Abstract
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is accompanied by an increase in the bloodstream circulation of some adult progenitor cells. Extramedullary hematopoiesis observed in this setting might remind some features related to foetal hematopoiesis.
We looked for evidence in favour of this hypothesis in blood samples of a small cohort of untreated patients with PMF (4 pre-fibrotic (PF) and 4 fibrotic (F), defined according to the WHO and Thiele's histopathology score (Blood, 2011)). Patient baseline characteristics are shown below.
| ID . | Sex . | Age . | Phase . | V617F JAK2 . | Hemoglobin (g/dL) . | Platelets (x109/L) . | WBC (x109/L) . | Spleen (cm) . | General signs . | IPSS . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | M | 53 | F | + | 7.2 | 8 | 2.4 | 20 | + | 2 |
| P2 | M | 83 | PF | + | 11.8 | 447 | 55.8 | 10 | - | 2 |
| P4 | M | 70 | F | + | 8.3 | 138 | 5.4 | 23 | - | 3 |
| P5 | M | 63 | F | - | 12.9 | 186 | 25.4 | 18 | - | 2 |
| P6 | M | 64 | F | + | 8.2 | 14 | 60.0 | 25 | + | 4 |
| P7 | F | 65 | PF | + | 12. | 590 | 58.3 | 21 | - | 1 |
| P8 | M | 64 | PF | - | 8.8 | 523 | 24.7 | 22 | + | 2 |
| P9 | M | 64 | PF | - | 9.7 | 566 | 33.1 | 18 | - | 3 |
| ID . | Sex . | Age . | Phase . | V617F JAK2 . | Hemoglobin (g/dL) . | Platelets (x109/L) . | WBC (x109/L) . | Spleen (cm) . | General signs . | IPSS . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | M | 53 | F | + | 7.2 | 8 | 2.4 | 20 | + | 2 |
| P2 | M | 83 | PF | + | 11.8 | 447 | 55.8 | 10 | - | 2 |
| P4 | M | 70 | F | + | 8.3 | 138 | 5.4 | 23 | - | 3 |
| P5 | M | 63 | F | - | 12.9 | 186 | 25.4 | 18 | - | 2 |
| P6 | M | 64 | F | + | 8.2 | 14 | 60.0 | 25 | + | 4 |
| P7 | F | 65 | PF | + | 12. | 590 | 58.3 | 21 | - | 1 |
| P8 | M | 64 | PF | - | 8.8 | 523 | 24.7 | 22 | + | 2 |
| P9 | M | 64 | PF | - | 9.7 | 566 | 33.1 | 18 | - | 3 |
We performed a) flow-cytometric analysis for cell subsets related to VSEL, PEC, MPC, HPC; b) RT-PCR for embryonic transcriptional factors NANOG, OCT4, SOX2, LIN28 from MNC fraction (positive control hES, negative control CPRE2 c) in-vitro development of embryonic stem like cells (ESlC) under specific culture conditions. In addition we looked for SRSF2 mutations in order to better characterize PMF stages.
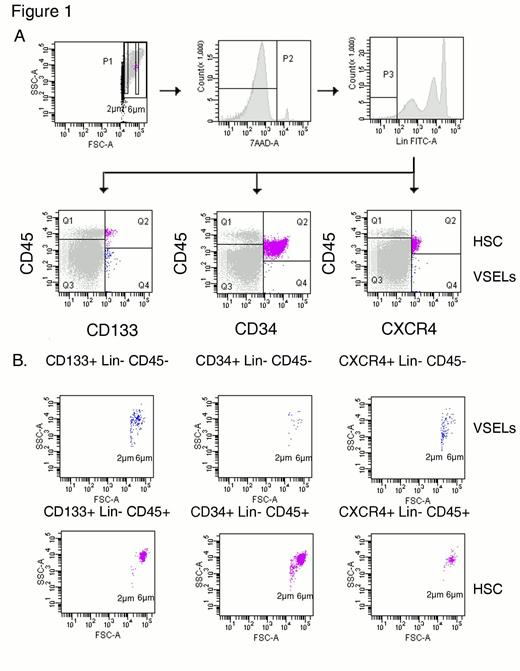
As expected we detected high numbers of circulating CD34+ cells (HPC) (mean 233083±307148/ml (range 4600-783000), with similar numbers in PF- (231125±289553/ml) and F-PMF (235040 ±369156/ml). We were able to detect small numbers of the following cell subsets related to VSEL (size 2-4m) (Fig 1)
Lin-/CD45-/CD34+ (mean 124±239/ml), Lin-/CD45-/CD133+ (mean 1178±971/ml), Lin-/CD45-/CXCR4+ (mean 1572±1622/ml). Lin-/CD45-CD34+AC133+CXCR4+ cells were detected in 6 of 8 patients (mean 186±375/ml) with F-PMF patients showing higher numbers (279±416/ml) than PF-PMF (63±71/ml). NANOG and OCT4 expression was detected by RT-PCR in all the patients tested. Mean OCT4 expression was about 50% the level of hES, but F-PMF showed higher levels. NANOG expression was similar to that of hES, whereas Sox2 and Lin28 were not expressed in most patients. We failed to observe the in-vitro development of ESlC in the 2 tested patients. PEC (Lin-/CD45-CD34+AC133+KDR+) were detected in all the PF-PMF (185±332/ml) and in 1 of 4 F-PMF (mean 9±18/ml). MPC (Lin-/CD45-CD90+CD105+) were detected in higher numbers in PF-PMF (mean 413±528/ml) than in F-PMF (mean 157±216/ml). We were not able to detect mutations in the hot spot of SRSF2 (codons 93,94,95).
Small numbers of cell subsets displaying morphologic and immunophenotypic features of VSELs were detected in PMF patients. However, we are not able to define these as fully specific VSELs according to previous works that defined them (Kucia, Leukemia 2006). Interestingly Lin-/CD45-CD34+AC133+CXCR4+ cells were observed in higher numbers in F-PMF, supporting in part our hypothesis that PMF evolution can be associated to the recruitment and circulation of some primitive progenitors (dormant in the adult life) as it can be observed during the foetal period. This recruitment also involves HPC. Moreover although all patients expressed OCT4 and NANOG, OCT4 expression was higher in F-PMF. As expected PEC circulate in higher numbers in PF-PMF compared to F-PMF. Interestingly both F-PMF and PF-PMF were associated to the circulation of significant numbers of MPC but higher numbers observed in PF-MFP might be interpreted either as a necessary recruitment to establish extra-medullary stroma or due to the exit from bone marrow of highly proliferative MPC. Whether all these different circulating progenitor cells, are clonally or not clonally related to the PMF pathogenesis or to unspecific mobilisation secondary to bone marrow microenvironment injury cannot be determined from these preliminary results.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal