA or other CA in terms of OS and PFS. Conversely patients with no CA fared worse with the fractionated MEL-approach although statistical difference was not yet observed.
van Rhee:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millenium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal