Abstract
Janus kinases (JAKs), including JAK1, mediate the signaling of cytokines and growth factors implicated in the pathogenesis of myelofibrosis (MF). The objective of this ongoing study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of INCB039110, a selective JAK1 inhibitor, in patients with MF. The results of an interim analysis are presented.
Men and women aged ≥18 years with primary MF (PMF), post-polycythemia vera MF (PPV-MF), or post-essential thrombocythemia MF (PET-MF) irrespective of JAK2V617F mutation status, and classified as intermediate-1 or higher by Dynamic International Prognostic Scoring System (DIPSS) were enrolled. Patients were required to have a platelet count of ≥ 50 x 109/L, hemoglobin ≥ 8.0 g/dL (transfusions permitted to achieve these levels), and a palpable spleen or prior splenectomy.
Patients assessed the severity of 19 disease-related symptoms daily using the modified Myelofibrosis Symptom Assessment Form (MFSAF) v3.0 electronic diary. Spleen volume (SV) was evaluated by MRI or CT at baseline, week 12, and week 24. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with a ≥ 50% reduction in total symptom score (TSS) from baseline as measured by the modified MFSAF v3.0. TSS is the sum of 6 individual symptom scores: night sweats, itchiness, abdominal discomfort, pain under left ribs, early satiety, and bone/muscle pain. Efficacy data were summarized for patients completing the week 12 visit, and safety data were included for all patients.
The study used a Simon 2-stage design to assess 3 separate dose cohorts (100 mg BID, 200 mg BID, and 600 mg QD). A dose cohort could be expanded if at least 3 of the first 10 patients had at least a 50% improvement in TSS from baseline to week 12 (intent-to-treat method). The 600 mg QD cohort is currently enrolling.
At the time of the data cutoff for this interim analysis, 65 patients have been treated with INCB039110: 10 in the 100 mg BID, 45 in the 200 mg BID, and 10 in the 600 mg QD group; 10, 43, and 4 patients, respectively, were evaluable for the primary endpoint. The 200 mg BID and 600 mg QD cohorts met criteria for expansion, while the 100 mg BID cohort did not.
The mean age was 64 years. Enrolled patients had PMF (61.5%), PPV-MF (20.0%), and PET-MF (18.5%), and most patients were intermediate-1 (40%) and intermediate-2 (45%) by DIPSS. Mean SV at baseline was 2672.3 cm3. Mean hemoglobin was 10.1 g/dL and mean platelet count was 197 x 109/L.
A greater proportion of patients in the 200 mg BID dose group achieved at least a 50% reduction in TSS from baseline to week 12 compared with those in the 100 mg BID group (Table). Preliminary results suggest a trend toward greater efficacy in the 600 mg QD cohort. Higher dose groups also demonstrated modest reductions in SV.
| INCB039110 Dose . | 100 mg BID . | 200 mg BID . | 600 mg QD . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Responder Analysis* | |||
| Number (%) patients with ≥50% improvement in TSS at week 12 | 2/10 (20%) | 15/43 (35%) | 3/4 (75%) |
| Median Change from Baseline† | |||
| % Change in TSS at week 12 | -28.5% | -45.8% | -90.3% |
| % Change in SV at week 12 | 5.0% | -14.1% | -12.9% |
| INCB039110 Dose . | 100 mg BID . | 200 mg BID . | 600 mg QD . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Responder Analysis* | |||
| Number (%) patients with ≥50% improvement in TSS at week 12 | 2/10 (20%) | 15/43 (35%) | 3/4 (75%) |
| Median Change from Baseline† | |||
| % Change in TSS at week 12 | -28.5% | -45.8% | -90.3% |
| % Change in SV at week 12 | 5.0% | -14.1% | -12.9% |
Patients who discontinued prior to the week 12 visit were considered nonresponders.
Only patients with baseline and week 12 data were included. Negative change = improvement.
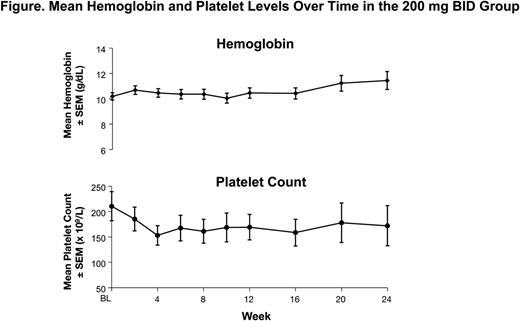
In the 200 mg BID group, mean hemoglobin levels remained stable over time, and mean platelet levels declined by approximately 25% from baseline to week 12 (Figure). Preliminary data from the 600 mg QD group suggest similar trends.
Among enrolled patients, the most common nonhematologic adverse events (occurring in >15% patients overall regardless of causality) were fatigue (21.9%), constipation (17.2%), and nausea (15.6%); most of these events were grade 1 or 2. A total of 23.3% and 0% of patients experienced new onset grade 3 and grade 4 anemia, respectively, and 24.2% and 3.2% experienced new onset grade 3 and grade 4 thrombocytopenia.
This is the first report describing the efficacy and safety of a JAK1 inhibitor in the treatment of patients with MF. These preliminary data suggest that INCB039110 doses of 200 mg BID and 600 mg QD may result in meaningful improvements in MF-related symptoms and modest decreases in spleen size, while preserving mean hemoglobin levels over time. Updated results from this ongoing study will be presented. These data will contribute to a better understanding of JAK1 inhibition as a disease target in MF.
Mascarenhas:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Genzyme: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding. Talpaz:Ariad: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Ariad: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gupta:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Inctye Corporation: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Novartis: Speakers Bureau. Coughlin:Bayer: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Winton:Incyte Corporation: Research Funding; Incyte Corporation: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hunter:Incyte Corporation: Employment, stock equity Other; Incyte Corporation: Equity Ownership. Mookerjee:Incyte Corporation: Employment, stock equity Other; Incyte Corporation: Equity Ownership. Leopold:Incyte Corporation: Employment; Incyte Corporation: Equity Ownership. Clark:Incyte Corporation: Employment, stock equity Other; Incyte Corporation: Equity Ownership. O'Neill:Incyte Corporation: Employment, stock equity Other; Incyte Corporation: Equity Ownership. Verstovsek:Incyte: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal