Key Points
A conserved enhancer, needed for Bcl11b expression in early T cells and developmentally activated in parallel with it, lies 850 kb downstream.
This enhancer binds TCF-1 and loops to the differentially methylated Bcl11b promoter to mediate lineage-specific activation and silencing.
Abstract
Bcl11b is a T-cell specific gene in hematopoiesis that begins expression during T-lineage commitment and is required for this process. Aberrant expression of BCL11B or proto-oncogene translocation to the vicinity of BCL11B can be a contributing factor in human T-ALL. To identify the mechanism that controls its distinctive T-lineage expression, we corrected the identified Bcl11b transcription start site and mapped a cell-type–specific differentially methylated region bracketing the Bcl11b promoter. We identified a 1.9-kb region 850 kb downstream of Bcl11b, “Major Peak,” distinguished by its dynamic histone marking pattern in development that mirrors the pattern at the Bcl11b promoter. Looping interactions between promoter-proximal elements including the differentially methylated region and downstream elements in the Major Peak are required to recapitulate the T-cell specific expression of Bcl11b in stable reporter assays. Functional dissection of the Major Peak sequence showed distinct subregions, in which TCF-1 sites and a conserved element were required for T-lineage–specific activation and silencing in non-T cells. A bacterial artificial chromosome encompassing the full Bcl11b gene still required the addition of the Major Peak to exhibit T-cell specific expression. Thus, promoter-proximal and Major Peak sequences are cis-regulatory elements that interact over 850 kb to control expression of Bcl11b in hematopoietic cells.
Introduction
Bcl11b is a major regulator of T-cell development and immune functions of mature T cells. It is required from early in the CD4- CD8- (DN) thymocyte stages. At lineage commitment, between DN2a (Kit++ CD44+ CD25+ DN) and DN2b (Kit+ CD44+ CD25+ DN), Bcl11b is required to repress self-renewal and alternative lineage developmental potentials, to make the T-cell fate the only remaining developmental choice. Deletion of Bcl11b from prethymic precursors causes a developmental block at this checkpoint with extensive proliferation possible for the uncommitted cells.1,2 The blocked Bcl11b-deficient cells have increased potential to differentiate into Natural Killer (NK) cells and myeloid cells.1-3 Later in development at the DN3 stage, Bcl11b is required for the final steps of recombination and surface expression of TCRβ.4 Bcl11b is also essential for positive selection of both CD4+ and CD8+ single positive (SP) cells and for survival of double positive (DP) cells.5 Removal of Bcl11b from mature CD8+ cells results in defects in antigen-specific clonal expansion and CD8+ cell function.6 In regulatory T cells, Bcl11b may also be involved in the development and function of these cells by positively regulating Foxp3.7
The expression of Bcl11b is strictly T-lineage specific among hematopoietic cells,3,8 making Bcl11b a T cell identity gene. In the T lineage, Bcl11b is still silent in the Early T-cell Precursor (ETP)/Kit+ DN1 stage (Kit++ CD44+ CD25- DN), and only starts to express at DN2a stage.8 After this point, the expression of Bcl11b is detectable in every stage and every lineage of T cells. Bcl11b is one of only a few genes in the genome with onset of expression at this crucial stage.9
The correct triggering of Bcl11b expression in DN2a cells may also be important for inhibiting oncogenic transformation of these rapidly dividing cells. The earliest studies on Bcl11b identified it as a tumor suppressor, because mutations and deletions of Bcl11b by γ-irradiation in mouse models could result in immature thymocyte transformation, T cell leukemia, and thymic lymphomas.10 In human T cell leukemia, deletion and mutation of BCL11B even in heterozygous form have been proposed to play roles in many cases of T-ALL.11-13 However, noncoding sequences linked with the BCL11B locus may also contribute to its oncogenic function.11,14,15 Studies of cancer cells from T-ALL patients identified BCL11B as the translocation partner of TLX3 and NKX2-5 in t(5;14)(q35;q32.2) T-ALL.12,16 The translocation actually juxtaposes TLX3 and NKX2-5 to a gene desert 3′ of BCL11B (relative to the direction of BCL11B transcription) and causes ectopic expression of these oncogenes, leading to T-ALL. Although the mechanism that activates TLX3 and NKX2-5 is unknown, it has been proposed that cis-regulatory elements of BCL11B could underlie this oncogenic activity.14,15 Clearly the translocation enables these oncogenes to acquire a T-cell specific enhancer, but its relationship to BCL11B regulation has been only conjectural. Therefore, identifying genetic inputs that activate the expression of Bcl11b in DN2a cells will offer insight into both T-lineage commitment and oncogenesis linked to Bcl11b.
In this report, we aimed to identify the cis-regulatory elements that control the unique expression pattern of Bcl11b. We first determined the actual transcription start site (TSS) of Bcl11b in developing T cells, mapping it within a cell-type specific differentially DNA methylated region (DMR) of the promoter area of Bcl11b. However, this region is insufficient to promote T-cell specific gene expression. Based on cell-type specific and stage-specific histone modifications in developing early T cells, we discovered a 1.9-kb sequence located about 850-kb downstream of Bcl11b that mirrored the same developmentally regulated histone marks as the promoter of Bcl11b in early T cells. This downstream putative cis-regulatory element was needed to cooperate with promoter-linked and intragenic elements to drive T cell specific expression of reporter genes in stable transfection assays. The studies thus map the core sequence of the Bcl11b promoter plus a key T-cell specific downstream enhancer, providing a molecular basis for the further understanding of Bcl11b regulation in developing T cells and in T cell leukemia.
Materials and methods
P2C2 (SCID.adh2C2), 32D, and Raw264.7 cells were cultured and transfected with a series of Bcl11b-sequence linked luciferase and yellow fluorescent protein (mCitrine, YFP) reporter constructs as described herein.17,18 DNA methylation was measured by bisulfite-DNA-sequencing. Major Peak (MP) mutations were generated by fusion PCR with primers shown in supplemental Table 1 (available on the Blood Web site). Long-range DNA interaction was measured by Chromatin Conformation Capture assay.19,20 Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) reporters were generated by recombineering.21,22 Accession number for TCF-1 ChIP-seq data: GSE46662. Detailed methods are given in supplemental Materials and methods. In one figure, cells were used from mouse thymus and spleen. These animals were bred and maintained in our colony at Caltech and were used entirely according to Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee-approved protocols.
Results
Identification of the Bcl11b TSS
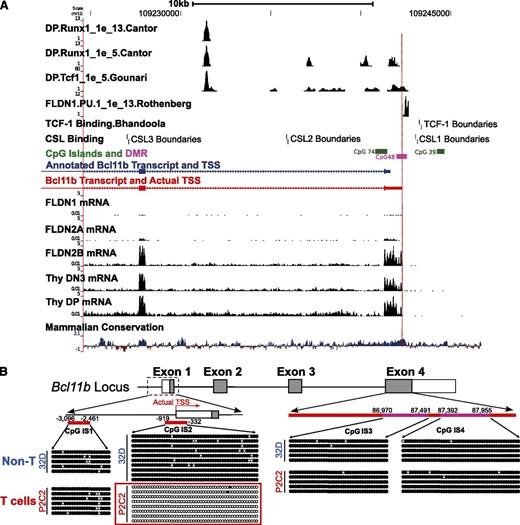
The expression pattern of Bcl11b in hematopoietic cells and its mRNA levels in early T cells have been extensively analyzed. Microarray (http://www.immgen.org), qPCR,8,23 and RNA-seq9 results confirm that Bcl11b is a T-cell specific gene. In T-lineage development, it starts to express in DN2a cells, and the mRNA signals reach high levels in DN3 cells, including Rag2−/− DN3 thymocytes and DN3-like P2C2 cells. The Bcl11b promoter region is rich in sites for regulatory inputs from Notch, Runx, and TCF factors (Figure 1A).3,9,24-26 However, RNA-seq analysis of early T cells9 showed that the actual start of the Bcl11b transcripts is about 640 bp upstream of the TSS annotated in RefSeq and the Mouse Genome Informatics Jax representative transcript (Figure 1A). To avoid confusion on base positions, however, in this paper we still refer to the annotated RefSeq TSS (mm9, chr12:1009241624) as +1 of the Bcl11b gene for all DNA sequences studied here, setting the true TSS at −640.
Identification of transcription start site and a differentially methylated region in the 5′-flanking area of Bcl11b. (A) RNA-seq on early T cells identified the actual TSS (red) of Bcl11b transcripts, which is about 640 bp upstream of the annotated one (blue). RNA-seq data from ref. 9, transcription factor binding sites from refs. 3, 9, 24,-26. (B) The DNA methylation of three CpG islands on the Bcl11b locus was measured by bisulfite-DNA sequencing. IS1, CpG island 1. IS2, CpG island 2. IS3 and IS4, 2 representative regions on CpG island 4. Because of technical issues, the methylation of an additional CpG island in intron 2 was not analyzed. The closed dots represent methylated CpG sites, and the open dots represented unmethylated sites. The positions of the CpG islands are relative to the annotated TSS of Bcl11b.
Identification of transcription start site and a differentially methylated region in the 5′-flanking area of Bcl11b. (A) RNA-seq on early T cells identified the actual TSS (red) of Bcl11b transcripts, which is about 640 bp upstream of the annotated one (blue). RNA-seq data from ref. 9, transcription factor binding sites from refs. 3, 9, 24,-26. (B) The DNA methylation of three CpG islands on the Bcl11b locus was measured by bisulfite-DNA sequencing. IS1, CpG island 1. IS2, CpG island 2. IS3 and IS4, 2 representative regions on CpG island 4. Because of technical issues, the methylation of an additional CpG island in intron 2 was not analyzed. The closed dots represent methylated CpG sites, and the open dots represented unmethylated sites. The positions of the CpG islands are relative to the annotated TSS of Bcl11b.
Promoter-spanning sequence from −919 bp to −332 bp at the Bcl11b locus is a cell-type specific differentially methylated region (DMR)
DNA methylation of CpG islands is involved in transcriptional silencing of many developmentally important genes and can be removed selectively at sites where cell-type specific factors exert differential regulation.27-29 Several major CpG islands occur in the Bcl11b locus. To identify sites that may be specifically targeted for demethylation during T lineage-specific activation of the gene, we measured DNA methylation across four CpG islands by bisulfite-DNA sequencing. We compared P2C2 cells, which are Bcl11b-expressing DN3-like T lineage cells, with an immature myeloid cell line, 32D, that does not express Bcl11b. The methylation of the CpG island encompassing the actual TSS of Bcl11b, IS2, showed a cell-type specific pattern, highly methylated in immature myeloid 32D cells but unmethylated in the early T-lineage P2C2 cells (Figure 1B). In contrast, the further upstream CpG island in the 5′-flanking region (IS1) and the two regions in the CpG island in exon 4 (IS3, IS4) are all highly methylated in P2C2 and 32D cells alike. In accord with our data, Ji et al30 also found that the Bcl11b promoter-proximal region becomes demethylated at the DN2 and DN3 stage of T-cell development, based on a genome-wide mapping approach (http://aryee.mgh.harvard.edu/data/charm_hsc). Thus, the −919 bp to −332 bp region, spanning the actual promoter, is a cell-type specific DMR for Bcl11b.
The Bcl11b promoter-DMR alone is not sufficient to drive T-cell specific expression of reporter genes
We used the TSS-associated DMR and regions of high sequence conservation as a starting point to map the sequences functionally required for the T-lineage specific expression of Bcl11b (supplemental Figure 1). Predicted sites for transcription factors likely to regulate Bcl11b expression, positively or negatively, were also specifically considered: GATA-3,31 TCF-1,26 Notch/RBPJκ,3 and PU.132 (Figure 1A). To test transcriptional regulatory function of the DMR, we cloned candidate Bcl11b promoter regions into pGL3-Basic, a promoter-less and enhancer-less luciferase reporter, and measured luciferase activity after transient or stable transfections of the vectors into P2C2 cells and Raw264.7 cells. Stable transfection gives greater cell-type specificity in gene regulation, more robust results, and greater dynamic range than transient transfection using these cell lines.17,18 In this assay, constructs beginning at the annotated Bcl11b promoter (supplemental Figure 3: PR1 and PR2) were inactive in both P2C2 and Raw264.7 cells. However, even with the Bcl11b DMR and true TSS included (PR3), the promoter lacked activity. Further analysis of the 10-kb DNA sequence upstream of Bcl11b identified three conserved regions (supplemental Figure 1A: CS1, CS2, and CS3). These conserved sequences were cloned into pGL3-Basic reporter with the Bcl11b DMR-promoter in different combinations and tested in P2C2 and Raw264.7 cells. However, as shown in supplemental Figure 2 and 3, none of these constructs activated luciferase in a T-cell specific way, suggesting that elements from the 5′-flanking region of Bcl11b are not sufficient to recapitulate the Bcl11b expression pattern.
The 5-kb 3′-UTR of Bcl11b is one of the most conserved regions on mouse chromosome 12, and it is predicted to be a target of several microRNAs (supplemental Figure 4A). To test whether mRNA stability regulated by miR-3′-UTR interaction contributed to the cell-type specific regulation of Bcl11b, the Bcl11b 3′UTR was cloned into the pGL3-Control vector into the 3′ untranslated region of the luciferase reporter (supplemental Figure 4B), and was tested by stable transfection into P2C2 and Raw264.7 cells. However, inclusion of the Bcl11b conserved 3′-untranslated sequences did not increase the T-lineage specificity of expression, as it did not specifically reduce luciferase expression in the non-T Raw264.7 cells (supplemental Figure 4C).
A downstream region shares with the Bcl11b promoter developmental stage-specific and cell-type specific histone modification marks
As these elements in or near the Bcl11b locus were insufficient to recapitulate its expression pattern, we searched for potential cis-regulatory elements in a larger area. There is a 2-Mb gene desert downstream of Bcl11b, relative to the direction of Bcl11b transcription, without any annotated protein-coding genes. Further upstream of Bcl11b, by contrast, are multiple constitutively expressed genes, separated from the Bcl11b locus even in Bcl11b-expressing T-lineage cells by a block of chromatin with H3K27me3 marks, suggesting polycomb-complex mediated repression or barrier function.9 We therefore sought loci across the downstream gene desert where histone modification marks H3Ac, H3K4me2, and H3K27me3 might correlate developmentally with those on the Bcl11b locus itself. A 1.9-kb region ∼850 kb downstream of Bcl11b was the most significant T-lineage histone modification peak in this 2-Mb gene desert. Conspicuously, this “Major Peak” shares the same histone modification marks as the promoter region of Bcl11b, not only in cell-type specificity, but also in the dynamics of developmental activation (Figure 2).9 In DN1 stage, before cells turn on Bcl11b, Bcl11b promoter chromatin lacks histone H3Ac or H3K4me2, but is enriched for the repressive mark H3K27me3. In DN2b cells, which express high levels of Bcl11b, the promoter shows high levels of H3Ac and H3K4me2, whereas H3K27me3 is specifically removed. In parallel, the active histone marks on Major Peak increase from DN1 to DN2b, whereas the repressive histone marks decrease (Figure 2A). Comparing the histone marks on Bcl11b and Major Peak regions in different hematopoietic cells, we found H3Ac on Bcl11b promoter and Major Peak specifically restricted to Bcl11b-expressing T cells, whereas the repressive mark H3K27me3 was concentrated on both regions in cell types that do not express Bcl11b, such as pre-proB cells (Figure 2B).33 In human mature CD4+ T cells with BCL11B expression, the histone marks on Major Peak also mirror those on BCL11B locus (supplemental Figure 5).34 H3K4Me1, an enhancer-associated histone mark, was well enriched on the Major Peak locus in human CD4+ T cells, but not in human cell lines without BCL11B expression (ENCODE lines Gm12878 and H1 ES cells) (supplemental Figure 5).35 An EST or LincRNA from this region has been reported (Gm16084). However, tissue specific enhancers are often sites of low-level RNA transcription correlated with activity.36
Histone modifications identify a far downstream Major Peak that shares with the Bcl11b promoter its patterns of histone marks. (A) Distinct epigenetic modification and gene expression patterns at the genomic region spanning Bcl11b and several downstream and upstream gene loci in T-cell precursors from DN1 to DN2b.9 Black arrow: Major Peak. The Major Peak displays similar dynamics of epigenetic modifications as Bcl11b. H3Ac: blue, H3K4me2: red, H3K27me3: green, RNA-seq: black. (y-axis units in RPM). (B) Epigenetic modification patterns at the same genomic region in EBF−/− pre-pro B cells.33
Histone modifications identify a far downstream Major Peak that shares with the Bcl11b promoter its patterns of histone marks. (A) Distinct epigenetic modification and gene expression patterns at the genomic region spanning Bcl11b and several downstream and upstream gene loci in T-cell precursors from DN1 to DN2b.9 Black arrow: Major Peak. The Major Peak displays similar dynamics of epigenetic modifications as Bcl11b. H3Ac: blue, H3K4me2: red, H3K27me3: green, RNA-seq: black. (y-axis units in RPM). (B) Epigenetic modification patterns at the same genomic region in EBF−/− pre-pro B cells.33
Chromatin conformation capture identifies direct T-lineage specific interactions between the Bcl11b promoter and Major Peak regions
We tested whether Major Peak physically interacts with Bcl11b in early T-lineage cells using chromatin conformation capture (3C) assays (Figure 3A). A series of forward primers was designed across the Bcl11b locus with a series of reverse primers spanning the Major Peak (Figure 3B; sequences in supplemental Table 1). As negative controls, we evaluated interaction between sequences around the Major Peak and its neighbor on the opposite site, Vrk1, between Major Peak and the coinduced T-cell specific Cd3gde gene cluster, and between Bcl11b and known cis-regulatory elements of the Sfpi1 locus (supplemental Figure 6). The assays identified several interactions between the Bcl11b promoter and first intron region (F3) and the Major Peak (R4), with possible additional contacts involving the 5′ flanking region of Major Peak (R3) and first intron sequences of Bcl11b near a second major TCF-1 binding peak (R5). In contrast, interactions between Major Peak and Vrk1, between Major Peak and Cd3gde, and between Bcl11b and Sfpi1, were at levels similar to background controls with unligated DNA (supplemental Figures 6 and 7; Figure 3A). The interactions between Bcl11b and Major Peak were considerably stronger in T-lineage cells than in myeloid or nonhematopoietic cells (Figure 3A, P < .02, Mann-Whitney U test), and T-cell specific interactions were hinted also to involve sequences in Bcl11b intron 3 (F14-18), another site of expression-linked histone marking.9 Apparent lineage-nonspecific interactions at particular sites, for example, between F5 and R5, could be traced to cross-reactions of specific pairs of primers with other loci in genomic DNA (see supplemental Methods). Thus, despite the 850-kb separation, a structural basis exists in T-lineage cells to allow Major Peak to participate in Bcl11b transcriptional regulation.
T-cell specific chromatin looping between Bcl11b and the downstream Major Peak. (A) Chromatin conformational capture was performed on samples from T-lineage cells (B6 thymocytes, Rag1−/− or Rag2−/− thymocytes, P2C2 cells) and non-T cells (Rag1−/− or Rag2−/− splenocytes, Raw264.7 cells and NIH3T3 cells) to measure the physical interactions between Bcl11b and Major Peak regions. Rag-knockout thymocytes were included as naturally arrested DN3 thymocyte populations, the in vivo equivalent of P2C2 pro-T cells. Panels show the PCR signals resulting from linkage between the R3, R4, and R5 primers within the Major Peak region and the indicated forward primers spanning the Bcl11b promoter and first two introns. For schematics and controls, see supplemental Figures 6 and 7; sequences presented in supplemental Table 1. P values for cell-type specificity were calculated by Mann-Whitney U test, comparing the five independent T-lineage samples with the four indicated non-T samples; *P < .02. The lineage nonspecific R5-F5 signal is caused by a background anomaly with this specific primer combination. Additional negative controls, samples of normal and Rag-knockout thymocytes processed for 3C without addition of ligase (“unligated”), are shown for reference. (B) Map of positions of primers used.
T-cell specific chromatin looping between Bcl11b and the downstream Major Peak. (A) Chromatin conformational capture was performed on samples from T-lineage cells (B6 thymocytes, Rag1−/− or Rag2−/− thymocytes, P2C2 cells) and non-T cells (Rag1−/− or Rag2−/− splenocytes, Raw264.7 cells and NIH3T3 cells) to measure the physical interactions between Bcl11b and Major Peak regions. Rag-knockout thymocytes were included as naturally arrested DN3 thymocyte populations, the in vivo equivalent of P2C2 pro-T cells. Panels show the PCR signals resulting from linkage between the R3, R4, and R5 primers within the Major Peak region and the indicated forward primers spanning the Bcl11b promoter and first two introns. For schematics and controls, see supplemental Figures 6 and 7; sequences presented in supplemental Table 1. P values for cell-type specificity were calculated by Mann-Whitney U test, comparing the five independent T-lineage samples with the four indicated non-T samples; *P < .02. The lineage nonspecific R5-F5 signal is caused by a background anomaly with this specific primer combination. Additional negative controls, samples of normal and Rag-knockout thymocytes processed for 3C without addition of ligase (“unligated”), are shown for reference. (B) Map of positions of primers used.
The Major Peak is a T-cell specific enhancer of Bcl11b
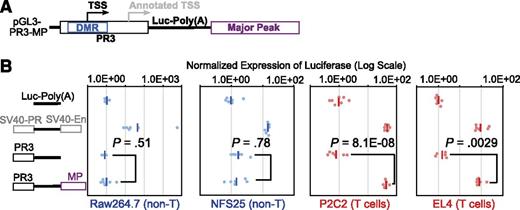
To determine whether Major Peak interacts functionally with the Bcl11b promoter, we tested its impact on activity of other possible Bcl11b regulatory sequences. Starting with a pGL3-Basic construct with the DMR-promoter region (PR3) driving expression of luciferase (supplemental Figure 3), the Major Peak sequence was inserted, downstream of the SV40-poly(A) addition site of the luciferase reporter, to rule out any activity that it might mediate as an alternative promoter (Figure 4A). The Major Peak also covers only a 5′ fraction of the region transcribed into Gm16084, so that any regulatory functions that might be mediated through the full noncoding RNA transcript itself would not be supported either. Stable transfection of these constructs into two T cell lines, P2C2 and EL4, now yielded high expression levels of luciferase reporter, at least 10-fold higher than expression from PR3 promoter alone, and comparable to the levels of the construct with a positive control enhancer (pGL3-Control) (Figure 4B). In contrast, when the constructs were stably transfected into two non-T cell lines, the macrophage Raw264.7, and the pre-B NFS25 cells, the Major Peak did not enhance the expression of luciferase reporter above the basal levels from the PR3 promoter alone. Furthermore, Major Peak could activate T-lineage expression from PR3 but not from PR1, the annotated promoter lacking the DMR, or from an SV40 promoter (Figure 5). Thus, the Major Peak confers T-lineage transcriptional activity specifically on the Bcl11b promoter-DMR.
Major Peak drives T-cell specific expression of luciferase in stable transfection assays. (A) The PR3 sequence of Bcl11b promoter region and Major Peak were cloned into the pGL3-Basic vector. (B) pGL3-Basic, pGL3-Control (SV40-PR; SV40-En), PR3, PR3-MP constructs were stably transfected into Raw264.7, NFS25, P2C2, and EL4 cells with pTracer-Renilla luciferase construct. The firefly luciferase activities were normalized to Renilla luciferase activities. The Normalized Expression was calculated by designation of the geomean of pGL3-Basic as 1 unit. •, relative firefly luciferase activities normalized by Renilla luciferase activities. -, geomeans of the data points in the same sample. Data shown are from one experiment representative of 3.
Major Peak drives T-cell specific expression of luciferase in stable transfection assays. (A) The PR3 sequence of Bcl11b promoter region and Major Peak were cloned into the pGL3-Basic vector. (B) pGL3-Basic, pGL3-Control (SV40-PR; SV40-En), PR3, PR3-MP constructs were stably transfected into Raw264.7, NFS25, P2C2, and EL4 cells with pTracer-Renilla luciferase construct. The firefly luciferase activities were normalized to Renilla luciferase activities. The Normalized Expression was calculated by designation of the geomean of pGL3-Basic as 1 unit. •, relative firefly luciferase activities normalized by Renilla luciferase activities. -, geomeans of the data points in the same sample. Data shown are from one experiment representative of 3.
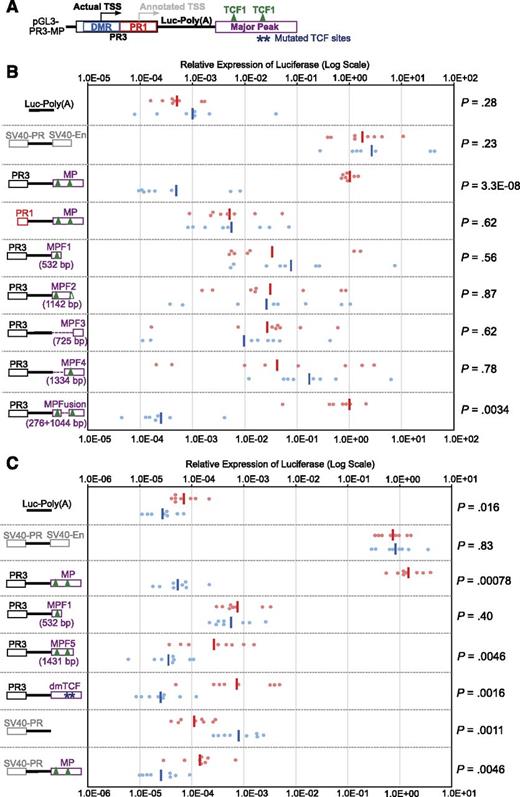
TCF-1 binding sites are essential cis-regulatory elements for the activity of Major Peak. (A) The structural framework of constructs used in the stable transfection assays. Stars, mutated TCF sites in dmTCF construct; triangles, major peaks of TCF-1 binding as shown in Figure 6. (B) Constructs with PR1 or PR3 promoters and serial deletions of the Major Peak (in a downstream enhancer position) were made as shown schematically. The major TCF-1 binding peaks in MP are marked for reference (coordinates of construct end points provided in supplemental Table 2). Note that the CAAAG/CTTTG motifs that presumably nucleate the second TCF-1 peak are just beyond the boundary of MP-fragment 2. Graph shows normalized luciferase expression in 8 parallel cultures with each construct, stably transfected into P2C2 (red) and Raw264.7 (blue) cells after two weeks of selection. The same results were seen for these constructs in 2-3 independent experiments. (C) Either specific deletion of the two central TCF-1 binding sites or removal of the 3′ conserved region (MPF5) decreases the enhancer activity of Major Peak in P2C2 cells. dmTCF, the construct with double mutation (deletion) of TCF-1 binding peaks shown in Figure 6. MPF5, truncated construct lacking 3′ conserved region.
TCF-1 binding sites are essential cis-regulatory elements for the activity of Major Peak. (A) The structural framework of constructs used in the stable transfection assays. Stars, mutated TCF sites in dmTCF construct; triangles, major peaks of TCF-1 binding as shown in Figure 6. (B) Constructs with PR1 or PR3 promoters and serial deletions of the Major Peak (in a downstream enhancer position) were made as shown schematically. The major TCF-1 binding peaks in MP are marked for reference (coordinates of construct end points provided in supplemental Table 2). Note that the CAAAG/CTTTG motifs that presumably nucleate the second TCF-1 peak are just beyond the boundary of MP-fragment 2. Graph shows normalized luciferase expression in 8 parallel cultures with each construct, stably transfected into P2C2 (red) and Raw264.7 (blue) cells after two weeks of selection. The same results were seen for these constructs in 2-3 independent experiments. (C) Either specific deletion of the two central TCF-1 binding sites or removal of the 3′ conserved region (MPF5) decreases the enhancer activity of Major Peak in P2C2 cells. dmTCF, the construct with double mutation (deletion) of TCF-1 binding peaks shown in Figure 6. MPF5, truncated construct lacking 3′ conserved region.
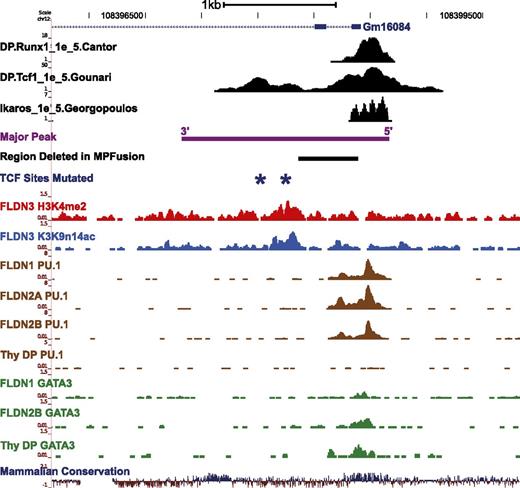
Both ends of the Major Peak sequence are highly conserved, and ChIP-seq results showed that Runx1, TCF-1, Ikaros, PU.1, and GATA-3 bind to the conserved end of Major Peak with promoter-like histone marks (“5′”), whereas TCF-1 also binds to another, central site pair (Figures 5A and 69,24,25,37 ). To determine which subregions are functional, constructs were made with serial deletions of Major Peak (Figure 5B, MP-F1, MP-F2, etc.). None of the constructs missing either end of Major Peak (PR3-MP-F1, PR3-MP-F2, PR3-MP-F3, and PR3-MP-F4) could recapitulate the expression pattern of PR3 with the intact Major Peak in stable transfection experiments. They poorly enhanced expression in P2C2 cells, showed high inter-culture variability, and gave equal expression in Raw264.7 cells. However, the PR3-MPFusion, which deletes a 528-bp sequence between the two TCF-1 binding peaks, mediated full MP function. It promoted reporter expression consistently at levels comparable to that of PR3-MP and pGL3-Control in P2C2 cells, while silencing expression in Raw264.7 cells (Figure 5B). Even with the 5′ region intact, deletion of the centrally located TCF-1 sites (dmTCF), or deletion of the 3′ conserved region (MPF5), was sufficient to cancel enhancer activity (Figures 5C and 6). This implies functional requirements for at least three subregions, comprising two conserved terminal blocks and at least one additional region of TCF-1 binding.
Transcription factor binding sites and histone modifications on the Major Peak. The binding profiles of Runx1, TCF-1, Ikaros, PU.1, and GATA-3 at the Major Peak region in T cells, measured by ChIP-seq, are shown.9,24,25,37 Also shown are the alignments of the full MP sequence and the 528-bp region between the two TCF-1 binding peaks, which was deleted from Major Peak to make the MPFusion construct. Dark blue stars mark the two central TCF-1 sites that were mutated in the dmTCF construct. The 3′ conserved region is also indicated. For coordinates, see supplemental Table 2.
Transcription factor binding sites and histone modifications on the Major Peak. The binding profiles of Runx1, TCF-1, Ikaros, PU.1, and GATA-3 at the Major Peak region in T cells, measured by ChIP-seq, are shown.9,24,25,37 Also shown are the alignments of the full MP sequence and the 528-bp region between the two TCF-1 binding peaks, which was deleted from Major Peak to make the MPFusion construct. Dark blue stars mark the two central TCF-1 sites that were mutated in the dmTCF construct. The 3′ conserved region is also indicated. For coordinates, see supplemental Table 2.
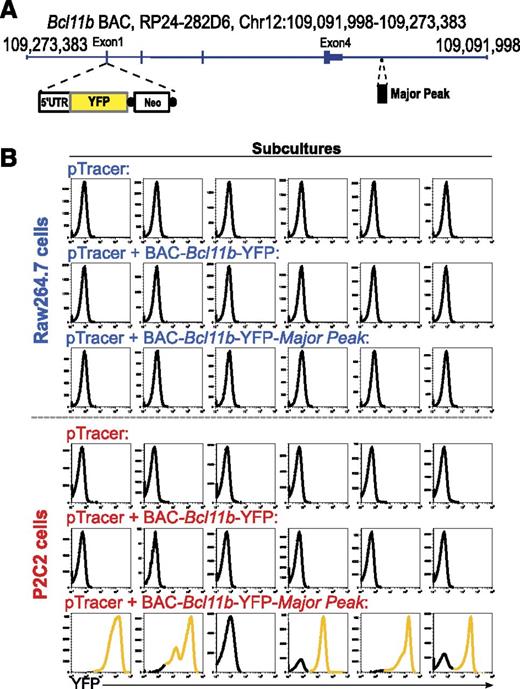
Major Peak can thus cooperate with the promoter-DMR region to provide both lineage-specific enhancer and silencing functions. Still, it is possible that intron 1 and intron 3 of Bcl11b might also contain intragenic cis-regulatory elements3,9 (Figures 1A and 3), and other regions in or around the Bcl11b locus might assist its regulation.26 Therefore, to test whether the Major Peak is required for T-cell specific regulation in the context of a full complement of intragenic and promoter-associated elements, we measured the functional effects of Major Peak when added to a whole-locus Bcl11b BAC. A YFP reporter was knocked into exon 1 of Bcl11b, in a 193-kb BAC that spans the Bcl11b locus from 31.8 kb upstream to 56.6 kb downstream (Figure 7A). This BAC-Bcl11b-YFP construct expresses no Bcl11b protein but preserves all required intragenic elements for Bcl11b expression, since a knock-in mouse with a reporter in this site showed the correct Bcl11b expression pattern in hematopoietic cells (HYK and EVR, to be reported elsewhere). The 1.9-kb Major Peak was further cloned into the BAC, 9.8-kb downstream of Bcl11b, to generate the BAC-Bcl11b-YFP-MP construct. The 2 constructs with and without Major Peak were then compared for the ability to drive YFP expression on stable transfection into T-lineage P2C2 and myeloid-lineage Raw264.7 cells.
Stable Transfections of a BAC reporter construct containing Bcl11b and Major Peak confirm the T-cell specific enhancer activity of Major Peak in a chromatin context. (A) Generation of BAC-Bcl11b-YFP-MP construct. A YFP cassette replaced the Exon 1 of Bcl11b. Major Peak was cloned into the BAC at 9.8-kb downstream of 3′UTR of Bcl11b. (B) Stable transfections of the BAC constructs into P2C2 and Raw264.7 cells: histograms of YFP fluorescence in individual subcultures after selection are shown. Results are representative of two independent experiments.
Stable Transfections of a BAC reporter construct containing Bcl11b and Major Peak confirm the T-cell specific enhancer activity of Major Peak in a chromatin context. (A) Generation of BAC-Bcl11b-YFP-MP construct. A YFP cassette replaced the Exon 1 of Bcl11b. Major Peak was cloned into the BAC at 9.8-kb downstream of 3′UTR of Bcl11b. (B) Stable transfections of the BAC constructs into P2C2 and Raw264.7 cells: histograms of YFP fluorescence in individual subcultures after selection are shown. Results are representative of two independent experiments.
Figure 7B shows YFP expression levels in 6 parallel stably transfected subcultures with each construct in each of the 2 cell lines. The BAC-Bcl11b-YFP construct, although it covers the entire Bcl11b locus, did not promote any YFP expression in either T cells or myeloid cells. In contrast, the construct with Major Peak, BAC-Bcl11b-YFP-MP, expressed YFP in 5/6 T-lineage cell subcultures, whereas none of the myeloid cell subcultures had YFP expression. To verify the presence of stably transfected BAC DNA, YFP copy number was measured by qPCR in genomic DNA from each subculture. There was some minor copy number variation (supplemental Figure 8), but the YFP-transfected cultures without YFP expression had at least as many copies of YFP DNA integrated into chromosomes as the subcultures with expression of YFP, yet only those with Major Peak in T cells expressed. Thus, though the cis-regulatory sequences within the Bcl11b locus might play some roles in the regulation of Bcl11b expression, they were not powerful enough to drive expression in this system without Major Peak. These results imply that Major Peak confers an essential, rate-limiting function for T-lineage specific expression of Bcl11b.
Discussion
Bcl11b is one of only a few T-cell specific regulatory genes with highly stage-specific onset of expression during commitment. Uniquely among hematopoietic lineages, Bcl11b is turned on in T-cell precursors at DN2a stage and maintained through all later stages, and it is required for lineage commitment, viability, and T-cell function starting almost immediately after it is turned on. In this paper, we have identified two regulatory regions that cooperate to control this expression. First, we have corrected the location of the promoter and shown that it is embedded in a CpG island with cell-type–specific differential DNA methylation. In T-lineage cells specifically, we have shown that this promoter-DMR region interacts functionally with the second element, an extremely distal 1.9-kb sequence >850 kb downstream of the gene, which was mapped originally based on its dynamic and highly cell-type specific pattern of histone marks in developing T cells. This “Major Peak” region also interacts specifically with the Bcl11b locus, especially in T-lineage cells. It proves to be a bipartite cis-regulatory element that confers both lineage-specific positive and negative regulation, specifically in cooperation with the full promoter-DMR. The results suggest that the downstream Major Peak is an essential cis-regulatory element that activates Bcl11b expression in early T cells.
Besides T cells, Bcl11b is expressed in the central nervous system and in skin cells as well. Precedents from the SCL gene indicate that different cis-regulatory elements are likely to promote expression of the same gene in such different tissues.38 Although noncoding sequence conservation implies likely function, it might not be sufficient to identify the cis-regulatory elements needed by Bcl11b specifically in T cells. We therefore focused on regions where T-lineage-specific activity could be indicated by epigenetic clues. Lineage-specific demethylation of the promoter-DMR, in contrast to three other CpG islands around the Bcl11b locus, implied that it may be an important target of cell-type specific transcription factor action. Indeed, the DMR is required to enable the Bcl11b promoter to cooperate with the Major Peak in stable transfection assays. Lineage-specific histone marking dynamics enabled us to locate the Major Peak.
Our results leave open possible roles for intragenic cis-regulatory elements, which were not systematically tested here. The first intron of Bcl11b is likely to contribute, since activating histone marks appear here,9 TCF-1 binds strongly (Figure 1), and binding of the Notch-dependent transcription factor CSL has also been described.3 Intron 3 may also play a role. In our assays, the CpG islands contained within exon 4 did not show methylation differences between T and non-T cells. However, the CpG “shore” of this CpG island, located in intron 3 immediately upstream of Exon 4, may also be specifically demethylated in Bcl11b-expressing T cells30 and has T-cell specific H3K4me2 marking from the DN2b stage onward.9 Nevertheless, our BAC transfection assays showed that a BAC-Bcl11b-YFP construct that includes all of these intragenic sequences along with substantial 5′ and 3′ flanking sequence still did not express the YFP reporter, unless Major Peak was present as well. Thus, although intragenic Bcl11b cis-regulatory elements may affect Bcl11b levels or play a role in initial developmental activation, they do not replace the requirement for Major Peak to drive the T-cell specific expression of Bcl11b in early T lineage cells.
Major Peak contains sites for positive regulatory inputs that have been implicated in activation of Bcl11b, including TCF-1 and Runx1 as well as a weaker site for GATA-3. Interestingly, two separate subelements within Major Peak appear to be needed for its activity, each including TCF-1 sites and a highly conserved region. The T-cell specific positive regulatory activity is coupled tightly with a locus control region-like effect on consistency of expression, and also with a lineage-specific silencing effect on expression in myeloid cells, perhaps required because of the ability of PU.1 to bind to this element as well. This suggests a more complex cis-regulatory function of Major Peak than a simple enhancer.
A mechanism that may promote the interaction of Major Peak with the Bcl11b locus across 850-kb is suggested by the binding pattern of CTCF, a mediator of chromosome looping in its roles both to define domain boundaries and to mediate enhancer-promoter collaboration.39,40 In both Bcl11b-expressing and nonexpressing cells, CTCF binding sites are profuse upstream of Bcl11b and downstream of the Major Peak. A constitutive CTCF binding peak is also present in Bcl11b intron 1. However, the first CTCF site downstream of Bcl11b is just beyond Major Peak (supplemental Figures 5 and 9). Hi-C assays detect a chromatin interaction topological domain with one boundary on Bcl11b and the other boundary just beyond Major Peak41 (supplemental Figure 9). This topological domain is conserved across species and cell types irrespective of Bcl11b expression. Thus, chromatin interactions between the Major Peak and Bcl11b loci could be maintained by CTCF constitutively, thus creating a permissive framework for the cell-type specific regulation of Bcl11b.
In many cases of human T-ALL, translocations of t(5;14)(q35;q32.2) juxtapose TLX3 and NKX2-5 to the BCL11B downstream gene desert, and cause ectopic expression of these oncogenes leading to T-ALL. Strikingly, the translocation break points at the BCL11B locus spread over >800-kb downstream of BCL11B, but end with a clear boundary right on the Major Peak (supplemental Figure 10). It has been speculated that sequences around that boundary contain cis-regulatory elements that are able to drive the expression of TLX3 and NKX2-5 in immature T cells,14 in particular DNase hypersensitive sites characterized by Nagel and coauthors.15 The Major Peak may be the cis-regulatory element that activates the oncogenes in t(5;14)(q35;q32.2) T-ALL. However, there is a further implication if this element is a key regulator of BCL11B. The translocation would not only create a gain of function of TLX3 or NKX2-5 in T cells, but also break the connection between BCL11B and a needed cis-element, and this would be predicted to cause some loss of Bcl11b function as well. Although a translocation may only affect one allele of BCL11B, an emerging consensus is that BCL11B is haploinsufficient as a tumor suppressor. Frequently, it appears most dangerous for oncogenesis when it is present in only one copy—enough to sustain T-lineage viability but not to prevent transformation10-12,42,43 Thus these translocations that separate Bcl11b from Major Peak may promote oncogenesis by two mechanisms at once.
Extremely long-range tissue-specific cis-regulatory elements such as Major Peak are difficult to study. The longest-distance cases before this were discovered by mutational serendipity: for example, ZRS, the limb bud-specific enhancer of sonic hedgehog (Shh), located within intron 5 of Lmbr1, a gene about 1-Mb upstream of Shh.44 A tissue-specific chromatin interaction between Shh and its enhancer ZRS activates its expression in the limb bud-forming cells,45 similar to Major Peak interaction with Bcl11b. Several central nervous system specific Shh enhancers were also identified located across the 700-kb gene desert upstream of Shh.46 Other examples include the T/NK cell specific enhancer of Gata3, 280-kb away,47 and the 1-Mb upstream enhancer of Sox9 to control sex determination.48 These latter cases, like Bcl11b, involve a gene flanked by a gene desert of hundreds of kilobases or more, containing tissue-specific enhancers. Adding to these precedents, our study emphasizes the need to search for megabase scale cell-type specific chromatin interactions to identify cis-regulatory elements, and illustrates a strategy that can be used to find them.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is an Inside Blood commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mark A. Zarnegar and members of the Rothenberg laboratory for helpful discussions and for sharing data before publication.
This work was supported by a California Institute for Regenerative Medicine fellowship (L.L.), National Institutes of Health grants R33HL089123, RC2CA148278, R01AI095943 (E.V.R.), and R21 AI076720 (F.G.), by American Cancer Society/Research Scholar Grants, LIB-113428 (F.G.), and the Louis A. Garfinkle Memorial Laboratory Fund, the Al Sherman Foundation, and the Albert Billings Ruddock Professorship (E.V.R.).
Authorship
Contribution: L.L. designed and performed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; J.A.Z. analyzed data; M.D. performed research and analyzed data; H.Y.K. and R.M. contributed new reagents; F.G. analyzed data; and E.V.R. designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for J.A.Z. is Genentech, South San Francisco, CA. The current affiliation for M.D. is Laboratory of Molecular Immunogenomics, Genomics and Immunity Section, National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD.
Correspondence: Ellen V. Rothenberg, Division of Biology 156-29, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125; e-mail: evroth@its.caltech.edu.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal